Abstract
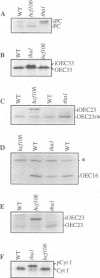
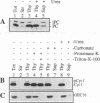
Results of in vitro experiments have suggested the existence of at least three pathways by which nuclear-encoded proteins are targeted to the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. However, few components of the targeting machinery have been identified and the relationship between the three pathways is not clear. To investigate mechanisms underlying thylakoid protein targeting, we identified nuclear mutations in maize that cause targeting defects. We found two mutations, tha1 and hcf106, that disrupt the localization of different sets of proteins to the thylakoid lumen. The tha1 mutation interferes with the targeting of one chloroplast-encoded protein, cytochrome f, and three nuclear-encoded proteins, plastocyanin, the psaF gene product and the 33 kDa subunit of the oxygen-evolving complex. The hcf106 mutation interferes with the targeting of the 16 and 23 kDa subunits of the oxygen-evolving complex. The tha1 and hcf106 phenotypes provide the first in vivo evidence supporting the existence of two distinct thylakoid-targeting pathways. Their phenotypes also provide evidence that one chloroplast-encoded protein, cytochrome f, engages the 'tha1' pathway, indicating that nuclear- and chloroplast-encoded proteins can be targeted via common machinery.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkan A., Miles D., Taylor W. C. Chloroplast gene expression in nuclear, photosynthetic mutants of maize. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1421–1427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Nuclear Mutants of Maize with Defects in Chloroplast Polysome Assembly Have Altered Chloroplast RNA Metabolism. Plant Cell. 1993 Apr;5(4):389–402. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A., Walker M., Nolasco M., Johnson D. A nuclear mutation in maize blocks the processing and translation of several chloroplast mRNAs and provides evidence for the differential translation of alternative mRNA forms. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3170–3181. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassham D. C., Bartling D., Mould R. M., Dunbar B., Weisbeek P., Herrmann R. G., Robinson C. Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Delineation of envelope "transit" and thylakoid "transfer" signals within the pre-sequences of three imported thylakoid lumen proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23606–23610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyton C., de Vitry C., Popot J. L. Membrane association of cytochrome b6f subunits. The Rieske iron-sulfur protein from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is an extrinsic protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7597–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Ettinger W. F., Theg S. M. Protein-specific energy requirements for protein transport across or into thylakoid membranes. Two lumenal proteins are transported in the absence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2688–2696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Henry R., Li C., Yuan J. Multiple pathways for protein transport into or across the thylakoid membrane. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4105–4114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbey R. E., Wickner W. Leader peptidase catalyzes the release of exported proteins from the outer surface of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15925–15931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobberstein B. Protein transport. On the beaten pathway. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):599–600. doi: 10.1038/367599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douwe de Boer A., Weisbeek P. J. Chloroplast protein topogenesis: import, sorting and assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 13;1071(3):221–253. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90015-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin A. E., Hoffman N. E. Characterization of a chloroplast homologue of the 54-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22175–22180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R., Kapazoglou A., McCaffery M., Cline K. Differences between lumen targeting domains of chloroplast transit peptides determine pathway specificity for thylakoid transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10189–10192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Franklin A. E. Evidence for a stromal GTP requirement for the integration of a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide into thylakoid membranes. Plant Physiol. 1994 May;105(1):295–304. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulford A., Hazell L., Mould R. M., Robinson C. Two distinct mechanisms for the translocation of proteins across the thylakoid membrane, one requiring the presence of a stromal protein factor and nucleotide triphosphates. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3251–3256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Schnabelrauch L. S., Sears B. B. A plastome mutation affects processing of both chloroplast and nuclear DNA-encoded plastid proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00282648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnauchov I., Cai D., Schmidt I., Herrmann R. G., Klösgen R. B. The thylakoid translocation of subunit 3 of photosystem I, the psaF gene product, depends on a bipartite transit peptide and proceeds along an azide-sensitive pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 30;269(52):32871–32878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwin P. M., Elderfield P. D., Robinson C. Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Partial purification of a thylakoidal processing peptidase involved in plastocyanin biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16386–16390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwin P. M., Meadows J. W., Shackleton J. B., Musgrove J. E., Elderfield P. D., Mould R., Hay N. A., Robinson C. ATP-dependent import of a lumenal protein by isolated thylakoid vesicles. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2251–2255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Henry R., Yuan J., Cline K., Hoffman N. E. A chloroplast homologue of the signal recognition particle subunit SRP54 is involved in the posttranslational integration of a protein into thylakoid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3789–3793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madueño F., Bradshaw S. A., Gray J. C. The thylakoid-targeting domain of the chloroplast Rieske iron-sulfur protein is located in the N-terminal hydrophobic region of the mature protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17458–17463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mant A., Nielsen V. S., Knott T. G., Møller B. L., Robinson C. Multiple mechanisms for the targeting of photosystem I subunits F, H, K, L, and N into and across the thylakoid membrane. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27303–27309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martienssen R. A., Barkan A., Freeling M., Taylor W. C. Molecular cloning of a maize gene involved in photosynthetic membrane organization that is regulated by Robertson's Mutator. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1633–1639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Bennoun P., Rochaix J. D. Expression of the nuclear encoded OEE1 protein is required for oxygen evolution and stability of photosystem II particles in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):313–318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Rahire M., Frank G., Zuber H., Rochaix J. D. Expression of the nuclear gene encoding oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 2 is required for high levels of photosynthetic oxygen evolution in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):749–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl D., Robinson C., Shackleton J. B., Herrmann R. G., Klösgen R. B. Targeting of proteins to the thylakoids by bipartite presequences: CFoII is imported by a novel, third pathway. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1310–1317. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould R. M., Robinson C. A proton gradient is required for the transport of two lumenal oxygen-evolving proteins across the thylakoid membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12189–12193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai M., Goto A., Nohara T., Sugita D., Endo T. Identification of the SecA protein homolog in pea chloroplasts and its possible involvement in thylakoidal protein transport. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31338–31341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen V. S., Mant A., Knoetzel J., Møller B. L., Robinson C. Import of barley photosystem I subunit N into the thylakoid lumen is mediated by a bipartite presequence lacking an intermediate processing site. Role of the delta pH in translocation across the thylakoid membrane. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3762–3766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plückthun A., Pfitzinger I. Membrane-bound beta-lactamase forms in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14315–14322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The complete general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):50–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.50-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C., Cai D., Hulford A., Brock I. W., Michl D., Hazell L., Schmidt I., Herrmann R. G., Klösgen R. B. The presequence of a chimeric construct dictates which of two mechanisms are utilized for translocation across the thylakoid membrane: evidence for the existence of two distinct translocation systems. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):279–285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C., Klösgen R. B. Targeting of proteins into and across the thylakoid membrane--a multitude of mechanisms. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Oct;26(1):15–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00039516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Gatenby A. A., Willey D. L., Gray J. C. Binding of pea cytochrome f to the inner membrane of Escherichia coli requires the bacterial secA gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7955–7959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Nielsen V. S., Knoetzel J., Andersen R., Møller B. L. Import of the barley PSI-F subunit into the thylakoid lumen of isolated chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Nov;26(4):1223–1229. doi: 10.1007/BF00040704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton J. B., Robinson C. Transport of proteins into chloroplasts. The thylakoidal processing peptidase is a signal-type peptidase with stringent substrate requirements at the -3 and -1 positions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12152–12156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. A., Kohorn B. D. Mutations in a signal sequence for the thylakoid membrane identify multiple protein transport pathways and nuclear suppressors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):365–374. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theg S. M., Scott S. V. Protein import into chloroplasts. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90212-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L. From the elephant to E. coli: SRP-dependent protein targeting. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):787–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Cline K. Plastocyanin and the 33-kDa subunit of the oxygen-evolving complex are transported into thylakoids with similar requirements as predicted from pathway specificity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18463–18467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Henry R., McCaffery M., Cline K. SecA homolog in protein transport within chloroplasts: evidence for endosymbiont-derived sorting. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):796–798. doi: 10.1126/science.7973633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vitry C. Characterization of the gene of the chloroplast Rieske iron-sulfur protein in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Indications for an uncleaved lumen targeting sequence. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7603–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]