Abstract
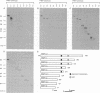
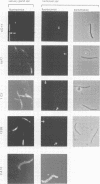
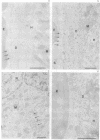
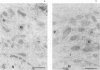
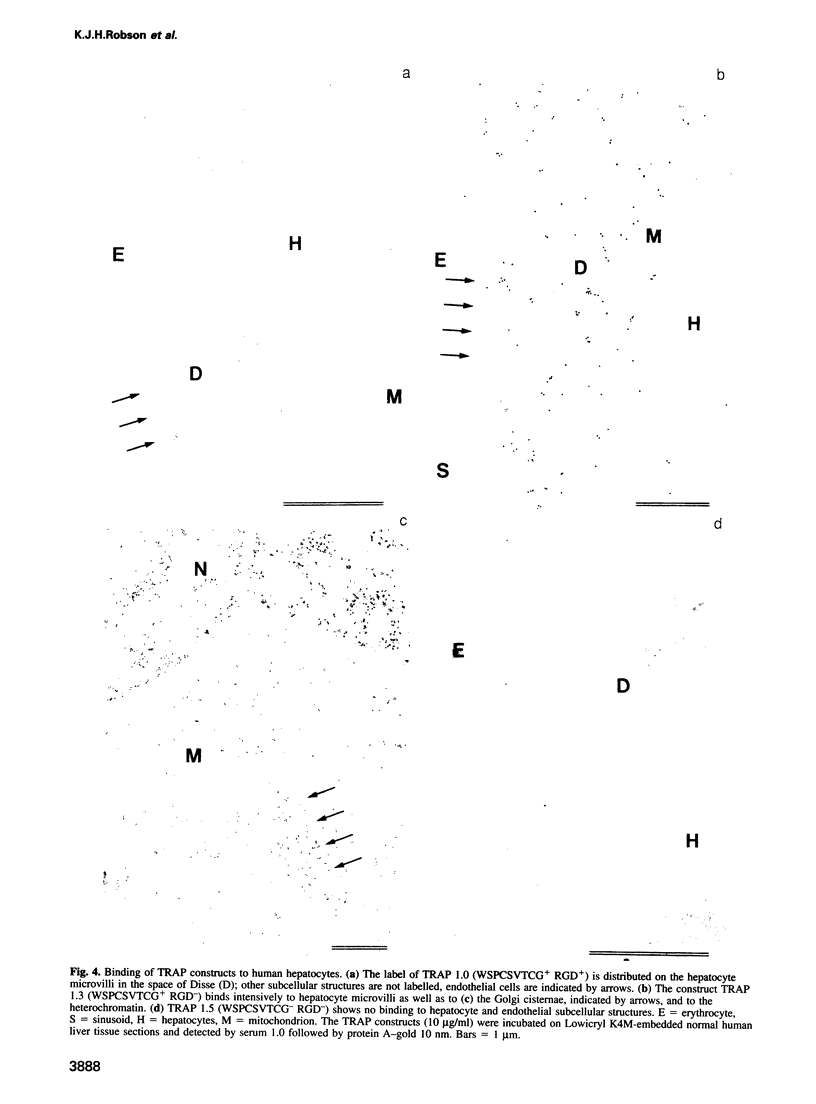
Plasmodium sporozoites collected from oocysts, haemocoel and salivary glands of the mosquito show profound differences in their biological properties such as motility, ability to induce protective immune response and infectivity for vertebrate host cells. Sporozoites from salivary glands are much more infectious than those from oocysts and haemocoel. Differential expression of proteins, such as the circumsporozoite (CS) protein and the thrombospondin-related adhesive protein (TRAP), implicated in sporozoite recognition and entry into hepatocytes may account for the development of infectivity during ontogeny. We have carried out a series of experiments to: (i) analyse the expression and localization of TRAP in P.falciparum sporozoites during development in the mosquito; and (ii) elucidate the biochemical and adhesive properties of recombinant TRAP. Our data indicate that TRAP is not expressed in oocysts, whereas variable amounts of CS protein are found in this parasite developmental stage. Hemocoel sporozoites display the distinct phenotypes TRAP- CS protein+ and TRAP+ CS protein+ at a frequency of 98.5 and 1.5% respectively. Salivary gland sporozoites are all TRAP+ CS protein+. We also provide experimental evidence showing that recombinant TRAP binds to the basolateral cell membrane of hepatocytes in the Disse's space and that sulfated glycoconjugates function as TRAP ligands on human hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF

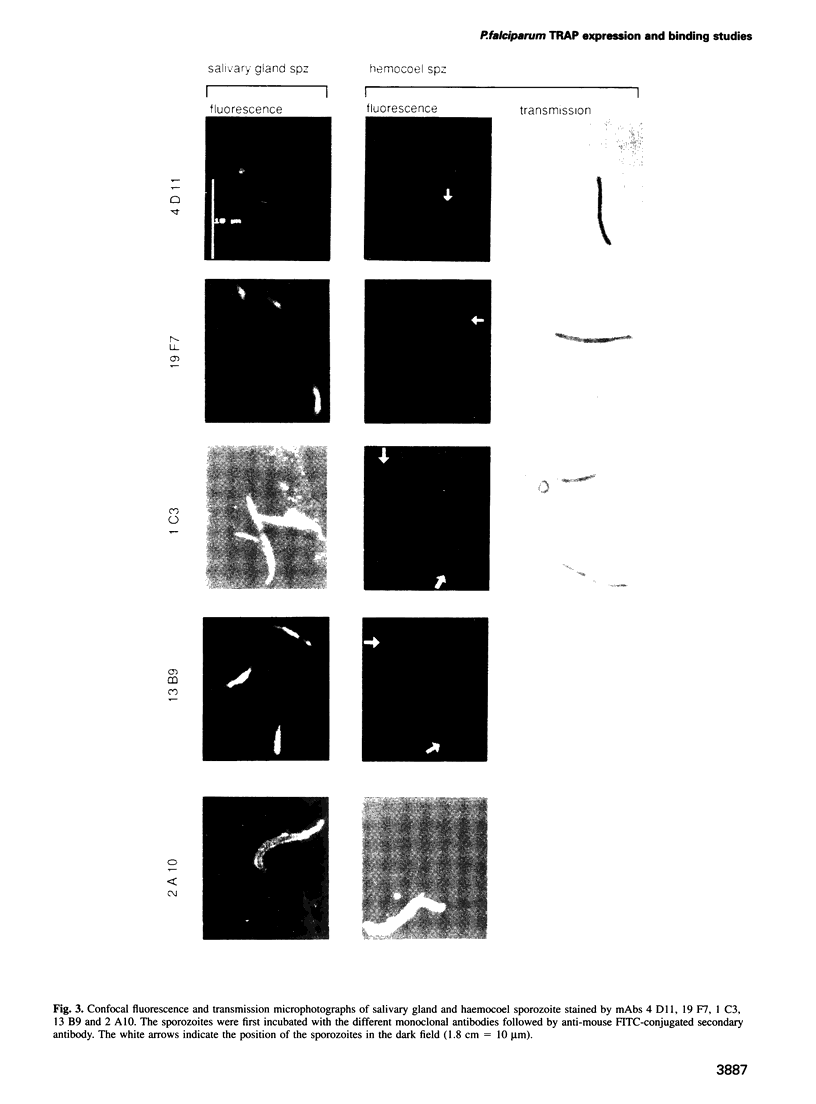


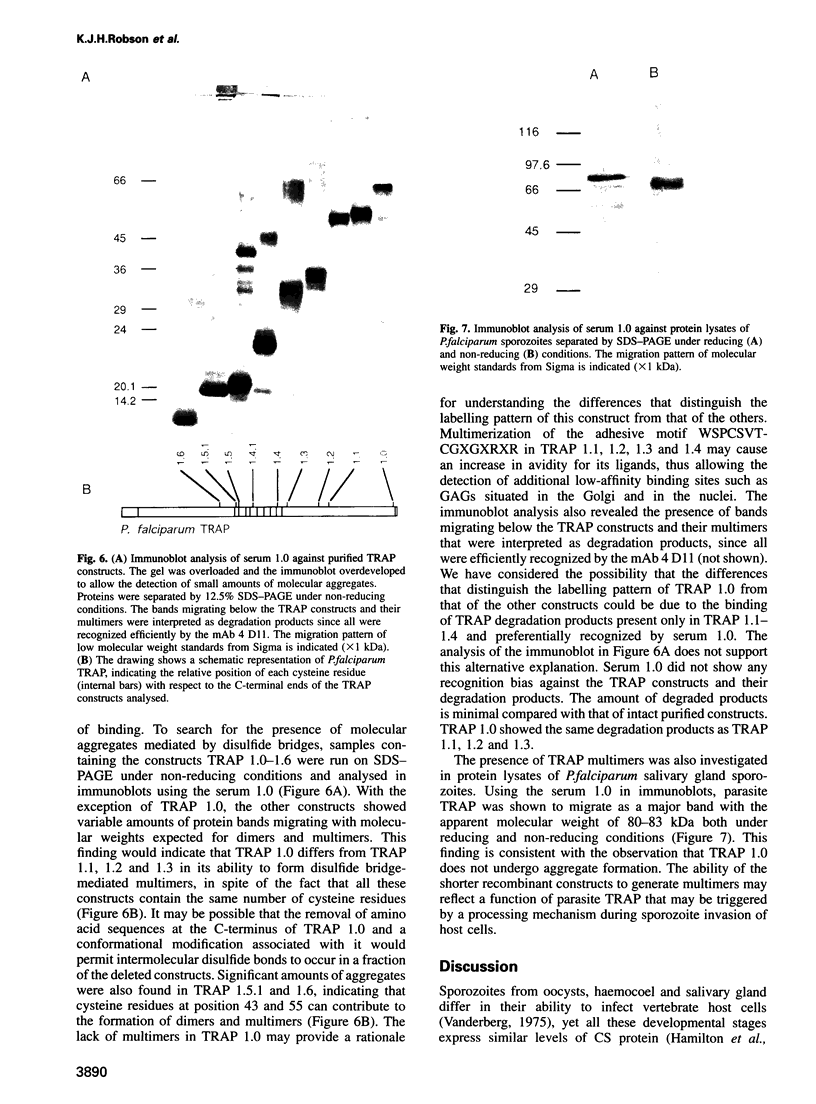




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. The protective antigen of malarial sporozoites (Plasmodium berghei) is a differentiation antigen. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2494–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami C., Frevert U., Sinnis P., Takacs B., Clavijo P., Santos M. J., Nussenzweig V. The basolateral domain of the hepatocyte plasma membrane bears receptors for the circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. E., Tomley F. M., Wisher M. H., Foulds I. J., Boursnell M. E. Regions of an Eimeria tenella antigen contain sequences which are conserved in circumsporozoite proteins from Plasmodium spp. and which are related to the thrombospondin gene family. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jun;41(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90190-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan G., Krishna S., Crisanti A., Robson K. Expression of thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Lancet. 