Abstract
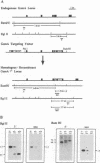
Granzyme A, a granule-associated serine proteinase of activated cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells, has been reported to play a critical role in DNA fragmentation of target cells. To address the question of the biological role of granzyme A, we have now generated a granzyme A-deficient mouse mutant by homologous recombination. Western blot analysis, enzyme assays and reverse transcription-PCR confirmed the absence of granzyme A in activated T cells. In addition, deletion of granzyme A does not alter the expression patterns of other granule components, such as granzymes B-G and perforin. Granzyme A-deficient mice are healthy and show normal hematopoietic development. Most notably, their in vitro- and ex vivo-derived cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells are indistinguishable from those of normal mice in causing membrane disruption, apoptosis and DNA fragmentation in target cells. Furthermore, granzyme A-deficient mice readily recover from both lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus and Listeria monocytogenes infections and eradicate syngeneic tumors with kinetics similar to the wild-type strain. These results demonstrate that granzyme A does not play a primary role in cell-mediated cytotoxicity, as has been assumed previously.
Full text
PDF


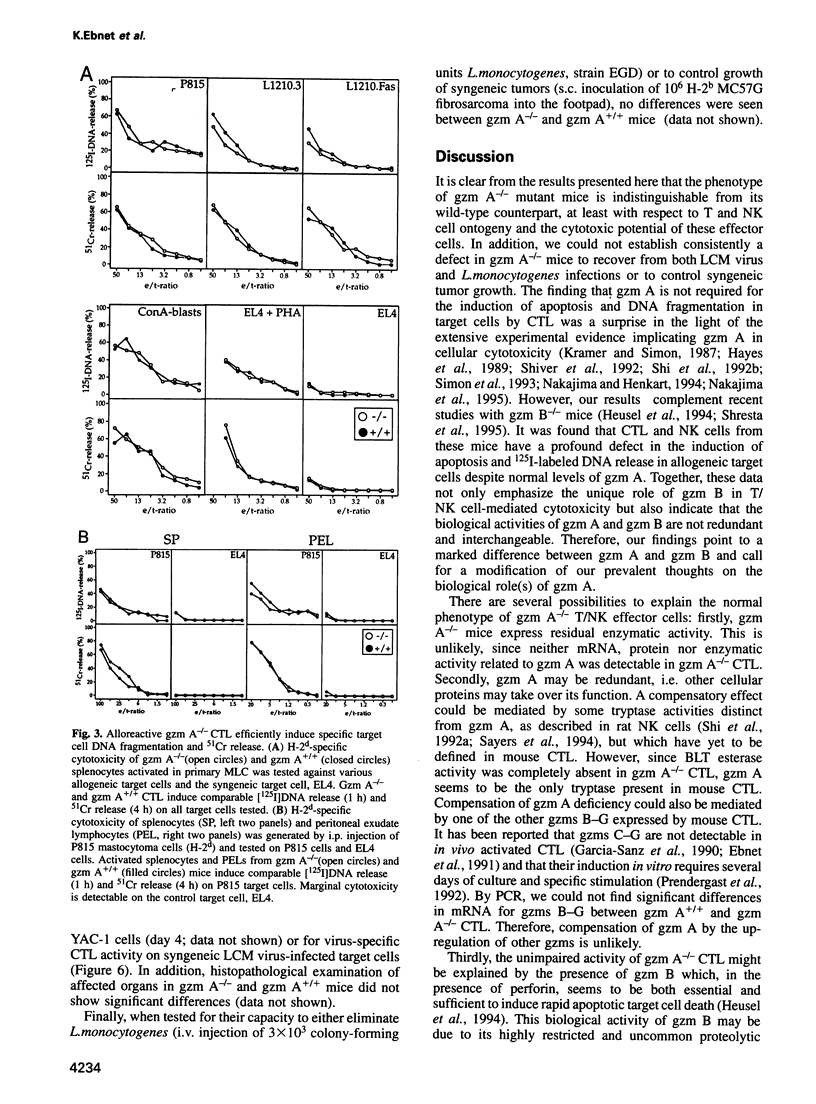
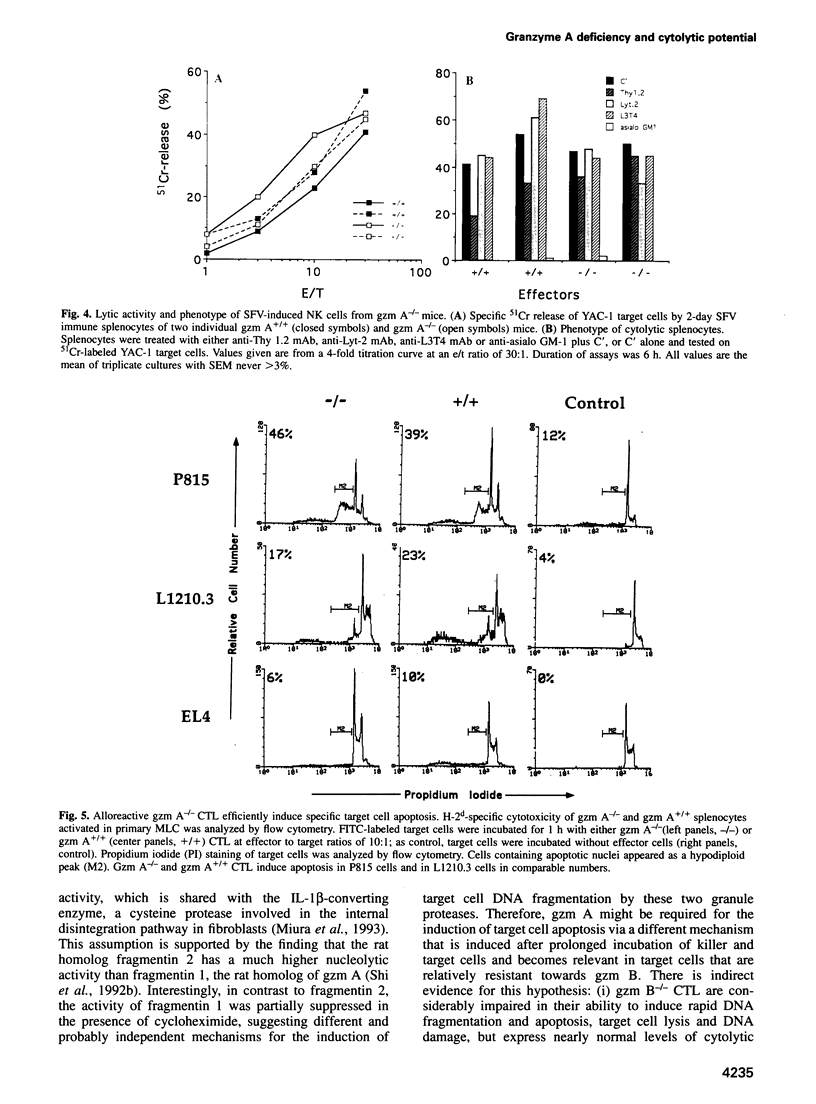
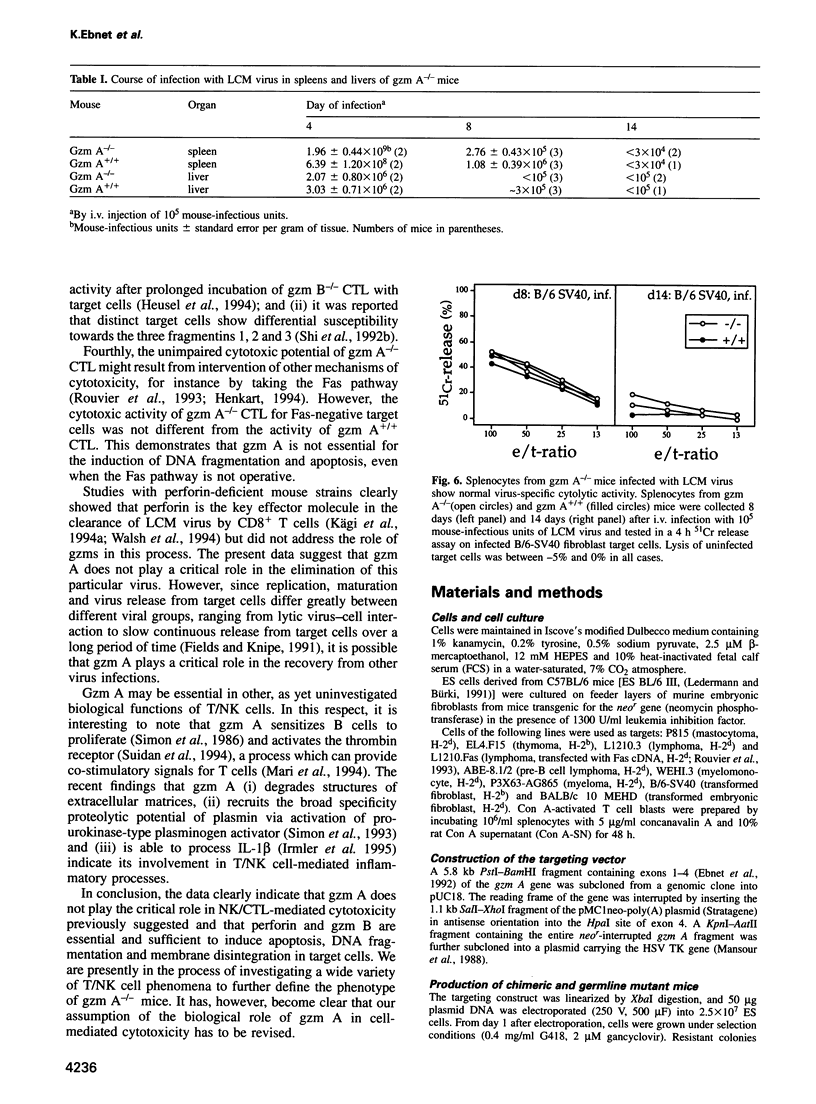



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ebnet K., Chluba-de Tapia J., Hurtenbach U., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. In vivo primed mouse T cells selectively express T cell-specific serine proteinase-1 and the proteinase-like molecules granzyme B and C. Int Immunol. 1991 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebnet K., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Organization of the gene encoding the mouse T-cell-specific serine proteinase "granzyme A". Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):502–508. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90117-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebnet K., Levelt C. N., Tran T. T., Eichmann K., Simon M. M. Transcription of granzyme A and B genes is differentially regulated during lymphoid ontogeny. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):755–763. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruth U., Prester M., Golecki J. R., Hengartner H., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. The T cell-specific serine proteinase TSP-1 is associated with cytoplasmic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):613–621. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanz J. A., MacDonald H. R., Jenne D. E., Tschopp J., Nabholz M. Cell specificity of granzyme gene expression. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3111–3118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossmann J., Lohler J., Utermohlen O., Lehmann-Grube F. Murine hepatitis caused by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. II. Cells involved in pathogenesis. Lab Invest. 1995 May;72(5):559–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G. M., Mueller C. Expression of perforin and granzymes in vivo: potential diagnostic markers for activated cytotoxic cells. Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90145-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. P., Berrebi G. A., Henkart P. A. Induction of target cell DNA release by the cytotoxic T lymphocyte granule protease granzyme A. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):933–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W., MacDonald H. R., Mueller C. Expression of genes encoding cytotoxic cell-associated serine proteases in thymocytes. Int Immunol. 1990;2(1):57–62. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity: two pathways and multiple effector molecules. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):343–346. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Millard P. J., Reynolds C. W., Henkart M. P. Cytolytic activity of purified cytoplasmic granules from cytotoxic rat large granular lymphocyte tumors. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):75–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Wesselschmidt R. L., Shresta S., Russell J. H., Ley T. J. Cytotoxic lymphocytes require granzyme B for the rapid induction of DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in allogeneic target cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):977–987. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honarvar N., Schaible U. E., Galanos C., Wallich R., Simon M. M. A 14,000 MW lipoprotein and a glycolipid-like structure of Borrelia burgdorferi induce proliferation and immunoglobulin production in mouse B cells at high frequencies. Immunology. 1994 Jul;82(3):389–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmler M., Hertig S., MacDonald H. R., Sadoul R., Becherer J. D., Proudfoot A., Solari R., Tschopp J. Granzyme A is an interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme. J Exp Med. 1995 May 1;181(5):1917–1922. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki A., Shinkai Y., Kuwana Y., Furuya A., Iigo Y., Hanai N., Itoh S., Yagita H., Okumura K. Perforin, a pore-forming protein detectable by monoclonal antibodies, is a functional marker for killer cells. Int Immunol. 1990;2(7):677–684. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.7.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima H., Shinohara N., Hanaoka S., Someya-Shirota Y., Takagaki Y., Ohno H., Saito T., Katayama T., Yagita H., Okumura K. Two distinct pathways of specific killing revealed by perforin mutant cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):357–364. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Simon M. M. Expression of cytoplasmic granules with T cell-associated serine proteinase-1 activity in Ly-2+(CD8+) T lymphocytes responding to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):151–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi D., Ledermann B., Bürki K., Seiler P., Odermatt B., Olsen K. J., Podack E. R., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):31–37. doi: 10.1038/369031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi D., Vignaux F., Ledermann B., Bürki K., Depraetere V., Nagata S., Hengartner H., Golstein P. Fas and perforin pathways as major mechanisms of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):528–530. doi: 10.1126/science.7518614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledermann B., Bürki K. Establishment of a germ-line competent C57BL/6 embryonic stem cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Dec;197(2):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Assmann U., Löliger C., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. I. Role of T lymphocytes in the clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):608–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowin B., Hahne M., Mattmann C., Tschopp J. Cytolytic T-cell cytotoxicity is mediated through perforin and Fas lytic pathways. