Abstract
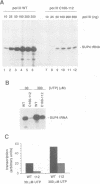
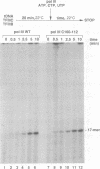
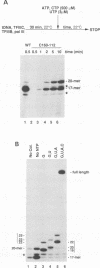
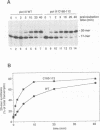
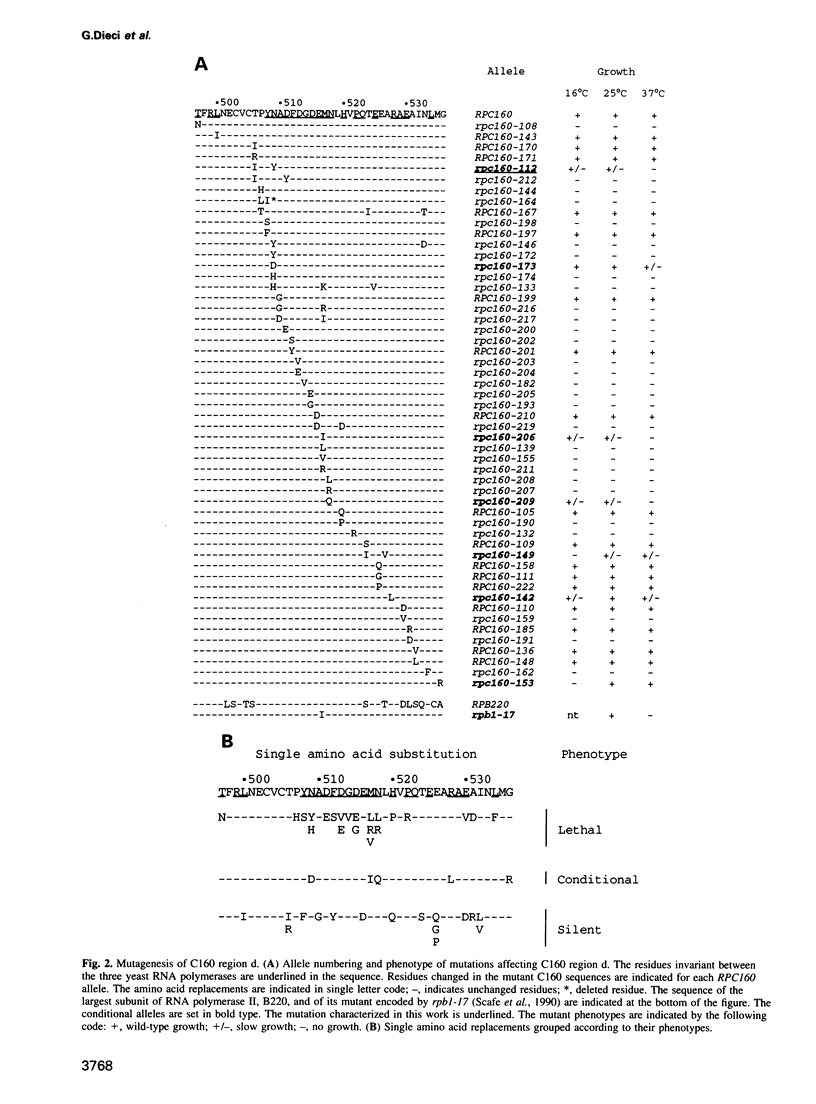
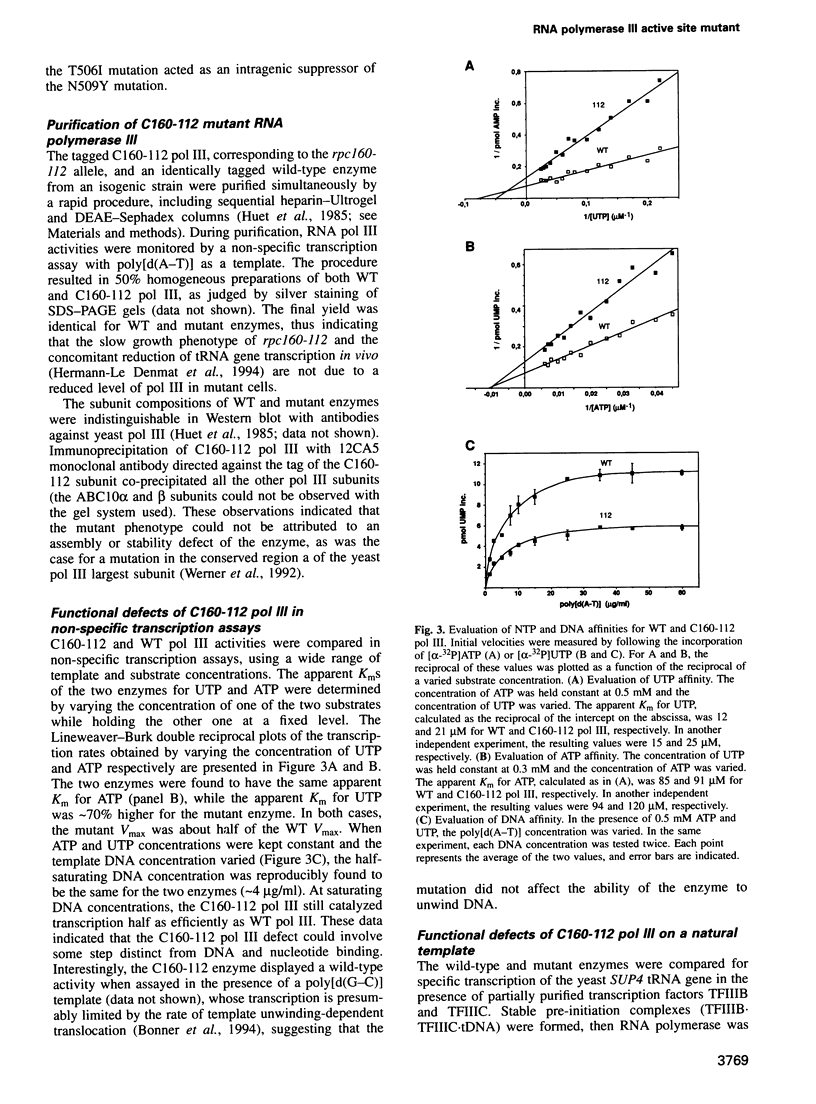
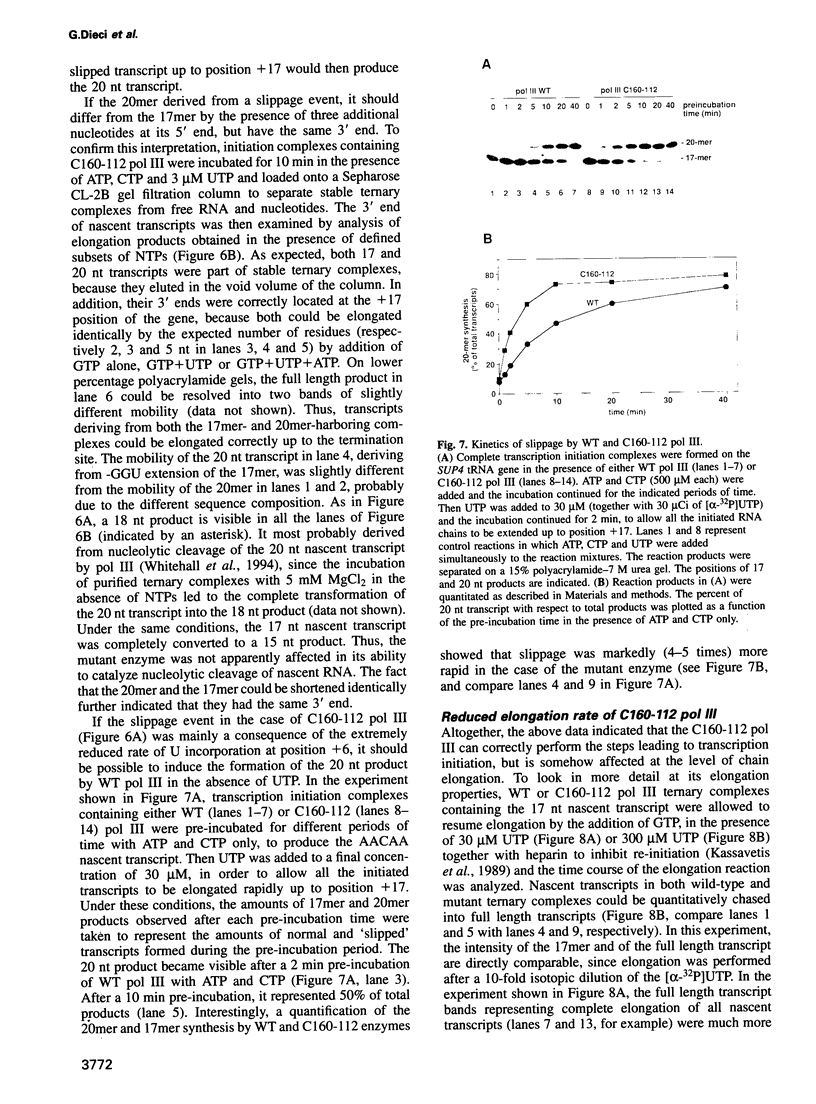
The largest subunits of the three eukaryotic nuclear RNA polymerase present extensive sequence homology with the beta' subunit of the bacterial enzymes over five major co-linear regions. Region d is the most highly conserved and contains a motif, (Y/F)NADFDGD(E/Q)M(N/A), which is invariant in all multimeric RNA polymerases. An extensive mutagenesis of that region in yeast RNA polymerase III led to a vast majority (16/22) of lethal single-site substitutions. A few conditional mutations were also obtained. One of them, rpc160-112, corresponds to a double substitution (T506I, N509Y) and has a slow growth phenotype at 25 degrees C. RNA polymerase III from the mutant rpc160-112 was severely impaired in its ability to transcribe a tRNA gene in vitro. The transcription defect did not originate from a deficiency in transcription complex formation and RNA chain initiation, but was mainly due to a reduced elongation rate. Under conditions of substrate limitation, the mutant enzyme showed increased pausing at the intrinsic pause sites of the SUP4 tRNA gene and an increased rate of slippage of nascent RNA, as compared with the wild-type enzyme. The enzyme defect was also detectable with poly[d(A-T)] as template, in the presence of saturating DNA, ATP and UTP concentrations. The mutant enzyme behavior is best explained by a distortion of the active site near the growing point of the RNA product.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner G., Lafer E. M., Sousa R. Characterization of a set of T7 RNA polymerase active site mutants. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):25120–25128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Lee J., Goldfarb A. Mapping of a contact for the RNA 3' terminus in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23932–23935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Josaitis C. A., Gourse R. L., Goldfarb A. Two modes of transcription initiation in vitro at the rrnB P1 promoter of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23477–23482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. Separation and characterization of the subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6168–6176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. New models for the mechanism of transcription elongation and its regulation. Harvey Lect. 1992 1993;88:1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiannilkulchai N., Moenne A., Sentenac A., Mann C. Biochemical and genetic dissection of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase C53 subunit through the analysis of a mitochondrially mis-sorted mutant construct. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23099–23107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. A mutation in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II alters RNA chain elongation in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13190–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Edwards A. M., Kubalek E. W., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of yeast RNA polymerase II at 16 A resolution. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90144-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darst S. A., Kubalek E. W., Kornberg R. D. Three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme determined by electron crystallography. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):730–732. doi: 10.1038/340730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Marzouki N., Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two polypeptide chains in yeast transcription factor tau interact with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7505–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F., Abdukayumov M. N., Rabinov I. V., Richter V. I., Skoblov Y. S., Chistyakov P. G. Studies of the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. A method for localization of the sites of affinity labelling. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann-Le Denmat S., Werner M., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Suppression of yeast RNA polymerase III mutations by FHL1, a gene coding for a fork head protein involved in rRNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):2905–2913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Riva M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Yeast RNA polymerase C and its subunits. Specific antibodies as structural and functional probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15304–15310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin D. J., Gross C. A. RpoB8, a rifampicin-resistant termination-proficient RNA polymerase, has an increased Km for purine nucleotides during transcription elongation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14478–14485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin D. J., Turnbough C. L., Jr An Escherichia coli RNA polymerase defective in transcription due to its overproduction of abortive initiation products. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):72–80. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Function and structure relationships in DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:777–822. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashlev M., Lee J., Zalenskaya K., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Blocking of the initiation-to-elongation transition by a transdominant RNA polymerase mutation. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1006–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.1693014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and termination of transcription within the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Stewart J., Lee D. N. Amino acid changes in conserved regions of the beta-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alter transcription pausing and termination. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1623–1636. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Kashlev M., Borukhov S., Goldfarb A. A beta subunit mutation disrupting the catalytic function of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6018–6022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. T., Muller D. K., Coleman J. E. Processivity in early stages of transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3966–3974. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki H., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Analysis of RNA chain elongation and termination by Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 28;235(4):1173–1192. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustaev A., Kashlev M., Lee J. Y., Polyakov A., Lebedev A., Zalenskaya K., Grachev M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. Mapping of the priming substrate contacts in the active center of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23927–23931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémet S., Gouy M., Marck C., Sentenac A., Buhler J. M. RPA190, the gene coding for the largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase A. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2830–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudler E., Goldfarb A., Kashlev M. Discontinuous mechanism of transcription elongation. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):793–796. doi: 10.1126/science.8047884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C. Synthesis of in vitro Co1E1 transcripts with 5'-terminal ribonucleotides that exhibit noncomplementarity with the DNA template. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6593–6598. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva M., Carles C., Sentenac A., Grachev M. A., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F. Mapping the active site of yeast RNA polymerase B (II). J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16498–16503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagitov V., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Dominant lethal mutations near the 5' substrate binding site affect RNA polymerase