1992 Jun 6;339(8806):1412–1413. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedarko N. S., Conrad H. E. A unique heparan sulfate in the nuclei of hepatocytes: structural changes with the growth state of the cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):587–599. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frevert U., Sinnis P., Cerami C., Shreffler W., Takacs B., Nussenzweig V. Malaria circumsporozoite protein binds to heparan sulfate proteoglycans associated with the surface membrane of hepatocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenda C. F., Starkweather W. H., Wirtz R. A. The distribution of circumsporozoite protein (CS) in Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes infected with Plasmodium falciparum malaria. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Apr;38(4):475–481. doi: 10.1177/38.4.2181019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goundis D., Reid K. B. Properdin, the terminal complement components, thrombospondin and the circumsporozoite protein of malaria parasites contain similar sequence motifs. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):82–85. doi: 10.1038/335082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. J., Davies C. S., Sinden R. E. Expression of circumsporozoite proteins revealed in situ in the mosquito stages of Plasmodium berghei by the Lowicryl-immunogold technique. Parasitology. 1988 Apr;96(Pt 2):273–280. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000058273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymerle H., Herz J., Bressan G. M., Frank R., Stanley K. K. Efficient construction of cDNA libraries in plasmid expression vectors using an adaptor strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8615–8624. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Campbell J. R., Leef M. L., Charoenvit Y., Carter M., Sedegah M., Beaudoin R. L., Hoffman S. L. A malaria sporozoite surface antigen distinct from the circumsporozoite protein. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68 (Suppl):152–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Krivan H. C., Gasic G. J., Ginsburg V. Antistasin, an inhibitor of coagulation and metastasis, binds to sulfatide (Gal(3-SO4) beta 1-1Cer) and has a sequence homology with other proteins that bind sulfated glycoconjugates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12138–12140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara M., Fedarko N. S., Conrad H. E. Transport of heparan sulfate into the nuclei of hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13575–13580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Hynes