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):650–652. doi: 10.1038/370650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mari B., Imbert V., Belhacene N., Far D. F., Peyron J. F., Pouysségur J., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Rossi B., Auberger P. Thrombin and thrombin receptor agonist peptide induce early events of T cell activation and synergize with TCR cross-linking for CD69 expression and interleukin 2 production. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8517–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Zhu H., Rotello R., Hartwieg E. A., Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90486-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morelli L., Lusignan Y., Lemieux S. Heterogeneity of natural killer cell subsets in NK-1.1+ and NK-1.1- inbred mouse strains and their progeny. Cell Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;141(1):148–160. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90134-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllbacher A., King N. J. Target cell lysis by natural killer cells is influenced by beta 2-microglobulin expression. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jul;30(1):21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Kägi D., Aebischer T., Odermatt B., Held W., Podack E. R., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Detection of perforin and granzyme A mRNA in infiltrating cells during infection of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1253–1259. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Henkart P. A. Cytotoxic lymphocyte granzymes trigger a target cell internal disintegration pathway leading to cytolysis and DNA breakdown. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1057–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Park H. L., Henkart P. A. Synergistic roles of granzymes A and B in mediating target cell death by rat basophilic leukemia mast cell tumors also expressing cytolysin/perforin. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):1037–1046. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti I., Migliorati G., Pagliacci M. C., Grignani F., Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jun 3;139(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odake S., Kam C. M., Narasimhan L., Poe M., Blake J. T., Krahenbuhl O., Tschopp J., Powers J. C. Human and murine cytotoxic T lymphocyte serine proteases: subsite mapping with peptide thioester substrates and inhibition of enzyme activity and cytolysis by isocoumarins. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2217–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Bleier K. J., McInerney T. N. Granzyme A binding to target cell proteins. Granzyme A binds to and cleaves nucleolin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14703–14708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast J. A., Helgason C. D., Bleackley R. C. