Abstract
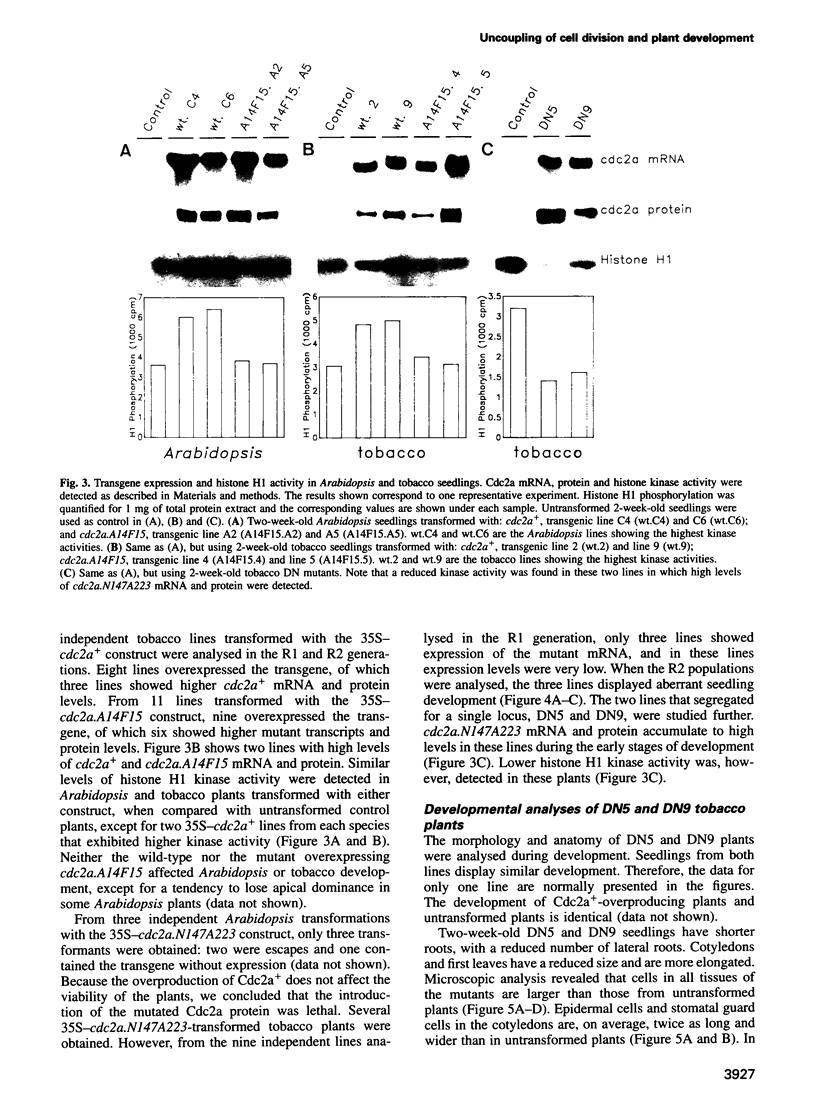
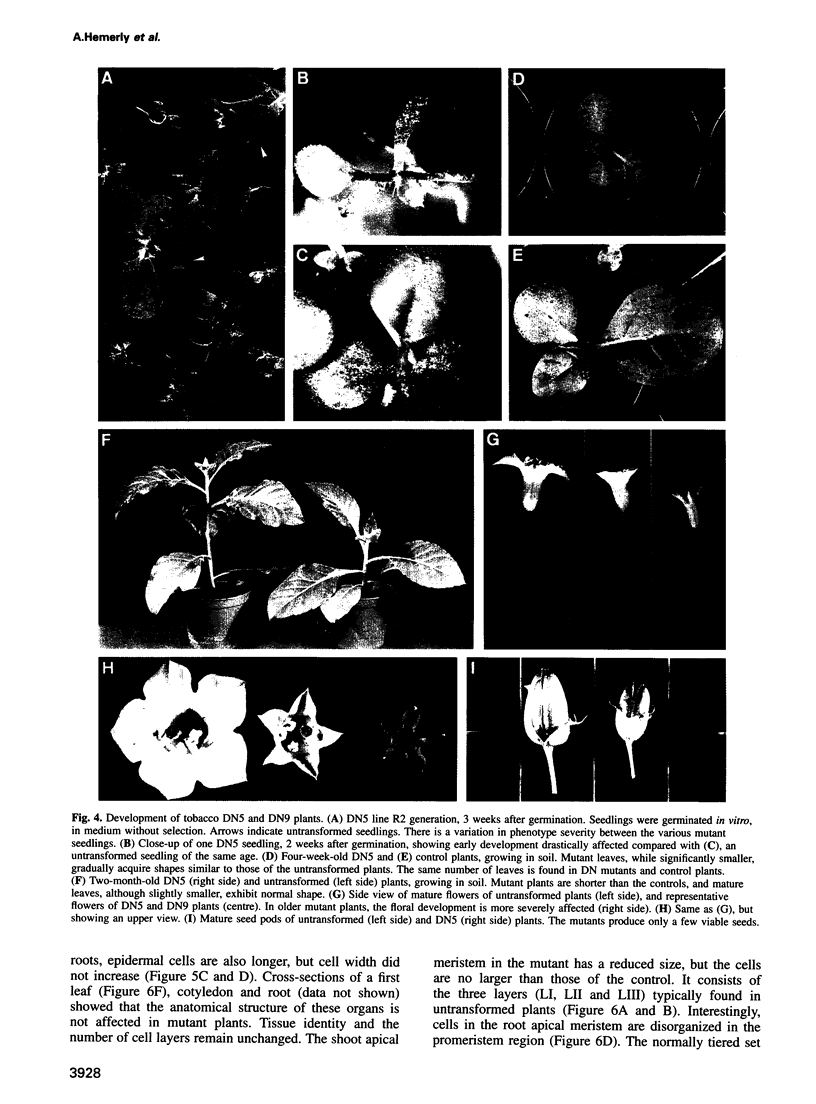
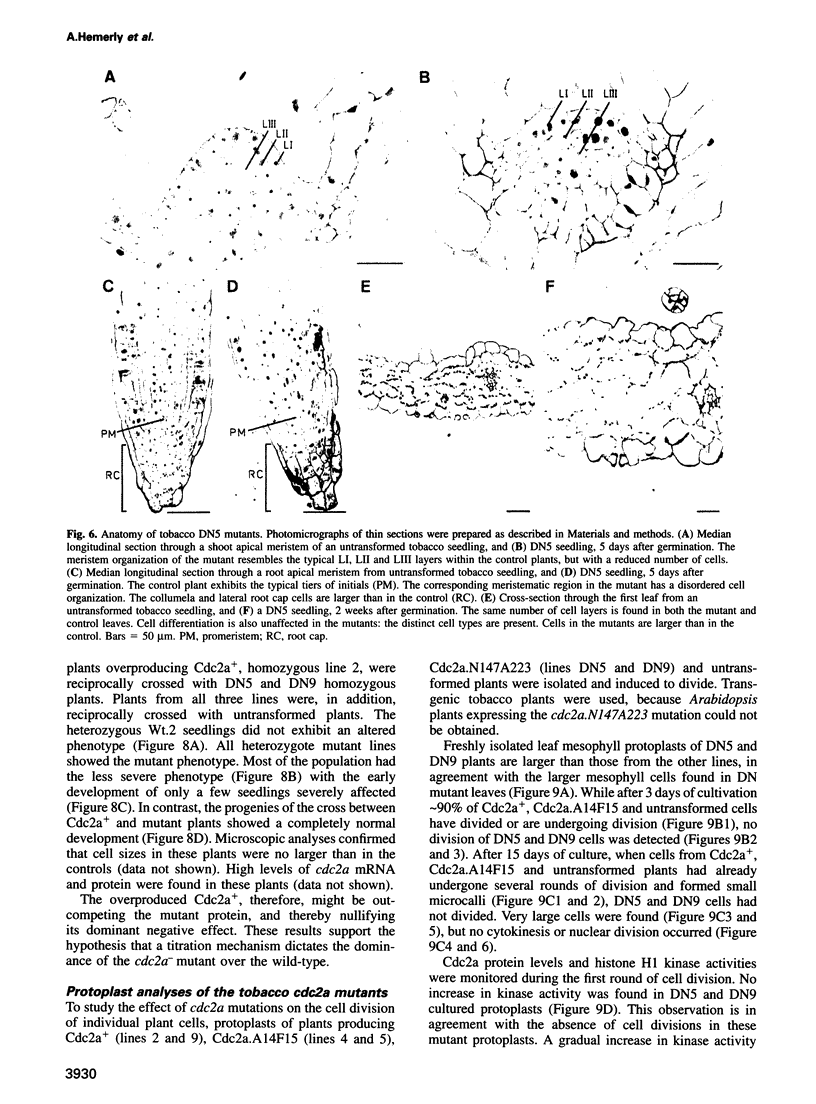
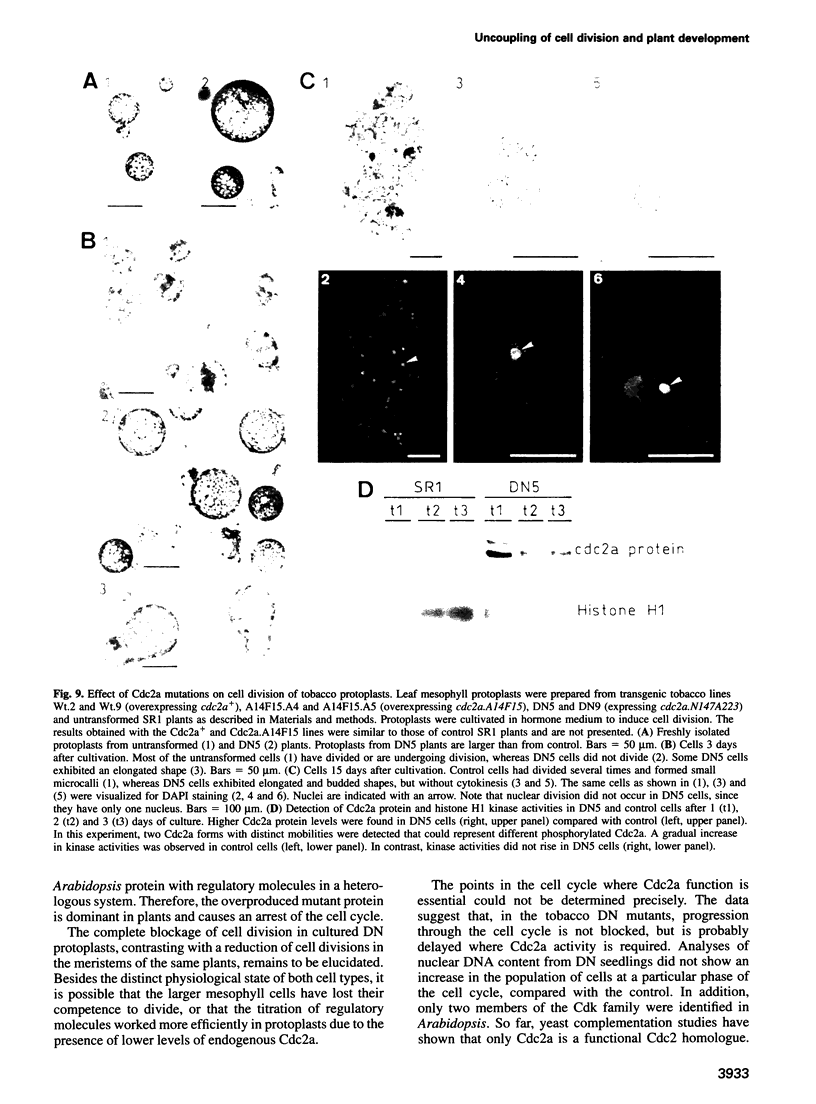
Because plant cells do not move and are surrounded by a rigid cell wall, cell division rates and patterns are believed to be directly responsible for generating new structures throughout development. To study the relationship between cell division and morphogenesis, transgenic tobacco and Arabidopsis plants were constructed expressing dominant mutations in a key regulator of the Arabidopsis cell cycle, the Cdc2a kinase. Plants constitutively overproducing the wild-type Cdc2a or the mutant form predicted to accelerate the cell cycle did not exhibit a significantly altered development. In contrast, a mutation expected to arrest the cell cycle abolished cell division when expressed in Arabidopsis, whereas some tobacco plants constitutively producing this mutant protein were recovered. These plants had a reduced histone H1 kinase activity and contained considerably fewer cells. These cells were, however, much larger and underwent normal differentiation. Morphogenesis, histogenesis and developmental timing were unaffected. The results indicate that, in plants, the developmental controls defining shape can act independently from cell division rates.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4691.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton-Fessler S., Hannig G., Piwnica-Worms H. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation and cell cycle control. Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;4(6):433–442. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi L., Meijer L., Reed S. I., Pidikiti R., Tung H. Y. Interaction between the cell-cycle-control proteins p34cdc2 and p9CKShs2. Evidence for two cooperative binding domains in p9CKShs2. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;203(3):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Tissue-specific expression from CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains in early stages of plant development. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1677–1684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergounioux C., Brown S. C. Plant cell cycle analysis with isolated nuclei. Methods Cell Biol. 1990;33:563–573. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busturia A., Lawrence P. A. Regulation of cell number in Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):561–563. doi: 10.1038/370561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkacz B., Carr A., Nurse P. Transcription of the cdc2 cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):369–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira P. C., Hemerly A. S., Villarroel R., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. The Arabidopsis functional homolog of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):531–540. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemerly A. S., Ferreira P., de Almeida Engler J., Van Montagu M., Engler G., Inzé D. cdc2a expression in Arabidopsis is linked with competence for cell division. Plant Cell. 1993 Dec;5(12):1711–1723. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.12.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérouart D., Van Montagu M., Inzé D. Developmental and environmental regulation of the Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cytosolic Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1994 Mar;104(3):873–880. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imajuku Y., Hirayama T., Endoh H., Oka A. Exon-intron organization of the Arabidopsis thaliana protein kinase genes CDC2a and CDC2b. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 8;304(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80592-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. Control of the cell cycle. Dev Biol. 1992 Sep;153(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90087-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G. Pattern formation in the flowering plant embryo. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Aug;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landt O., Grunert H. P., Hahn U. A general method for rapid site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90351-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Jørgensen J. E., Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J., Doerner P. W. Spatial pattern of cdc2 expression in relation to meristem activity and cell proliferation during plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. Thiamine-repressible expression vectors pREP and pRIP for fission yeast. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90551-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall M. D., Richardson H. E., Reed S. I. Dominant negative protein kinase mutations that confer a G1 arrest phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4426–4430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. Cell-cycle control: turning on mitosis. Curr Biol. 1993 May 1;3(5):291–293. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90182-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Okazaki N., Kume K., Jinno S., Tanaka K., Okayama H. High-frequency transformation method and library transducing vectors for cloning mammalian cDNAs by trans-complementation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6485–6489. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Clear as crystal? Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):544–547. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90053-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J. Activation of the various cyclin/cdc2 protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens D., Van Montagu M., Van Lijsebettens M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5536–5540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West MAL., Harada J. J. Embryogenesis in Higher Plants: An Overview. Plant Cell. 1993 Oct;5(10):1361–1369. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.10.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