R. O. The structure of human thrombospondin, an adhesive glycoprotein with multiple calcium-binding sites and homologies with several different proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1635–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. M., Reckmann I., Hollingdale M. R., Bujard H., Robson K. J., Crisanti A. Thrombospondin related anonymous protein (TRAP) of Plasmodium falciparum binds specifically to sulfated glycoconjugates and to HepG2 hepatoma cells suggesting a role for this molecule in sporozoite invasion of hepatocytes. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2881–2889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Aikawa M., Procell P. M., Campbell G. H., Collins W. E., Campbell C. C. Plasmodium malariae: distribution of circumsporozoite protein in midgut oocysts and salivary gland sporozoites. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Jun;66(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig V., Nussenzweig R. S. Rationale for the development of an engineered sporozoite malaria vaccine. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:283–334. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60695-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnudurai T., Meuwissen J. H., Leeuwenberg A. D., Verhave J. P., Lensen A. H. The production of mature gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum in continuous cultures of different isolates infective to mosquitoes. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(2):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potocnjak P., Yoshida N., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Monovalent fragments (Fab) of monoclonal antibodies to a sporozoite surface antigen (Pb44) protect mice against malarial infection. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1504–1513. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prater C. A., Plotkin J., Jaye D., Frazier W. A. The properdin-like type I repeats of human thrombospondin contain a cell attachment site. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):1031–1040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson K. J., Hall J. R., Jennings M. W., Harris T. J., Marsh K., Newbold C. I., Tate V. E., Weatherall D. J. A highly conserved amino-acid sequence in thrombospondin, properdin and in proteins from sporozoites and blood stages of a human malaria parasite. