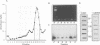Abstract
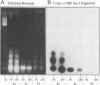
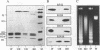
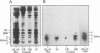
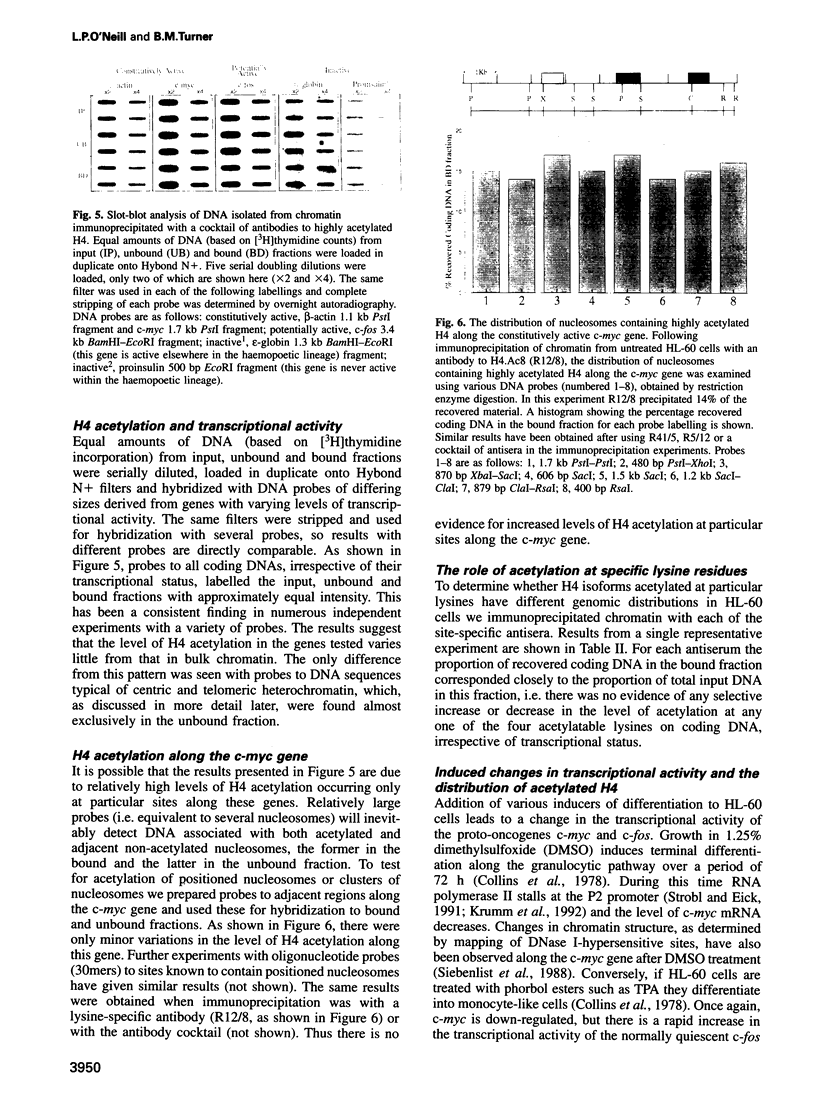
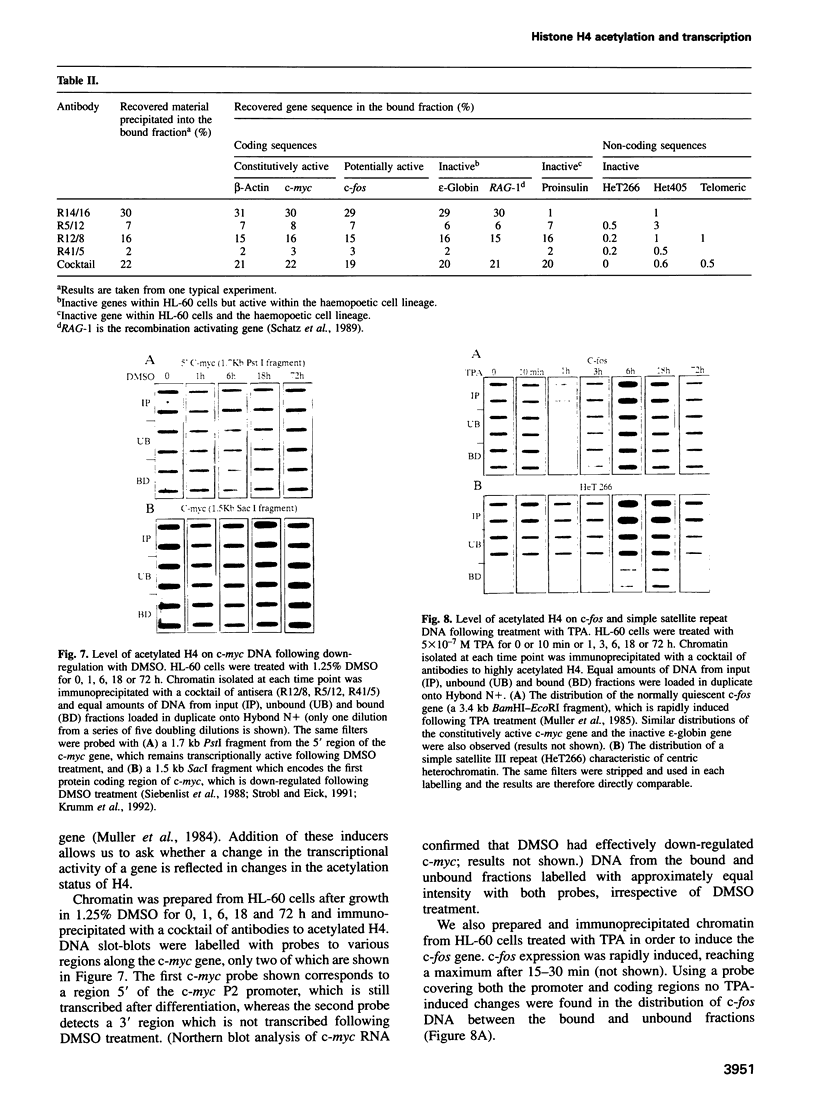
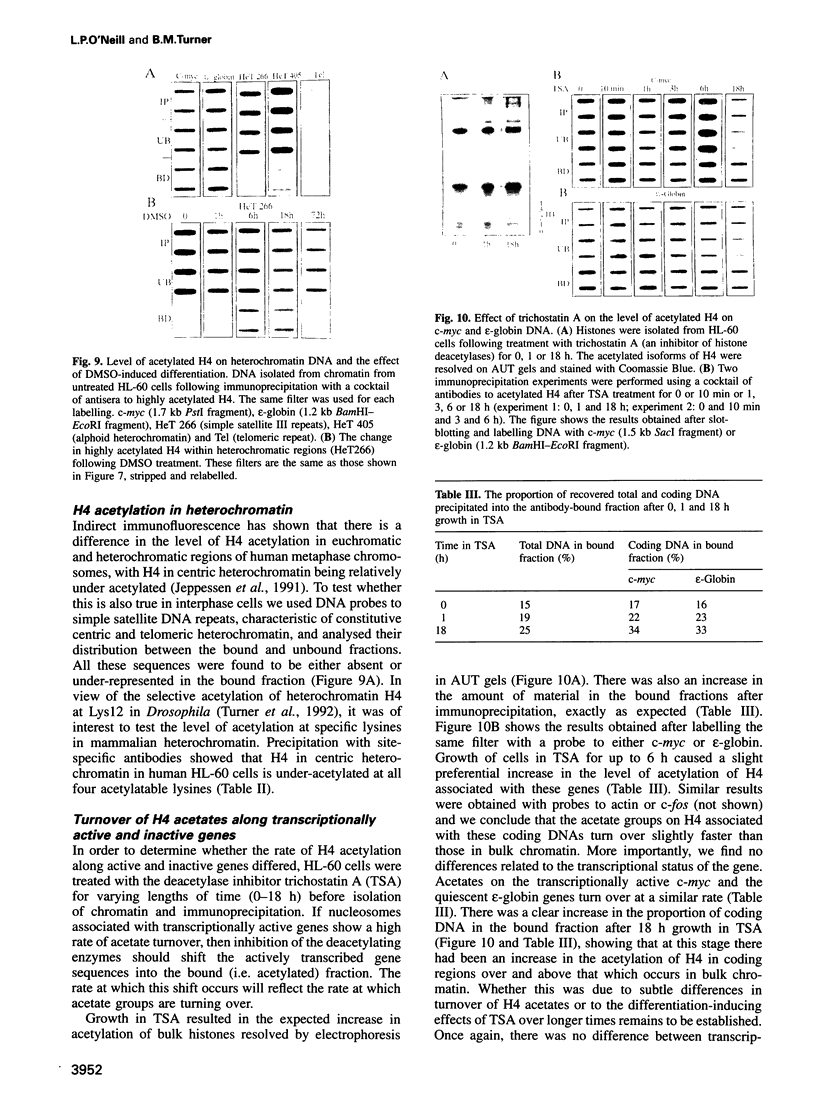
By immunoprecipitation of chromatin fragments from cultured human HL-60 cells with antibodies specific for H4 acetylated at specific lysine residues we have defined the level of H4 acetylation within transcriptionally active and inactive regions of the genome. H4 within or adjacent to coding regions had a similar level of overall acetylation to input (bulk) chromatin and a similar pattern of acetylation of individual lysines (i.e. 16 > 8, 12 > 5). The acetylation of H4 in coding (and adjacent) regions was not correlated with transcriptional activity and did not vary with position along the constitutively active c-myc gene. Turnover of H4 acetates was not selectively increased in transcriptionally active chromatin. H4 associated with centric heterochromatin or with the CCCTAA repeat of telomeric heterochromatin was infrequently acetylated (< 1%) at all lysines. We conclude that nucleosomes containing acetylated H4 are scattered infrequently and possibly randomly through coding and adjacent regions and are essentially absent from heterochromatin. Induction of differentiation of HL-60 cells by exposure to dimethylsulfoxide or 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) did not alter the level of H4 acetylation within either the c-myc or c-fos genes or other coding regions, but did induce a transient increase in H4 acetylation within centric heterochromatin.
Full text
PDF

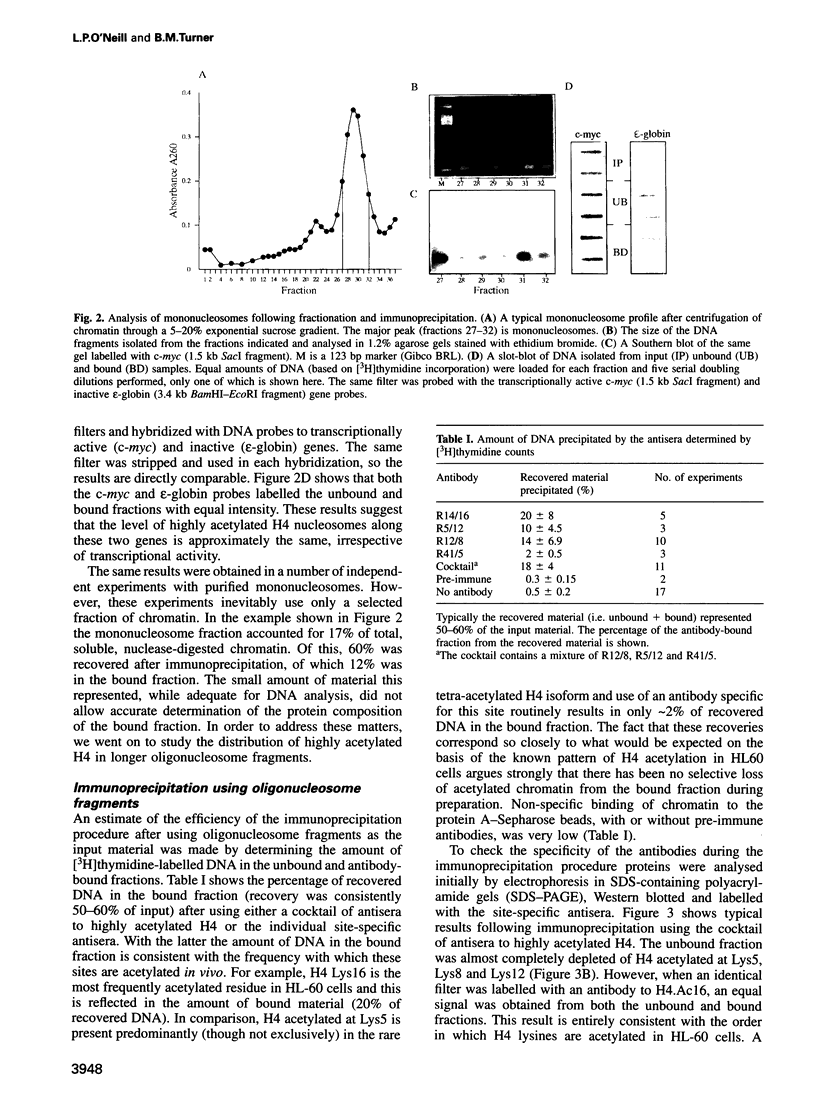






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLFREY V. G., FAULKNER R., MIRSKY A. E. ACETYLATION AND METHYLATION OF HISTONES AND THEIR POSSIBLE ROLE IN THE REGULATION OF RNA SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:786–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra P., Sterner R., Clayton D. F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatographic purification of nucleosomes containing transcriptionally active DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Walker J., Chen T. A., Sterner R., Mariani M. R., Allfrey V. G. Factors affecting nucleosome structure in transcriptionally active chromatin. Histone acetylation, nascent RNA and inhibitors of RNA synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):811–823. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., West M. H., Stedman J. D. Two-dimensional gel analysis of histones in acid extracts of nuclei, cells, and tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):17–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein M., Rose A. B., Holmes S. G., Allis C. D., Broach J. R. Transcriptional silencing in yeast is associated with reduced nucleosome acetylation. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):592–604. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Sterner R., Cozzolino A., Allfrey V. G. Reversible and irreversible changes in nucleosome structure along the c-fos and c-myc oncogenes following inhibition of transcription. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 5;212(3):481–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90327-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton A. L., Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. Histone acetylation and gene induction in human cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 20;336(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81601-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. M., Bickmore W. A. The distribution of CpG islands in mammalian chromosomes. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):376–382. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Isolation of oligonucleosomes from active chromatin using HMG17-specific monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3363–3376. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Mann R. K., Kayne P. S., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H4 N-terminal sequence is required for promoter activation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90554-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Clayton A. L., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. Core histone hyperacetylation co-maps with generalized DNase I sensitivity in the chicken beta-globin chromosomal domain. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1823–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Clayton A. L., Crane-Robinson C. Histone acetylation and globin gene switching. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1017–1022. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Jackson V., Meier J., Chalkley R. The separation of transcriptionally engaged genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14044–14052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie S., Sezaki M., Kato Y. A faithful double stain of proteins in the polyacrylamide gels with Coomassie blue and silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 1;126(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen P., Turner B. M. The inactive X chromosome in female mammals is distinguished by a lack of histone H4 acetylation, a cytogenetic marker for gene expression. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90419-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Fisher-Adams G., Grunstein M. Identification of a non-basic domain in the histone H4 N-terminus required for repression of the yeast silent mating loci. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2201–2209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure of transcriptionally competent and repressed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumm A., Meulia T., Brunvand M., Groudine M. The block to transcriptional elongation within the human c-myc gene is determined in the promoter-proximal region. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2201–2213. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl P. Histone acetylation: facts and questions. Chromosoma. 1994 Dec;103(7):441–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00337382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R. K., Grunstein M. Histone H3 N-terminal mutations allow hyperactivation of the yeast GAL1 gene in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3297–3306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew C. G., Goodwin G. H., Johns E. W. Studies on the association of the high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins with isolated nucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):167–179. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Landsman D., Druckmann S., Bustin M. Immunofractionation of chromatin regions associated with histone H1o. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Curran T., Müller D., Guilbert L. Induction of c-fos during myelomonocytic differentiation and macrophage proliferation. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):546–548. doi: 10.1038/314546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. The effect of histone hyperacetylation on the nuclease sensitivity and the solubility of chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Hamlyn P., Baer R. Effect of somatic mutation within translocated c-myc genes in Burkitt's lymphoma. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):592–597. doi: 10.1038/309592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlake T., Klehr-Wirth D., Yoshida M., Beppu T., Bode J. Gene expression within a chromatin domain: the role of core histone hyperacetylation. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 12;33(14):4197–4206. doi: 10.1021/bi00180a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Bressler P., Kelly K. Two distinct mechanisms of transcriptional control operate on c-myc during differentiation of HL60 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobl L. J., Eick D. Hold back of RNA polymerase II at the transcription start site mediates down-regulation of c-myc in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3307–3314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne A. W., Kmiciek D., Mitchelson K., Sautiere P., Crane-Robinson C. Patterns of histone acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):701–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Birley A. J., Lavender J. Histone H4 isoforms acetylated at specific lysine residues define individual chromosomes and chromatin domains in Drosophila polytene nuclei. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90417-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M. Decoding the nucleosome. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Fellows G. Specific antibodies reveal ordered and cell-cycle-related use of histone-H4 acetylation sites in mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M. Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 May;99(Pt 1):13–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., O'Neill L. P., Allan I. M. Histone H4 acetylation in human cells. Frequency of acetylation at different sites defined by immunolabeling with site-specific antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80947-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]