Abstract
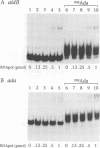
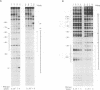
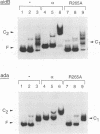
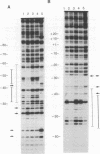
The ada and aidB genes are part of the adaptive response to DNA methylation damage in Escherichia coli. Transcription of the ada and the aidB genes is triggered by binding of the methylated Ada protein (meAda) to a specific sequence located 40-60 base pairs upstream of the transcriptional start, which is internal to an A/T-rich region. In this report we demonstrate that the Ada binding site is also a binding site for RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase is able to bind the -40 to -60 region of the ada and the aidB promoters in the absence of meAda, and its binding is mediated by the alpha subunit. This region resembles the UP element of the rrnB P1 promoter in location, sequence and mechanism of interaction with RNA polymerase. We discuss the function of UP-like elements in positively controlled promoters and provide evidence that Ada does not act by enhancing RNA polymerase binding affinity to the promoter region. Instead, Ada stimulates transcription by modifying the nature of the RNA polymerase-promoter interaction, allowing RNA polymerase to recognize the core promoter -35 and -10 elements in addition to the UP-like element.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimaru H., Sakumi K., Yoshikai T., Anai M., Sekiguchi M. Positive and negative regulation of transcription by a cleavage product of Ada protein. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowrin V., Brissette R., Tsung K., Inouye M. The alpha subunit of RNA polymerase specifically inhibits expression of the porin genes ompF and ompC in vivo and in vitro in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Jan 1;115(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai X. Y., Maxon M. E., Redfield B., Glass R., Brot N., Weissbach H. Methionine synthesis in Escherichia coli: effect of the MetR protein on metE and metH expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4407–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Kammerer W., Gentz R., Bujard H. Promoters of Escherichia coli: a hierarchy of in vivo strength indicates alternate structures. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2987–2994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario M., Ernsting B. R., Borst D. W., Wiese D. E., 2nd, Blumenthal R. M., Matthews R. G. The leucine-responsive regulatory protein of Escherichia coli negatively regulates transcription of ompC and micF and positively regulates translation of ompF. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):103–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.103-113.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi M., Yu C. G., Anai M., Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Regulatory elements for expression of the alkA gene in response to alkylating agents. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Dec;236(1):25–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00279639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit in transcription activation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3283–3288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafri S., Urbanowski M. L., Stauffer G. V. A mutation in the rpoA gene encoding the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase that affects metE-metR transcription in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1995 Feb;177(3):524–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.3.524-529.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeggo P. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants unable to induce the adaptive response to simple alkylating agents. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):783–791. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.783-791.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Hjelmgren T., Lindahl T. Induction of a DNA glycosylase for N-methylated purines is part of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):770–773. doi: 10.1038/296770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka H., Yamamoto Y., Sekiguchi M. A new gene (alkB) of Escherichia coli that controls sensitivity to methyl methane sulfonate. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1301–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1301-1307.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Toledano M. B., Tartaglia L. A., Storz G. Mutational analysis of the redox-sensitive transcriptional regulator OxyR: regions important for oxidation and transcriptional activation. J Bacteriol. 1995 Mar;177(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.5.1275-1284.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini P., Hajec L. I., Volkert M. R. Structure and transcriptional regulation of the Escherichia coli adaptive response gene aidB. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(21):6583–6589. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6583-6589.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini P., Volkert M. R. Transcriptional activation of the Escherichia coli adaptive response gene aidB is mediated by binding of methylated Ada protein. Evidence for a new consensus sequence for Ada-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):8285–8289. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.8285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawley B., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Pittard A. J. The TyrR protein of Escherichia coli is a class I transcription activator. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.238-241.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Regulatory mechanisms for induction of synthesis of repair enzymes in response to alkylating agents: ada protein acts as a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6297–6301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tokumoto Y., Sakumi K., Koike G., Nakabeppu Y., Sekiguchi M. Expression of the ada gene of Escherichia coli in response to alkylating agents. Identification of transcriptional regulatory elements. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):483–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Ross W., Appleman J. A., Gaal T., Leirmo S., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr, Gourse R. L. Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An "extended" promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1421–1435. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Igarashi K., Sekiguchi M., Ishihama A. The Ada protein is a class I transcription factor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2455–2457. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2455-2457.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Regulation of expression of the ada gene controlling the adaptive response. Interactions with the ada promoter of the Ada protein and RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):373–385. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Fenyo D., Chait B., Ebright R. H. Location, structure, and function of the target of a transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3058–3067. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo I., Sedgwick B., Kilpatrick M. W., McCarthy T. V., Lindahl T. The intracellular signal for induction of resistance to alkylating agents in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90396-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert M. R., Nguyen D. C. Induction of specific Escherichia coli genes by sublethal treatments with alkylating agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4110–4114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]