Abstract
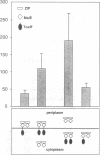
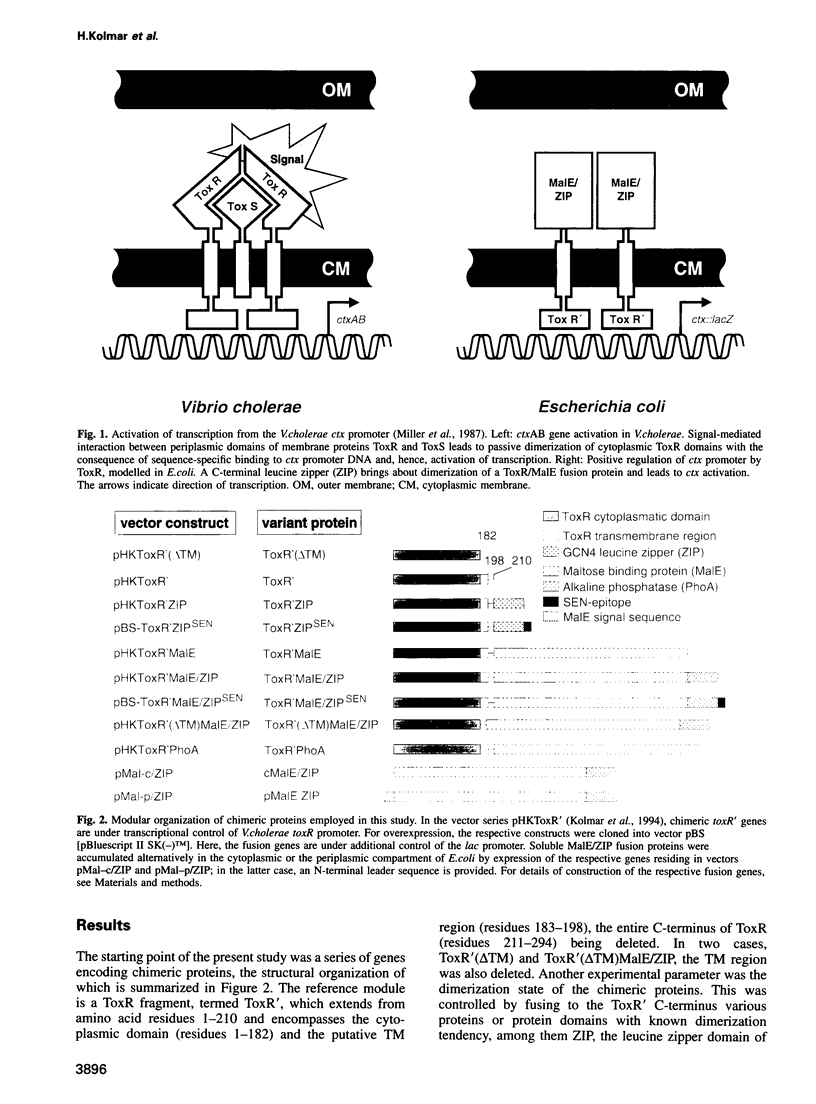
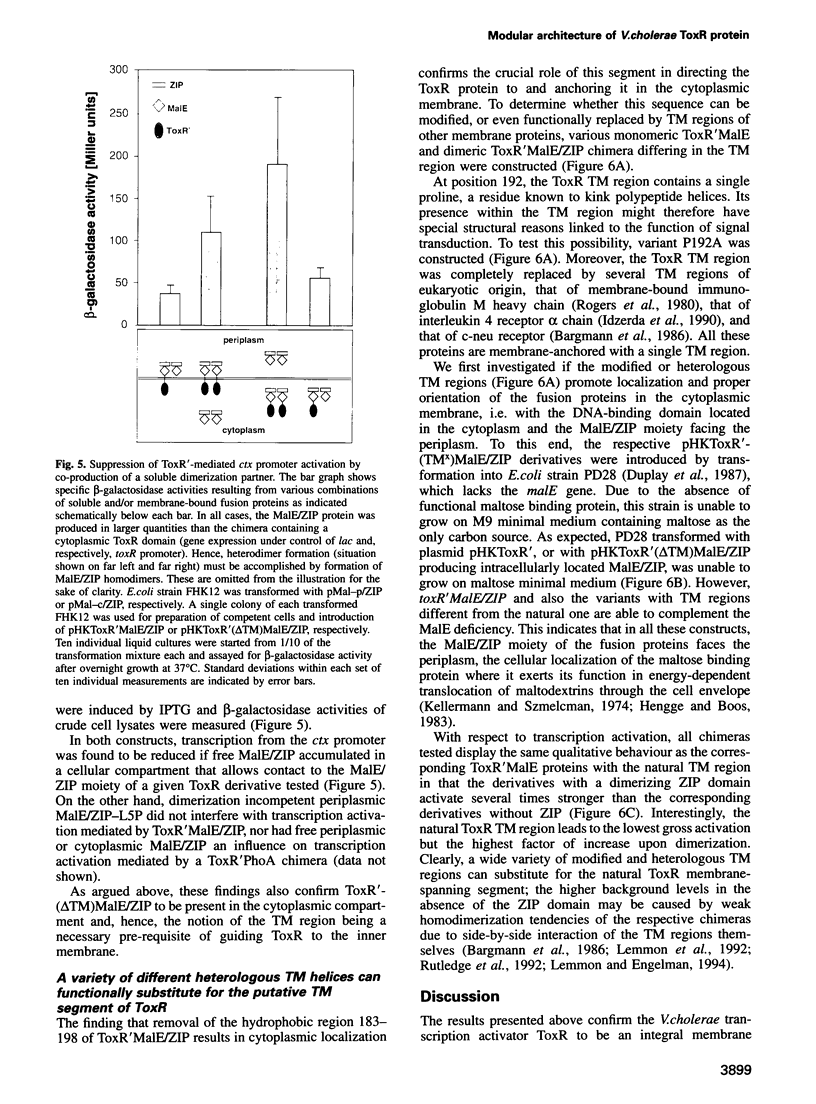
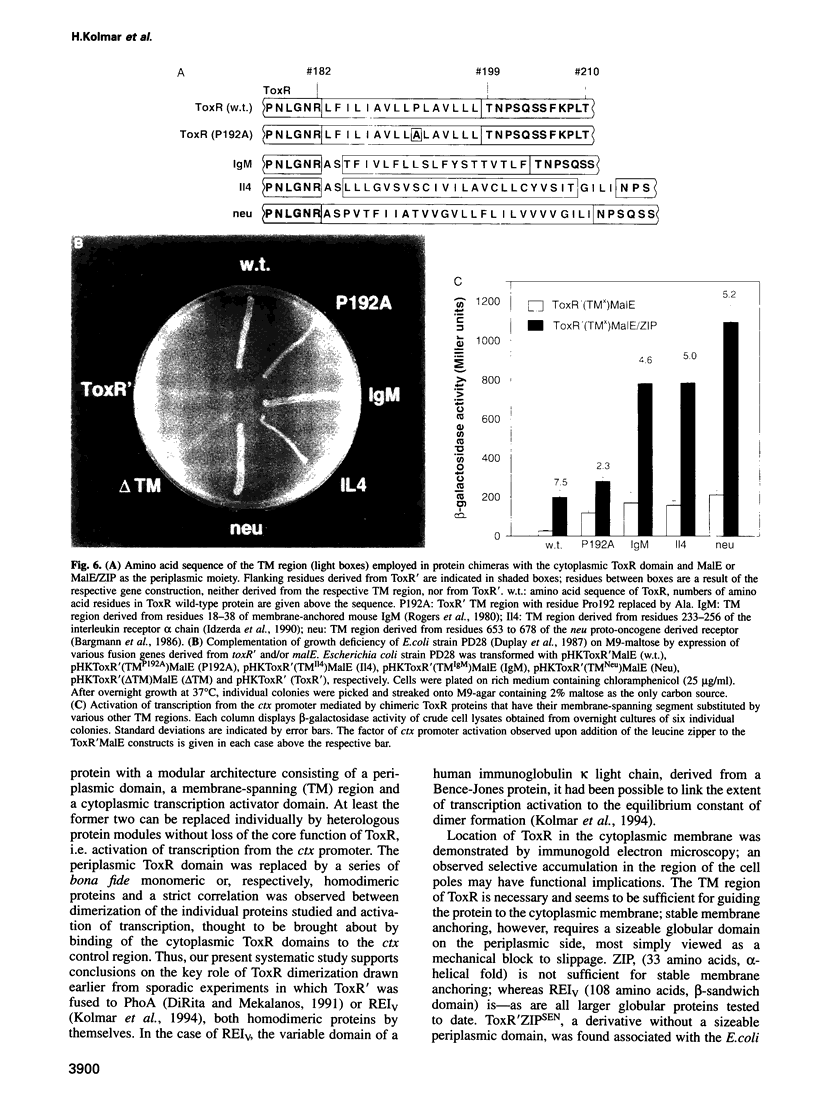
The Vibrio cholerae protein ToxR is an integral membrane protein that acts as a transcription activator in response to environmental signals; it controls expression of toxin genes ctxA and ctxB, along with a variety of other genes related to pathogenicity. Here it is shown that: (i) ToxR has a modular architecture and that activation of transcription starting at the ctx promoter depends strictly on dimerization of the periplasmic ToxR domain; (ii) the transmembrane (TM) region of ToxR is sufficient as a topogenic signal but not for stable membrane anchoring of the protein; (iii) the TM region has no special function in signal transduction and (iv) a proline residue located within the TM region minimizes background transcription activation, most plausibly by reducing TM-TM interaction. Possible applications of ToxR as a technical tool for analysing protein-protein interactions between pairs of arbitrary TM domains are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedouelle H., Duplay P. Production in Escherichia coli and one-step purification of bifunctional hybrid proteins which bind maltose. Export of the Klenow polymerase into the periplasmic space. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel A., Bedouelle H. Engineering the quaternary structure of an exported protein with a leucine zipper. Protein Eng. 1991 Apr;4(4):457–461. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J. Co-ordinate expression of virulence genes by ToxR in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Periplasmic interaction between two membrane regulatory proteins, ToxR and ToxS, results in signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90206-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederich L., Rasmussen L. J., Messer W. New cloning vectors for integration in the lambda attachment site attB of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Plasmid. 1992 Jul;28(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel R. C., Johnson D. A. Use of nonfat dry milk to block nonspecific nuclear and membrane staining by avidin conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jul;33(7):711–714. doi: 10.1177/33.7.2409130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplay P., Bedouelle H., Fowler A., Zabin I., Saurin W., Hofnung M. Sequences of the malE gene and of its product, the maltose-binding protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10606–10613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplay P., Szmelcman S., Bedouelle H., Hofnung M. Silent and functional changes in the periplasmic maltose-binding protein of Escherichia coli K12. I. Transport of maltose. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziejman M., Mekalanos J. J. Analysis of membrane protein interaction: ToxR can dimerize the amino terminus of phage lambda repressor. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(3):485–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einberger H., Mertz R., Hofschneider P. H., Neubert W. J. Purification, renaturation, and reconstituted protein kinase activity of the Sendai virus large (L) protein: L protein phosphorylates the NP and P proteins in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4274–4280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4274-4280.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge R., Boos W. Maltose and lactose transport in Escherichia coli. Examples of two different types of concentrative transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):443–478. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu J. C., O'Shea E. K., Kim P. S., Sauer R. T. Sequence requirements for coiled-coils: analysis with lambda repressor-GCN4 leucine zipper fusions. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1400–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2147779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzerda R. L., March C. J., Mosley B., Lyman S. D., Vanden Bos T., Gimpel S. D., Din W. S., Grabstein K. H., Widmer M. B., Park L. S. Human interleukin 4 receptor confers biological responsiveness and defines a novel receptor superfamily. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):861–873. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann O., Szmelcman S. Active transport of maltose in Escherichia coli K12. Involvement of a "periplasmic" maltose binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 15;47(1):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmar H., Ferrando E., Hennecke F., Wippler J., Fritz H. J. General mutagenesis/gene expression procedure for the construction of variant immunoglobulin domains in Escherichia coli. Production of the Bence-Jones protein REIv via fusion to beta-lactamase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90826-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolmar H., Frisch C., Kleemann G., Götze K., Stevens F. J., Fritz H. J. Dimerization of Bence Jones proteins: linking the rate of transcription from an Escherichia coli promoter to the association constant of REIV. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994 Jan;375(1):61–70. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1994.375.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Fritz H. J. Oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations via gapped duplex DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:350–367. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Engelman D. M. Specificity and promiscuity in membrane helix interactions. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Flanagan J. M., Treutlein H. R., Zhang J., Engelman D. M. Sequence specificity in the dimerization of transmembrane alpha-helices. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 29;31(51):12719–12725. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Identification of toxS, a regulatory gene whose product enhances toxR-mediated activation of the cholera toxin promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1288–1293. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1288-1293.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottemann K. M., Mekalanos J. J. Analysis of Vibrio cholerae ToxR function by construction of novel fusion proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Feb;15(4):719–731. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Associative properties of the Escherichia coli galactose binding protein and maltose binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):476–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91459-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Garavito M. Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 May;29(5):663–671. doi: 10.1177/29.5.6166664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge T., Cosson P., Manolios N., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Transmembrane helical interactions: zeta chain dimerization and functional association with the T cell antigen receptor. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3245–3254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Formation of a defective alkaline phosphatase subunit by a mutant of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1604–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowadski J. M., Handschumacher M. D., Murthy H. M., Foster B. A., Wyckoff H. W. Refined structure of alkaline phosphatase from Escherichia coli at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):417–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurlino J. C., Lu G. Y., Quiocho F. A. The 2.3-A resolution structure of the maltose- or maltodextrin-binding protein, a primary receptor of bacterial active transport and chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5202–5219. doi: 10.2210/pdb1mbp/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou N. E., Kay C. M., Hodges R. S. Synthetic model proteins. Positional effects of interchain hydrophobic interactions on stability of two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2664–2670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou N. E., Kay C. M., Hodges R. S. Synthetic model proteins: the relative contribution of leucine residues at the nonequivalent positions of the 3-4 hydrophobic repeat to the stability of the two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 30;31(25):5739–5746. doi: 10.1021/bi00140a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]