Abstract
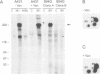
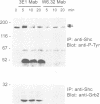
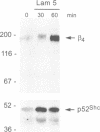
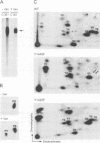
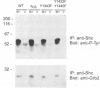
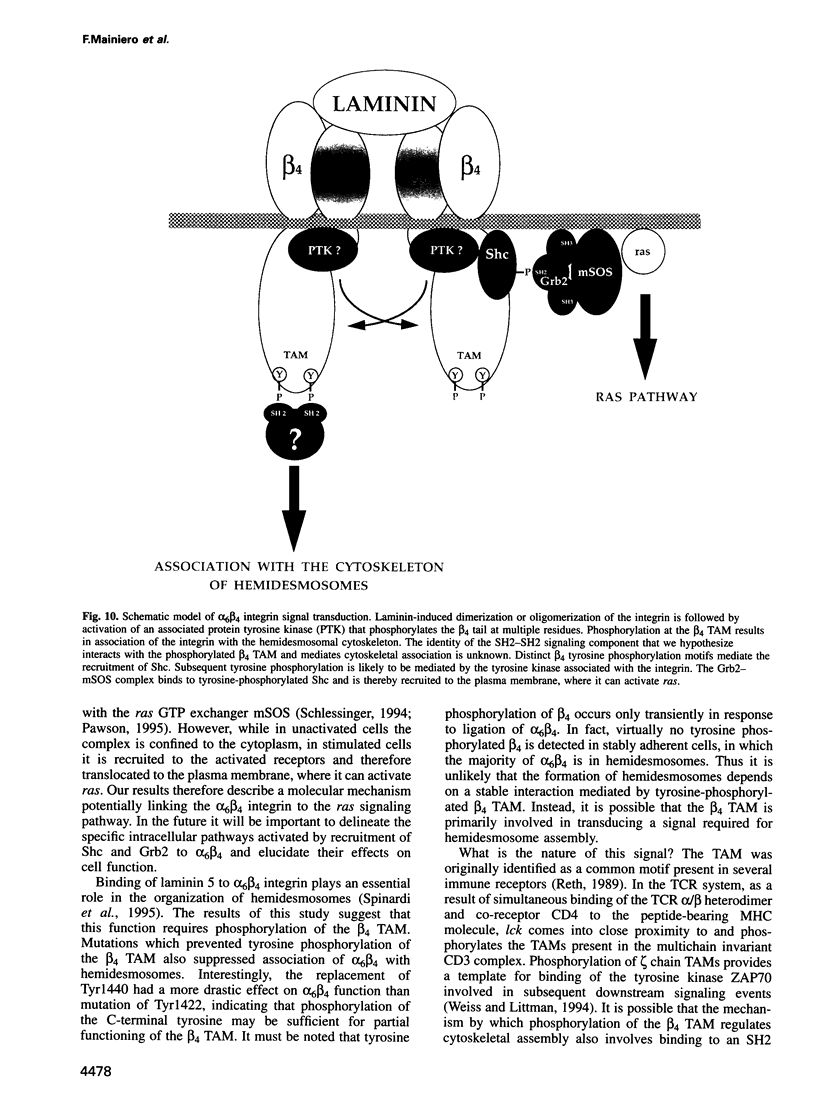
We have examined the mechanism of signal transduction by the hemidesmosomal integrin alpha 6 beta 4, a laminin receptor involved in morphogenesis and tumor progression. Immunoprecipitation and immune complex kinase assays indicated that antibody- or laminin-induced ligation of alpha 6 beta 4 causes tyrosine phosphorylation of the beta 4 subunit in intact cells and that this event is mediated by a protein kinase(s) physically associated with the integrin. Co-immunoprecipitation and GST fusion protein binding experiments showed that the adaptor protein Shc forms a complex with the tyrosine-phosphorylated beta 4 subunit. Shc is then phosphorylated on tyrosine residues and recruits the adaptor Grb2, thereby potentially linking alpha 6 beta 4 to the ras pathway. The beta 4 subunit was found to be phosphorylated at multiple tyrosine residues in vivo, including a tyrosine-based activation motif (TAM) resembling those found in T and B cell receptors. Phenylalanine substitutions at the beta 4 TAM disrupted association of alpha 6 beta 4 with hemidesmosomes, but did not interfere with tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc and recruitment of Grb2. These results indicate that signal transduction by the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin is mediated by an associated tyrosine kinase and that phosphorylation of distinct sites in the beta 4 tail mediates assembly of the hemidesmosomal cytoskeleton and recruitment of Shc/Grb2.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Watt F. M. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993 Apr;117(4):1183–1198. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.4.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer A. G., Blaikie P., Nelson K., Schlessinger J., Margolis B. The phosphotyrosine interaction domain of Shc binds an LXNPXY motif on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4403–4409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaikie P., Immanuel D., Wu J., Li N., Yajnik V., Margolis B. A region in Shc distinct from the SH2 domain can bind tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32031–32034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockholt S. M., Burridge K. Cell spreading on extracellular matrix proteins induces tyrosine phosphorylation of tensin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14565–14567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Margolis B. A phosphotyrosine interaction domain. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):693–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Turner C. E., Romer L. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):893–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Kaur P., Gil S. G., Gahr P. J., Wayner E. A. Distinct functions for integrins alpha 3 beta 1 in focal adhesions and alpha 6 beta 4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3141–3154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Traynor-Kaplan A., Bokoch G. M., Schwartz M. A. The small GTP-binding protein Rho regulates a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in mammalian cells. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio C. M., Jackson D. A., Zaret K. S. The extracellular matrix coordinately modulates liver transcription factors and hepatocyte morphology. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4405–4414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einheber S., Milner T. A., Giancotti F., Salzer J. L. Axonal regulation of Schwann cell integrin expression suggests a role for alpha 6 beta 4 in myelination. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(5):1223–1236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.5.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enenstein J., Kramer R. H. Confocal microscopic analysis of integrin expression on the microvasculature and its sprouts in the neonatal foreskin. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Sep;103(3):381–386. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12395390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Laminin variants: why, where and when? Kidney Int. 1993 Jan;43(1):2–6. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Mainiero F. Integrin-mediated adhesion and signaling in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 May 27;1198(1):47–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Ruoslahti E. Elevated levels of the alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90098-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Spinardi L., Mainiero F., Sanders R. Expression of heterologous integrin genes in cultured eukaryotic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1994;245:297–316. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)45017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti F. G., Stepp M. A., Suzuki S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Proteolytic processing of endogenous and recombinant beta 4 integrin subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):951–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Shalloway D. Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):690–692. doi: 10.1038/358690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Calalb M. B., Harper M. C., Patel S. K. Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8487–8491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst F., Kuikman I., von dem Borne A. E., Sonnenberg A. Cloning and sequence analysis of beta-4 cDNA: an integrin subunit that contains a unique 118 kd cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):765–770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Lipfert L., Cunningham M., Brugge J. S., Ginsberg M. H., Shattil S. J. Adhesive ligand binding to integrin alpha IIb beta 3 stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of novel protein substrates before phosphorylation of pp125FAK. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):473–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):577–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn-Perles B., Boyer C., Arnold B., Sanderson A. R., Ferrier P., Lemonnier F. A. Acquisition of HLA class I W6/32 defined antigenic determinant by heavy chains from different species following association with bovine beta 2-microglobulin. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2190–2196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiji S., Tamura R. N., Quaranta V. A novel integrin (alpha E beta 4) from human epithelial cells suggests a fourth family of integrin adhesion receptors. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):673–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03425.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. PTB domain binding to signaling proteins through a sequence motif containing phosphotyrosine. Science. 1995 May 26;268(5214):1177–1179. doi: 10.1126/science.7539155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh W. M., Williams L. T. An alternative to SH2 domains for binding tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1862–1865. doi: 10.1126/science.7527937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Epler R. G., Lankford T. K., Foote L. J., Dickas V., Canamucio M., Cavalierie R., Cosimelli M., Venturo I., Falcioni R. Second generation monoclonal antibodies to the human integrin alpha 6 beta 4. Hybridoma. 1990 Jun;9(3):243–255. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1990.9.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel K. A., Carey T. E. Altered expression in squamous carcinoma cells of an orientation restricted epithelial antigen detected by monoclonal antibody A9. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3614–3623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Taga T., Akira S. Cytokine signal transduction. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipfert L., Haimovich B., Schaller M. D., Cobb B. S., Parsons J. T., Brugge J. S. Integrin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):905–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee H. P., Ingber D. E., Schwartz M. A. Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates inositol lipid synthesis and enhances PDGF-induced inositol lipid breakdown. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):673–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M. Laminin: multiple forms, multiple receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;2(5):845–849. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90082-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskelley C. D., Desprez P. Y., Bissell M. J. Extracellular matrix-dependent tissue-specific gene expression in mammary epithelial cells requires both physical and biochemical signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12378–12382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Integrins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI114957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoia P., Trusolino L., Pepino E., Cremona O., Marchisio P. C. Expression and topography of integrins and basement membrane proteins in epidermal carcinomas: basal but not squamous cell carcinomas display loss of alpha 6 beta 4 and BM-600/nicein. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Sep;101(3):352–358. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12365531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M. D., Borgman C. A., Cobb B. S., Vines R. R., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. pp125FAK a structurally distinctive protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk P. The fate of hemidesmosomes in laryngeal carcinoma. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1979;222(3):187–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00456315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Hanks S. K., Hunter T., van der Geer P. Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):786–791. doi: 10.1038/372786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. SH2/SH3 signaling proteins. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Haimovich B., Cunningham M., Lipfert L., Parsons J. T., Ginsberg M. H., Brugge J. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of pp125FAK in platelets requires coordinated signaling through integrin and agonist receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14738–14745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Shaw A. S., Rothbard J. B., Allen P. M. Partial T cell signaling: altered phospho-zeta and lack of zap70 recruitment in APL-induced T cell anergy. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinardi L., Einheber S., Cullen T., Milner T. A., Giancotti F. G. A recombinant tail-less integrin beta 4 subunit disrupts hemidesmosomes, but does not suppress alpha 6 beta 4-mediated cell adhesion to laminins. J Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;129(2):473–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinardi L., Ren Y. L., Sanders R., Giancotti F. G. The beta 4 subunit cytoplasmic domain mediates the interaction of alpha 6 beta 4 integrin with the cytoskeleton of hemidesmosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):871–884. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp M. A., Spurr-Michaud S., Tisdale A., Elwell J., Gipson I. K. Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8970–8974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., DeSimone D. W., Fonda D., Patel R. S., Buck C., Horwitz A. F., Hynes R. O. Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90744-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennenbaum T., Weiner A. K., Belanger A. J., Glick A. B., Hennings H., Yuspa S. H. The suprabasal expression of alpha 6 beta 4 integrin is associated with a high risk for malignant progression in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Oct 15;53(20):4803–4810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuori K., Ruoslahti E. Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with integrins. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1576–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.7527156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Halvorson M. J., Coligan J. E. Developmentally regulated expression of the beta 4 integrin on immature mouse thymocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):421–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]