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):79–82. doi: 10.1038/335079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers W. O., Malik A., Mellouk S., Nakamura K., Rogers M. D., Szarfman A., Gordon D. M., Nussler A. K., Aikawa M., Hoffman S. L. Characterization of Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite surface protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9176–9180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. E., Garnham P. C. A comparative study on the ultrastructure of Plasmodium sporozoites within the oöcyst and salivary glands, with particular reference to the incidence of the micropore. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1973;67(5):631–637. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(73)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnis P., Clavijo P., Fenyö D., Chait B. T., Cerami C., Nussenzweig V. Structural and functional properties of region II-plus of the malaria circumsporozoite protein. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):297–306. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling C. R., Aikawa M., Vanderberg J. P. The passage of Plasmodium berghei sporozoites through the salivary glands of Anopheles stephensi: an electron microscope study. J Parasitol. 1973 Aug;59(4):593–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Mosher D. F., Rapraeger A. Heparan sulfate-mediated binding of epithelial cell surface proteoglycan to thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2885–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomley F. M., Clarke L. E., Kawazoe U., Dijkema R., Kok J. J. Sequence of the gene encoding an immunodominant microneme protein of Eimeria tenella. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touray M. G., Warburg A., Laughinghouse A., Krettli A. U., Miller L. H. Developmentally regulated infectivity of malaria sporozoites for mosquito salivary glands and the vertebrate host. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1607–1612. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderberg J. P. Development of infectivity by the Plasmodium berghei sporozoite. J Parasitol. 1975 Feb;61(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderberg J. P. Studies on the motility of Plasmodium sporozoites. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):527–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderberg J., Nussenzweig R., Most H. Protective immunity produced by the injection of x-irradiated sporozoites of Plasmodium berghei. V. In vitro effects of immune serum on sporozoites. Mil Med. 1969 Sep;134(10):1183–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala F., Masuda A., Graves P. M., Nussenzweig V., Nussenzweig R. S. Ubiquity of the repetitive epitope of the CS protein in different isolates of human malaria parasites. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2790–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]