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of cytotoxic cell proteinase gene transcripts in T cells. Pattern of expression is dependent on the nature of the stimulus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5090–5095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvier E., Luciani M. F., Golstein P. Fas involvement in Ca(2+)-independent T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):195–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Internal disintegration model of cytotoxic lymphocyte-induced target damage. Immunol Rev. 1983;72:97–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers T. J., Wiltrout T. A., Smyth M. J., Ottaway K. S., Pilaro A. M., Sowder R., Henderson L. E., Sprenger H., Lloyd A. R. Purification and cloning of a novel serine protease, RNK-Tryp-2, from the granules of a rat NK cell leukemia. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2289–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Kam C. M., Powers J. C., Aebersold R., Greenberg A. H. Purification of three cytotoxic lymphocyte granule serine proteases that induce apoptosis through distinct substrate and target cell interactions. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1521–1529. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Kraut R. P., Aebersold R., Greenberg A. H. A natural killer cell granule protein that induces DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):553–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Nishioka W. K., Th'ng J., Bradbury E. M., Litchfield D. W., Greenberg A. H. Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.8108732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiver J. W., Su L., Henkart P. A. Cytotoxicity with target DNA breakdown by rat basophilic leukemia cells expressing both cytolysin and granzyme A. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90359-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shresta S., MacIvor D. M., Heusel J. W., Russell J. H., Ley T. J. Natural killer and lymphokine-activated killer cells require granzyme B for the rapid induction of apoptosis in susceptible target cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5679–5683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Hoschützky H., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. Purification and characterization of a T cell specific serine proteinase (TSP-1) from cloned cytolytic T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3267–3274. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suidan H. S., Bouvier J., Schaerer E., Stone S. R., Monard D., Tschopp J. Granzyme A released upon stimulation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes activates the thrombin receptor on neuronal cells and astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8112–8116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaux F., Vivier E., Malissen B., Depraetere V., Nagata S., Golstein P. TCR/CD3 coupling to Fas-based cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):781–786. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. M., Matloubian M., Liu C. C., Ueda R., Kurahara C. G., Christensen J. L., Huang M. T., Young J. D., Ahmed R., Clark W. R. Immune function in mice lacking the perforin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10854–10858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Welsh R. M. H-2 compatibility requirement for virus-specific T cell-mediated effector functions in vivo. I. Specificity of T cells conferring antiviral protection against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is associated with H-2K and H-2D. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1495–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]