propagation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2195–2202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Martin C., Nonet M., Podos S., Okamura S., Young R. A. Conditional mutations occur predominantly in highly conserved residues of RNA polymerase II subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1270–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P., Célia H., Riva M., Sentenac A., Oudet P. Three-dimensional model of yeast RNA polymerase I determined by electron microscopy of two-dimensional crystals. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2601–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Goldfarb A. Topology of the product binding site in RNA polymerase revealed by transcript slippage at the phage lambda PL promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31701–31705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaaban S. A., Krupp B. M., Hall B. D. Termination-altering mutations in the second-largest subunit of yeast RNA polymerase III. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1467–1478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R. Tagetitoxin inhibition of RNA polymerase III transcription results from enhanced pausing at discrete sites and is template-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20204–20211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuillier V., Stettler S., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P., Werner M. A mutation in the C31 subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III affects transcription initiation. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weilbaecher R., Hebron C., Feng G., Landick R. Termination-altering amino acid substitutions in the beta' subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase identify regions involved in RNA chain elongation. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 1;8(23):2913–2927. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.23.2913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Hermann-Le Denmat S., Treich I., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Effect of mutations in a zinc-binding domain of yeast RNA polymerase C (III) on enzyme function and subunit association. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1087–1095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehall S. K., Bardeleben C., Kassavetis G. A. Hydrolytic cleavage of nascent RNA in RNA polymerase III ternary transcription complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mercoyrol L., Job C., Job D. Studies on the inhibition by alpha-amanitin of single-step addition reactions and productive RNA synthesis catalysed by wheat-germ RNA polymerase II. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):165–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2580165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]