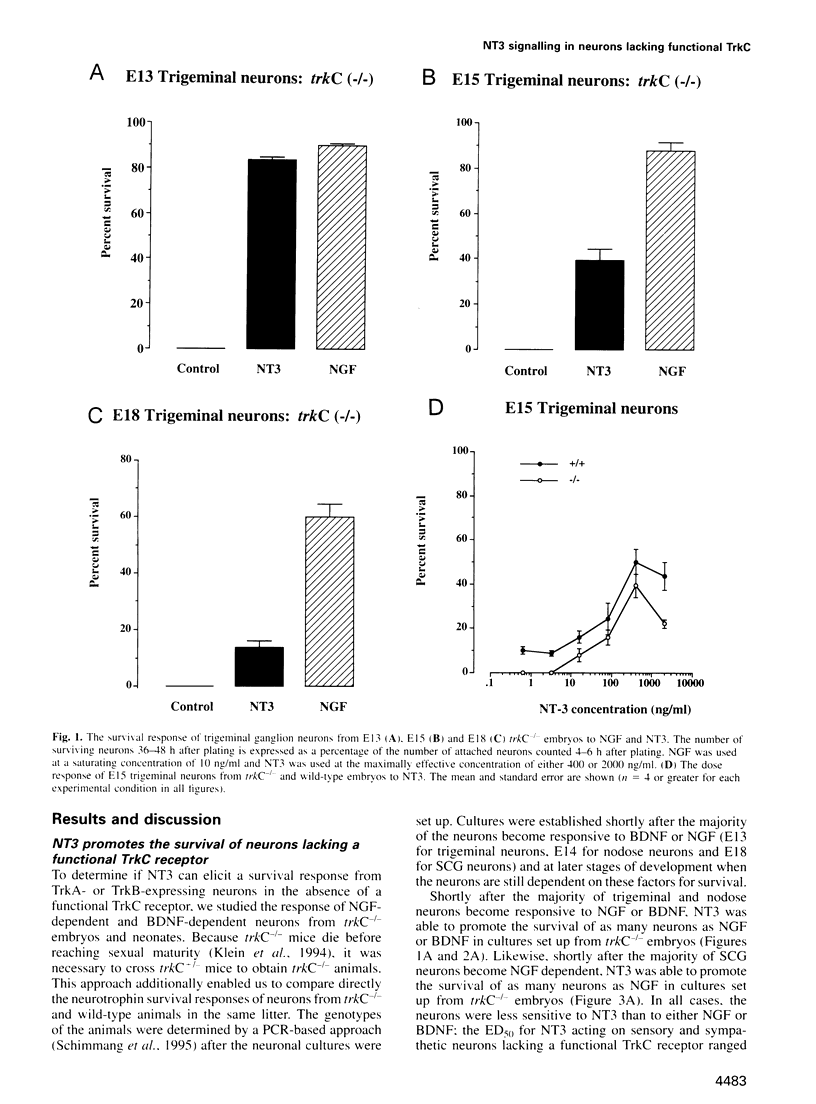
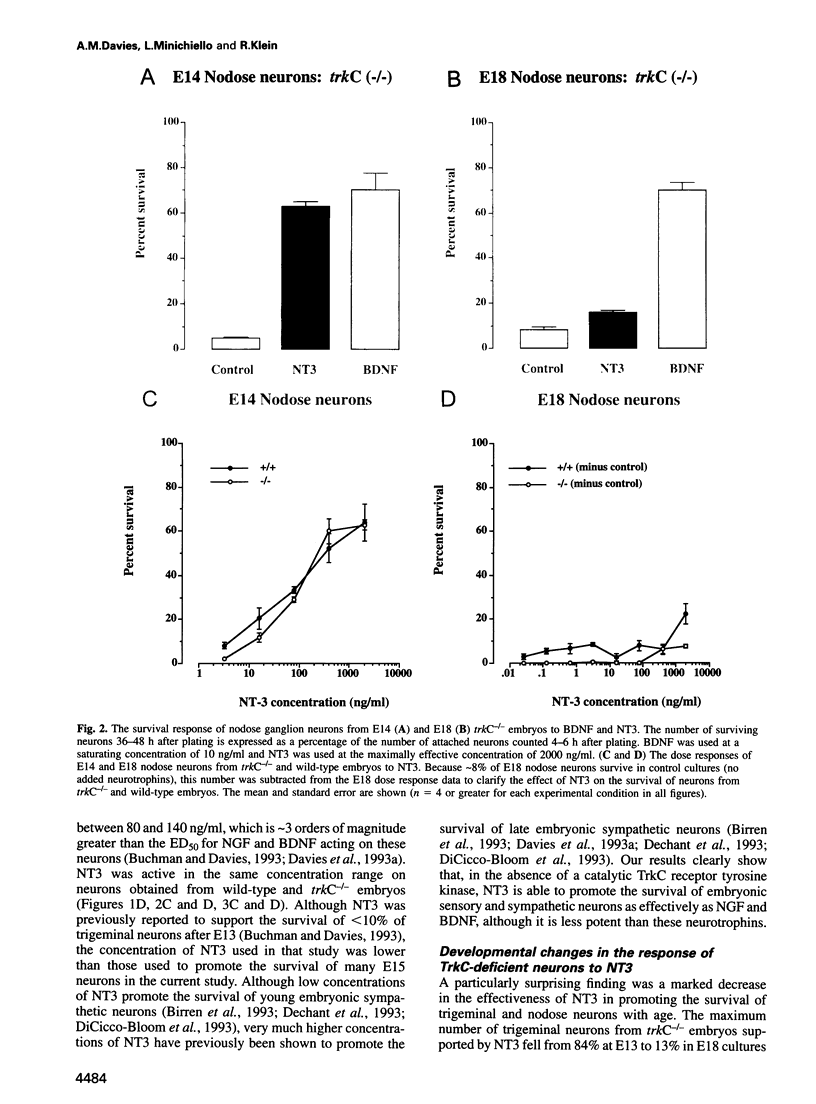
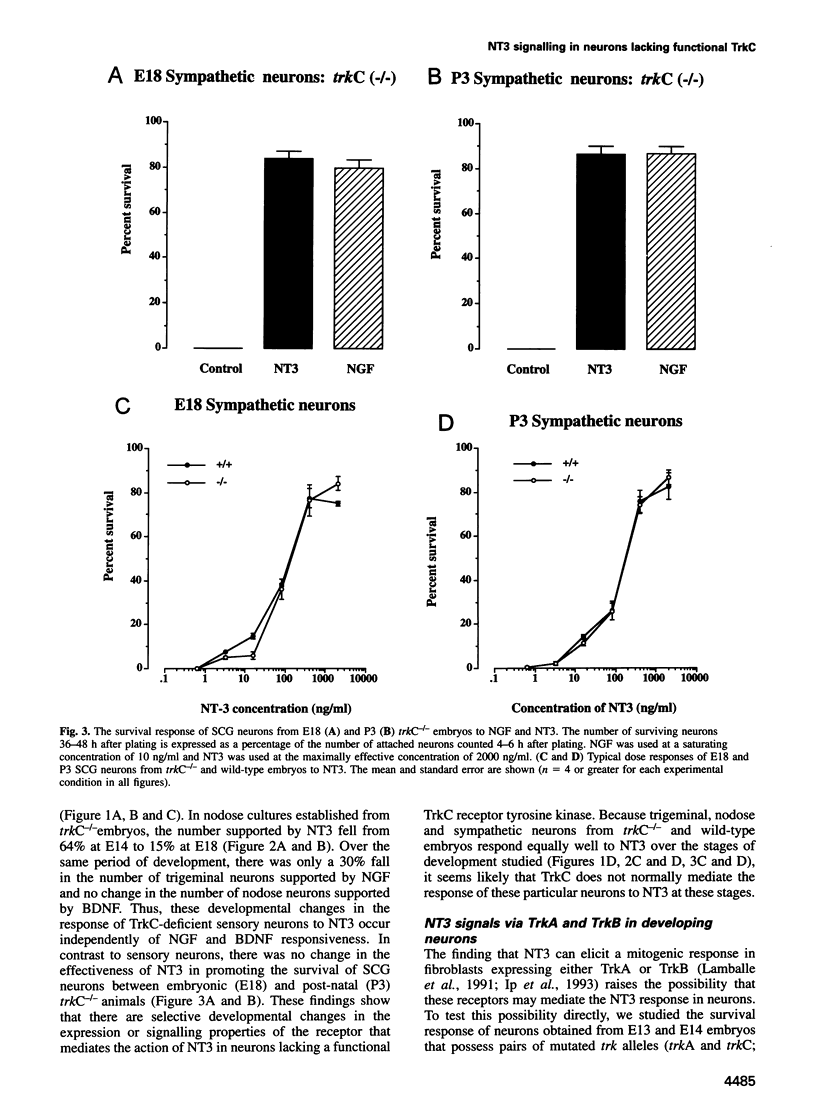
Abstract
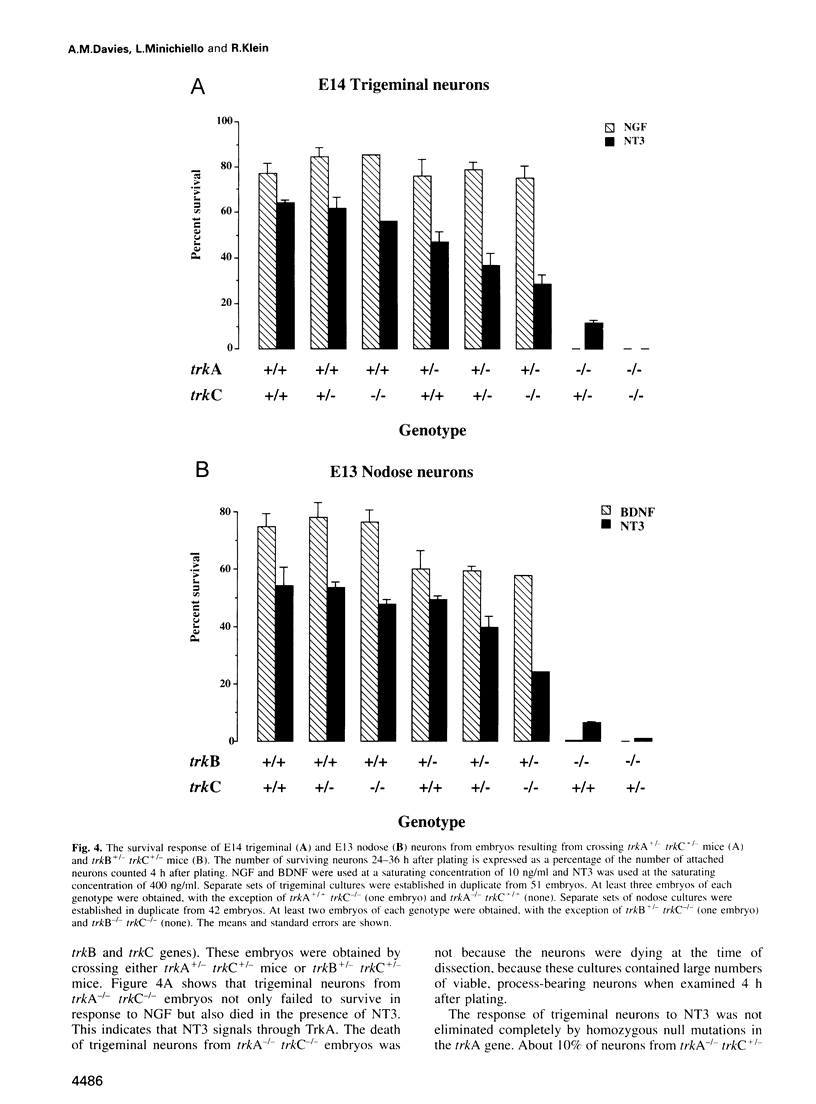
Neurotrophins promote neuronal survival by signalling through Trk receptor tyrosine kinases: nerve growth factor signals through TrkA, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin (NT)4 through TrkB and NT3 through TrkC. Although studies in some, but not all, cell lines indicate that NT3 can also signal through TrkA and TrkB, it is not known if such signalling can occur in neurons. We show that NT3 can promote the in vitro survival of sensory and sympathetic neurons isolated from embryos that are homozygous for a null mutation in the trkC gene. During the mid-embryonic period, NT3 promoted the survival of as many trigeminal and nodose neurons as the preferred neurotrophins, NGF and BDNF. However, later in development, these neurons lost their ability to respond to NT3. NT3 also promoted the survival of almost all sympathetic neurons, but no decrease in effectiveness was observed during development. Trigeminal neurons from trkC-/- trkA-/- embryos did not respond to NT3 and nodose neurons from trkB-/- embryos likewise failed to respond to NT3. These results show that NT3 can signal through TrkA and TrkB in neurons at certain stages of development and may explain why the phenotype of NT3-/- mice is more severe than that of trkC-/- mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker P. A., Lomen-Hoerth C., Gensch E. M., Meakin S. O., Glass D. J., Shooter E. M. Tissue-specific alternative splicing generates two isoforms of the trkA receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15150–15157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti M., Levi A., Chao M. V. Differential expression of nerve growth factor receptors leads to altered binding affinity and neurotrophin responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7859–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier L. R., Winslow J. W., Kaplan D. R., Nikolics K., Goeddel D. V., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren S. J., Lo L., Anderson D. J. Sympathetic neuroblasts undergo a developmental switch in trophic dependence. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):597–610. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman V. L., Davies A. M. Different neurotrophins are expressed and act in a developmental sequence to promote the survival of embryonic sensory neurons. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):989–1001. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman V. L., Sporn M., Davies A. M. Role of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in regulating the expression of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNA levels in embryonic cutaneous cells at different stages of development. Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1621–1629. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Reichardt L. F. An alternatively spliced form of the nerve growth factor receptor TrkA confers an enhanced response to neurotrophin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11133–11137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M., Horton A., Burton L. E., Schmelzer C., Vandlen R., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-4/5 is a mammalian-specific survival factor for distinct populations of sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Nov;13(11):4961–4967. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-11-04961.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M., Lee K. F., Jaenisch R. p75-deficient trigeminal sensory neurons have an altered response to NGF but not to other neurotrophins. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M. The role of neurotrophins in the developing nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1334–1348. doi: 10.1002/neu.480251103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechant G., Rodríguez-Tébar A., Kolbeck R., Barde Y. A. Specific high-affinity receptors for neurotrophin-3 on sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2610–2616. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02610.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Friedman W. J., Black I. B. NT-3 stimulates sympathetic neuroblast proliferation by promoting precursor survival. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1101–1111. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90223-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Lee K. F., Kucera J., Jaenisch R. Lack of neurotrophin-3 leads to deficiencies in the peripheral nervous system and loss of limb proprioceptive afferents. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fariñas I., Jones K. R., Backus C., Wang X. Y., Reichardt L. F. Severe sensory and sympathetic deficits in mice lacking neurotrophin-3. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):658–661. doi: 10.1038/369658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner A. S., Large T. H. Isoforms of the avian TrkC receptor: a novel kinase insertion dissociates transformation and process outgrowth from survival. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):457–472. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Nye S. H., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Squinto S. P., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90629-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Kaplan D. R., Parada L. F., Chao M. V. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):678–683. doi: 10.1038/350678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Ibáez C. F., Nye S. H., McClain J., Jones P. F., Gies D. R., Belluscio L., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Squinto S. P. Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Stitt T. N., Tapley P., Klein R., Glass D. J., Fandl J., Greene L. A., Barbacid M., Yancopoulos G. D. Similarities and differences in the way neurotrophins interact with the Trk receptors in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Lamballe F., Bryant S., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for neurotrophin-4. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90209-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Nanduri V., Jing S. A., Lamballe F., Tapley P., Bryant S., Cordon-Cardo C., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90628-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. Role of neurotrophins in mouse neuronal development. FASEB J. 1994 Jul;8(10):738–744. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.10.8050673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Silos-Santiago I., Smeyne R. J., Lira S. A., Brambilla R., Bryant S., Zhang L., Snider W. D., Barbacid M. Disruption of the neurotrophin-3 receptor gene trkC eliminates la muscle afferents and results in abnormal movements. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):249–251. doi: 10.1038/368249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Tapley P., Barbacid M. trkC encodes multiple neurotrophin-3 receptors with distinct biological properties and substrate specificities. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3083–3094. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. F., Davies A. M., Jaenisch R. p75-deficient embryonic dorsal root sensory and neonatal sympathetic neurons display a decreased sensitivity to NGF. Development. 1994 Apr;120(4):1027–1033. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.4.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Friedman B., Alderson R. F., Wiegand S. J., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor family of receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90047-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfas P., Soppet D., Escandon E., Tessarollo L., Mendoza-Ramirez J. L., Rosenthal A., Nikolics K., Parada L. F. The rat trkC locus encodes multiple neurogenic receptors that exhibit differential response to neurotrophin-3 in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):975–990. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90212-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela D. M., Maisonpierre P. C., Glass D. J., Rojas E., Nuñez L., Kong Y., Gies D. R., Stitt T. N., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]