Abstract
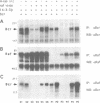
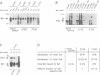
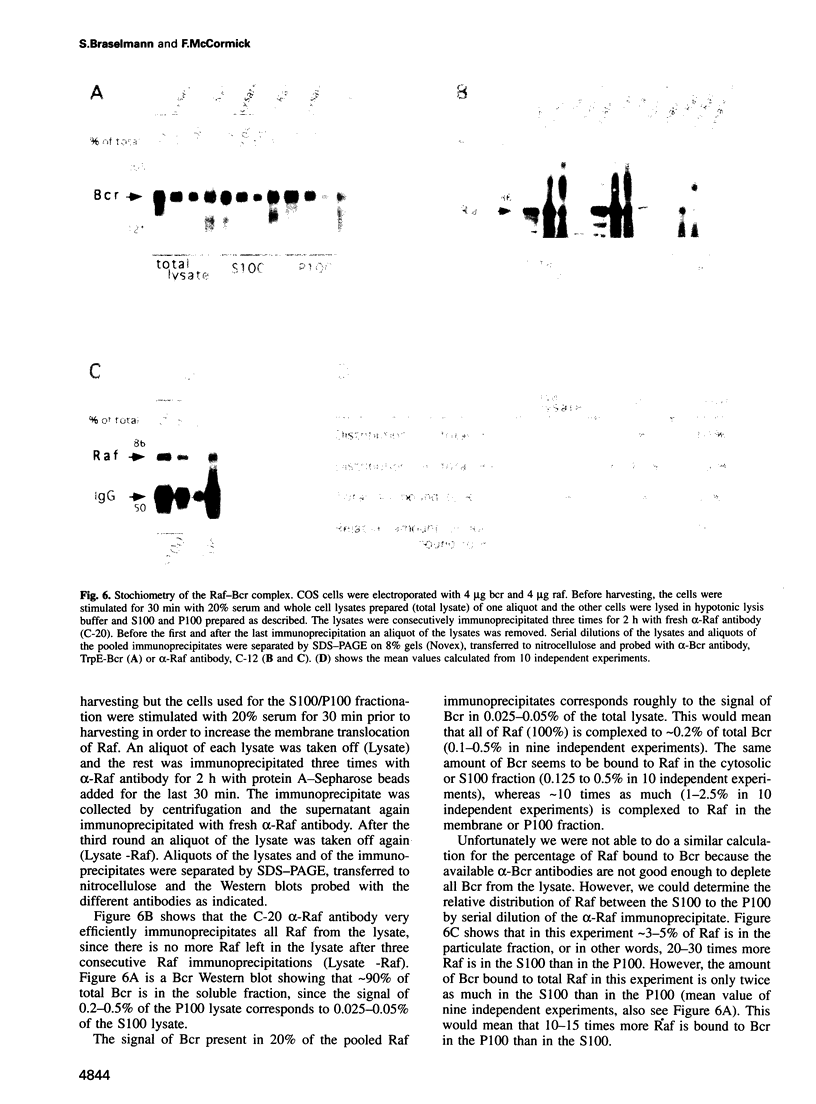
In a yeast two-hybrid screen we identified a member of the 14-3-3 family of proteins that can bind to Bcr. 14-3-3 beta binds to the serine/threonine rich region B in the kinase domain encoded by the first exon. In this paper we show by co-immunoprecipitation that Bcr binds to Raf in vivo and we argue that this interaction is mediated by 14-3-3 dimers, based on the following findings. First, 14-3-3 isoforms bind to both Raf and Bcr. Second, Bcr does not bind to Raf directly in the two-hybrid system, but co-expression of 14-3-3 beta allows complex formation. Third, Bcr, 14-3-3 proteins and Raf co-elute in gel filtration and in sequential ion exchange chromatography and the three proteins can be co-immunoprecipitated from the the separate fractions, indicating that they are present in a ternary complex. Moreover, approximately 10 times more Raf is bound to Bcr, and vice versa, in the membrane fraction (where Raf is activated) than in the cytosolic fraction. We suggest a new function for 14-3-3 proteins as a novel type of new function for 14-3-3 proteins as a novel type of adaptor which acts by dimerization and binding to different proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Collinge D. B., van Heusden B. P., Isobe T., Roseboom P. H., Rosenfeld G., Soll J. 14-3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eukaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Dec;17(12):498–501. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90339-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Brill S., Garrett M. D., Totty N., Hsuan J., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim L., Hall A. Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21rac. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):400–402. doi: 10.1038/351400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Muslin A. J., Kikuchi A., Martin J. A., MacNicol A. M., Gross R. W., Williams L. T. Activation of Raf-1 by 14-3-3 proteins. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):612–614. doi: 10.1038/371612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Sternglanz R. The two-hybrid system: an assay for protein-protein interactions. Trends Genet. 1994 Aug;10(8):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90012-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. C., al-Khodairy F., Fotou E., Sheldrick K. S., Griffiths D. J., Carr A. M. 14-3-3 protein homologs required for the DNA damage checkpoint in fission yeast. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):533–535. doi: 10.1126/science.8036497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E., Symons M., Macdonald S. G., McCormick F., Ruggieri R. Binding of 14-3-3 proteins to the protein kinase Raf and effects on its activation. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1713–1716. doi: 10.1126/science.8085158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H., Xia K., Pallas D. C., Cui C., Conroy K., Narsimhan R. P., Mamon H., Collier R. J., Roberts T. M. Interaction of the protein kinase Raf-1 with 14-3-3 proteins. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.7939632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. A biochemical function for ras--at last. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1413–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.8197454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Cadwallader K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4033–4039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Demetrick D., Beach D. Isolation of the Rb-related p130 through its interaction with CDK2 and cyclins. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2378–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. C., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Plasma membrane-targeted ras GTPase-activating protein is a potent suppressor of p21ras function. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2420–2431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Gotoh Y., Yashar B. M., Errede B., Nishida E., Matsumoto K. Stimulatory effects of yeast and mammalian 14-3-3 proteins on the Raf protein kinase. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1716–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.8085159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Martin H., Madrazo J., Robinson K. A., Nielsen P., Roseboom P. H., Patel Y., Howell S. A., Aitken A. Expression and structural analysis of 14-3-3 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jan 27;245(4):375–384. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Paterson H. F., Marshall C. J. Requirement for Ras in Raf activation is overcome by targeting Raf to the plasma membrane. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):411–414. doi: 10.1038/369411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Janosch P., Tanji M., Rosenfeld G. C., Waymire J. C., Mischak H., Kolch W., Sedivy J. M. Regulation of Raf-1 kinase activity by the 14-3-3 family of proteins. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):685–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugo T. G., Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Witte O. N. Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1079–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.2408149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maru Y., Witte O. N. The BCR gene encodes a novel serine/threonine kinase activity within a single exon. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90521-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. R., Galasso D. L., Wang J. Y. A coiled-coil oligomerization domain of Bcr is essential for the transforming function of Bcr-Abl oncoproteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7587–7595. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhirter J. R., Wang J. Y. Activation of tyrosinase kinase and microfilament-binding functions of c-abl by bcr sequences in bcr/abl fusion proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1553–1565. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Khaner H., Lopez J., Smith B. L. Intracellular receptors for activated protein kinase C. Identification of a binding site for the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14866–14868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. 14-3-3: modulators of signaling proteins? Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):56–57. doi: 10.1126/science.7939645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. J., Young J. C., Pendergast A. M., Pondel M., Landau N. R., Littman D. R., Witte O. N. BCR first exon sequences specifically activate the BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase oncogene of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemias. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1785–1792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Fu H., Haehnel L. C., Weller W., Collier R. J., Roberts T. M. Association of polyomavirus middle tumor antigen with 14-3-3 proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):535–537. doi: 10.1126/science.8036498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Havlik M. H., Maru Y., Witte O. N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Quilliam L. A., Cripe L. D., Bassing C. H., Dai Z., Li N., Batzer A., Rabun K. M., Der C. J., Schlessinger J. BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):175–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puil L., Liu J., Gish G., Mbamalu G., Bowtell D., Pelicci P. G., Arlinghaus R., Pawson T. Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):764–773. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu R. G., Chen J., Kirn D., McCormick F., Symons M. An essential role for Rac in Ras transformation. Nature. 1995 Mar 30;374(6521):457–459. doi: 10.1038/374457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuther G. W., Fu H., Cripe L. D., Collier R. J., Pendergast A. M. Association of the protein kinases c-Bcr and Bcr-Abl with proteins of the 14-3-3 family. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):129–133. doi: 10.1126/science.7939633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Zannini M., Lewis M., Wickner R. B., Hunt L. T., Graziani G., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Eva A. A region of proto-dbl essential for its transforming activity shows sequence similarity to a yeast cell cycle gene, CDC24, and the human breakpoint cluster gene, bcr. New Biol. 1991 Apr;3(4):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., McLaughlin J., Witte O. N. Genetic requirement for Ras in the transformation of fibroblasts and hematopoietic cells by the Bcr-Abl oncogene. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):307–313. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Jones J., Haigler H. T. Inhibition of protein kinase C by annexin V. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1886–1891. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Macdonald S. G., Cadwallader K., Symons M., Hancock J. F. Activation of Raf as a result of recruitment to the plasma membrane. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1463–1467. doi: 10.1126/science.7811320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmons M. S., Witte O. N. Structural characterization of the BCR gene product. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toker A., Sellers L. A., Amess B., Patel Y., Harris A., Aitken A. Multiple isoforms of a protein kinase C inhibitor (KCIP-1/14-3-3) from sheep brain. Amino acid sequence of phosphorylated forms. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):453–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse S., Cohen P., Paterson H., Marshall C., Rapp U., Grand R. J. Specific association of activated MAP kinase kinase kinase (Raf) with the plasma membranes of ras-transformed retinal cells. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3175–3181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartmann M., Davis R. J. The native structure of the activated Raf protein kinase is a membrane-bound multi-subunit complex. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6695–6701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N. Role of the BCR-ABL oncogene in human leukemia: fifteenth Richard and Hinda Rosenthal Foundation Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):485–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]