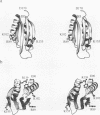Abstract
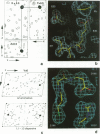
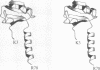
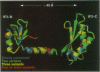
The structures of the two domains of translational initiation factor IF3 from Bacillus stearothermophilus have been solved by X-ray crystallography using single wavelength anomalous scattering and multiwavelength anomalous diffraction. Each of the two domains has an alpha/beta topology, with an exposed beta-sheet that is reminiscent of several ribosomal and other RNA binding proteins. An alpha-helix that protrudes out from the body of the N-terminal domain towards the C-terminal domain suggests that IF3 consists of two RNA binding domains connected by an alpha-helix and that it may bridge two regions of the ribosome. This represents the first high resolution structural information on a translational initiation factor.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cummings H. S., Hershey J. W. Translation initiation factor IF1 is essential for cell viability in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.198-205.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bellis D., Liveris D., Goss D., Ringquist S., Schwartz I. Structure-function analysis of Escherichia coli translation initiation factor IF3: tyrosine 107 and lysine 110 are required for ribosome binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):11984–11990. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Moine H., Mougel M., Dondon J., Grunberg-Manago M., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Cross-linking of initiation factor IF3 to Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II): characterization of two cross-linking sites in 16S rRNA; a possible way of functioning for IF3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4803–4821. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. D., Waugh D. S., Scheffler J. E., Tsao K. L., Prinzo K. M., Fry D. C. Chemical shift assignments and folding topology of the Ras-binding domain of human Raf-1 as determined by heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 28;33(25):7745–7752. doi: 10.1021/bi00191a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier P. L., Schmitter J. M., Garcia C., Dardel F. The N-terminal half of initiation factor IF3 is folded as a stable independent domain. Biochimie. 1994;76(5):376–383. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(94)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia C., Fortier P. L., Blanquet S., Lallemand J. Y., Dardel F. 1H and 15N resonance assignments and structure of the N-terminal domain of Escherichia coli initiation factor 3. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Mar 1;228(2):395–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden B. L., Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. Ribosomal protein L6: structural evidence of gene duplication from a primitive RNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):4901–4908. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg-Manago M., Dessen P., Pantaloni D., Godefroy-Colburn T., Wolfe A. D., Dondon J. Light-scattering studies showing the effect of initiation factors on the reversible dissociation of Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):461–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C. O., Pon C. L. Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5881–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., Binkley J., Hollingsworth T., Gold L. Domains of initiator tRNA and initiation codon crucial for initiator tRNA selection by Escherichia coli IF3. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1790–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Gold L. Selection of the initiator tRNA by Escherichia coli initiation factors. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1899–1912. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Determination of macromolecular structures from anomalous diffraction of synchrotron radiation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):51–58. doi: 10.1126/science.1925561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Davies C., Gerchman S. E., Kycia J. H., Porter S. J., White S. W., Ramakrishnan V. Crystal structure of prokaryotic ribosomal protein L9: a bi-lobed RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):205–212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Query C. C., Golden B. L., White S. W., Keene J. D. RNA-binding domain of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein analyzed by NMR spectroscopy is structurally similar to ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Wang R. Y., Shih J. W., Lo S. C. Identification of a putative infC-rpmI-rplT operon flanked by long inverted repeats in Mycoplasma fermentans (incognitus strain). Gene. 1993 May 15;127(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90619-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kycia J. H., Biou V., Shu F., Gerchman S. E., Graziano V., Ramakrishnan V. Prokaryotic translation initiation factor IF3 is an elongated protein consisting of two crystallizable domains. Biochemistry. 1995 May 9;34(18):6183–6187. doi: 10.1021/bi00018a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughrea M., Tam J. Ribosomal protein S1 and initiation factor IF3 do not promote the ribosomal binding of approximately 19-nucleotide-long mDNA and mRNA models. Biochem Cell Biol. 1989 Nov-Dec;67(11-12):812–817. doi: 10.1139/o89-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijonmarck M., Appelt K., Badger J., Liljas A., Wilson K. S., White S. W. Structural comparison of the prokaryotic ribosomal proteins L7/L12 and L30. Proteins. 1988;3(4):243–251. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liveris D., Schwartz J. J., Geertman R., Schwartz I. Molecular cloning and sequencing of infC, the gene encoding translation initiation factor IF3, from four enterobacterial species. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Sep 1;112(2):211–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKeen L. A., Kahan L., Wahba A. J., Schwartz I. Photochemical cross-linking of initiation factor-3 to Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10526–10531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Samaha R. R., Gualerzi C., Noller H. F. Specific protection of 16 S rRNA by translational initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 28;248(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(95)80042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muralikrishna P., Wickstrom E. Escherichia coli initiation factor 3 protein binding to 30S ribosomal subunits alters the accessibility of nucleotides within the conserved central region of 16S rRNA. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7505–7510. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Oubridge C., Jessen T. H., Li J., Evans P. R. Crystal structure of the RNA-binding domain of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):515–520. doi: 10.1038/348515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa H., Gualerzi C. Structure-function relationship in Escherichia coli initiation factors. Identification of a lysine residue in the ribosomal binding site of initiation factor by site-specific chemical modification with pyridoxal phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4905–4912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oubridge C., Ito N., Evans P. R., Teo C. H., Nagai K. Crystal structure at 1.92 A resolution of the RNA-binding domain of the U1A spliceosomal protein complexed with an RNA hairpin. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):432–438. doi: 10.1038/372432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pon C. L., Brombach M., Thamm S., Gualerzi C. O. Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster from Bacillus stearothermophilus comprising infC, rpmI and rplT. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):355–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00331290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V. R., Yabuki S., Sillers I. Y., Schindler D. G., Engelman D. M., Moore P. B. Positions of proteins S6, S11 and S15 in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):739–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90416-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. The structure of ribosomal protein S5 reveals sites of interaction with 16S rRNA. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):768–771. doi: 10.1038/358768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacerdot C., Fayat G., Dessen P., Springer M., Plumbridge J. A., Grunberg-Manago M., Blanquet S. Sequence of a 1.26-kb DNA fragment containing the structural gene for E.coli initiation factor IF3: presence of an AUU initiator codon. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):311–315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Davis B. D. Activity of initiation factor F3 in dissociating Escherichia coli ribosomes. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1273–1275. doi: 10.1038/2281273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J., Hershey J. W. Fluorescence polarization studies of the interaction of Escherichia coli protein synthesis initiation factor 3 with 30S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5859–5865. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J., Hershey J. W. The binding of fluorescein-labeled protein synthesis initiation factor 2 to Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits determined by fluorescence polarization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1215–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. Nuclease mapping of the secondary structure of the 49-nucleotide 3' terminal cloacin fragment of Escherichia coli 16s RNA and its interactions with initiation factor 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2035–2052. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. S., Appelt K., Badger J., Tanaka I., White S. W. Crystal structure of a prokaryotic ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker F. H., Hershey J. W. Binding of Escherichia coli protein synthesis initiation factor IF1 to 30S ribosomal subunits measured by fluorescence polarization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3682–3690. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]