Abstract
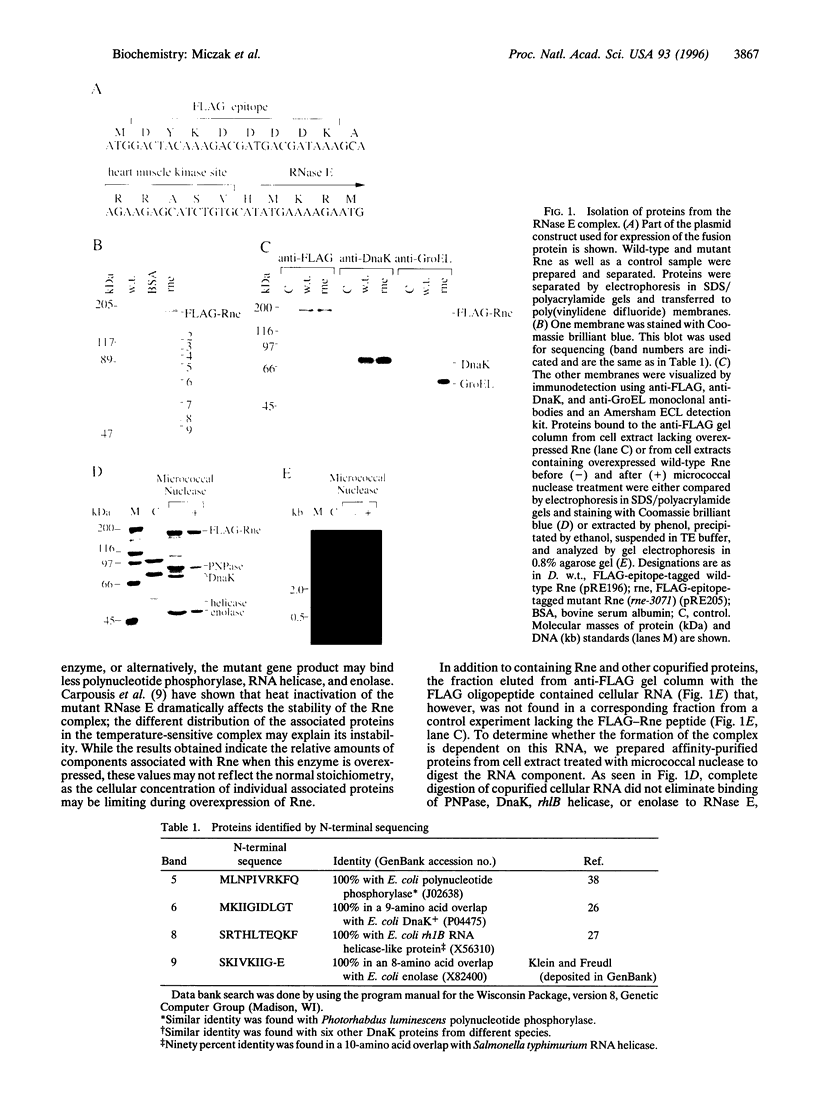
The Escherichia coli endoribonuclease RNase E is essential for RNA processing and degradation. Earlier work provided evidence that RNase E exists intracellularly as part of a multicomponent complex and that one of the components of this complex is a 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease, polynucleotide phosphorylase (EC 2.7.7.8). To isolate and identify other components of the RNase E complex, FLAG-epitope-tagged RNase E (FLAG-Rne) fusion protein was purified on a monoclonal antibody-conjugated agarose column. The FLAG-Rne fusion protein, eluted by competition with the synthetic FLAG peptide, was found to be associated with other proteins. N-terminal sequencing of these proteins revealed the presence in the RNase E complex not only of polynucleotide phosphorylase but also of DnaK, RNA helicase, and enolase (EC 4.2.1.11). Another protein associated only with epitope-tagged temperature-sensitive (Rne-3071) mutant RNase E but not with the wild-type enzyme is GroEL. The FLAG-Rne complex has RNase E activity in vivo and in vitro. The relative amount of proteins associated with wild-type and Rne-3071 expressed at an elevated temperature differed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B. Regulation of the Escherichia coli heat-shock response. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):671–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpousis A. J., Van Houwe G., Ehretsmann C., Krisch H. M. Copurification of E. coli RNAase E and PNPase: evidence for a specific association between two enzymes important in RNA processing and degradation. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):889–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90363-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casarégola S., Jacq A., Laoudj D., McGurk G., Margarson S., Tempête M., Norris V., Holland I. B. Cloning and analysis of the entire Escherichia coli ams gene. ams is identical to hmp1 and encodes a 114 kDa protein that migrates as a 180 kDa protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Roeder R. G. Expression and purification of general transcription factors by FLAG epitope-tagging and peptide elution. Pept Res. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(2):62–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie-Martin F., Diaz-Torres M. R., Yancey S. D., Kushner S. R. Analysis of the altered mRNA stability (ams) gene from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis, and homology of its product to MRP3, a mitochondrial ribosomal protein from Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2843–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack R. S., Genereaux J. L., Mackie G. A. RNase E activity is conferred by a single polypeptide: overexpression, purification, and properties of the ams/rne/hmp1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., van der Vies S. M. Molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghora B. K., Apirion D. Structural analysis and in vitro processing to p5 rRNA of a 9S RNA molecule isolated from an rne mutant of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum K., Apririon D. Inactivation of the ribonucleic acid-processing enzyme ribonuclease E blocks cell division. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):128–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.128-132.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Martin J., Neupert W. Protein folding in the cell: the role of molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp60. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:293–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iost I., Dreyfus M. mRNAs can be stabilized by DEAD-box proteins. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):193–196. doi: 10.1038/372193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani M. H., Maitra P. K. Properties of Escherichia coli mutants deficient in enzymes of glycolysis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):398–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.398-410.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain C., Belasco J. G. RNase E autoregulates its synthesis by controlling the degradation rate of its own mRNA in Escherichia coli: unusual sensitivity of the rne transcript to RNase E activity. Genes Dev. 1995 Jan 1;9(1):84–96. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. G., Inouye M. The cold-shock response--a hot topic. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(5):811–818. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman M., Murphy H., Cashel M. rhlB, a new Escherichia coli K-12 gene with an RNA helicase-like protein sequence motif, one of at least five such possible genes in a prokaryote. New Biol. 1991 Sep;3(9):886–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Georgopoulos C. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli heat shock response by the DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11019–11023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chao S., Cohen S. N. The rate of processing and degradation of antisense RNAI regulates the replication of ColE1-type plasmids in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1233–1242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90018-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Chao S., Wong T. T., McDowall K. J., Cohen S. N. Effects of nucleotide sequence on the specificity of rne-dependent and RNase E-mediated cleavages of RNA I encoded by the pBR322 plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10797–10803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall K. J., Cohen S. N. The N-terminal domain of the rne gene product has RNase E activity and is non-overlapping with the arginine-rich RNA-binding site. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jan 26;255(3):349–355. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall K. J., Hernandez R. G., Lin-Chao S., Cohen S. N. The ams-1 and rne-3071 temperature-sensitive mutations in the ams gene are in close proximity to each other and cause substitutions within a domain that resembles a product of the Escherichia coli mre locus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4245–4249. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4245-4249.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowall K. J., Kaberdin V. R., Wu S. W., Cohen S. N., Lin-Chao S. Site-specific RNase E cleavage of oligonucleotides and inhibition by stem-loops. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):287–290. doi: 10.1038/374287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miczak A., Apirion D. The rne gene and ribonuclease E. Biochimie. 1993;75(6):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miczak A., Srivastava R. A., Apirion D. Location of the RNA-processing enzymes RNase III, RNase E and RNase P in the Escherichia coli cell. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1801–1810. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd E. A., Higgins C. F. Escherichia coli endoribonuclease RNase E: autoregulation of expression and site-specific cleavage of mRNA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):557–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd E. A., Krisch H. M., Higgins C. F. RNase E, an endoribonuclease, has a general role in the chemical decay of Escherichia coli mRNA: evidence that rne and ams are the same genetic locus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2127–2135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Py B., Causton H., Mudd E. A., Higgins C. F. A protein complex mediating mRNA degradation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Nov;14(4):717–729. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Le Meur M., Portier C. E.coli polynucleotide phosphorylase expression is autoregulated through an RNase III-dependent mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2633–2641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M. K., Apirion D. Purification and properties of ribonuclease E, an RNA-processing enzyme from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 28;747(3):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier P., Grunberg-Manago M., Portier C. Nucleotide sequence of the pnp gene of Escherichia coli encoding polynucleotide phosphorylase. Homology of the primary structure of the protein with the RNA-binding domain of ribosomal protein S1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman MYu, Goldberg A. L. Involvement of the chaperonin dnaK in the rapid degradation of a mutant protein in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):71–77. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohlberg B., Lundberg U., Hartl F. U., von Gabain A. Functional interaction of heat shock protein GroEL with an RNase E-like activity in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):277–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu F., Cohen S. N. RNA degradation in Escherichia coli regulated by 3' adenylation and 5' phosphorylation. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):180–183. doi: 10.1038/374180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]