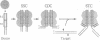Abstract
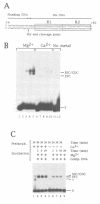
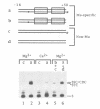
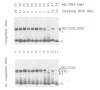
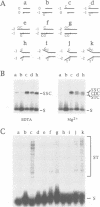
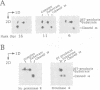
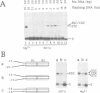
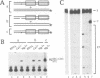
The two chemical steps of phage Mu transpositional recombination, donor DNA cleavage and strand transfer, take place within higher order protein-DNA complexes called transpososomes. At the core of these complexes is a tetramer of MuA (the transposase), bound to the two ends of the Mu genome. While transpososome assembly normally requires a number of cofactors, under certain conditions only MuA and a short DNA fragment are required. DNA requirements for this process, as well as the stability and activity of the ensuing complexes, were established. The divalent cation normally required for assembly of the stable complex could be omitted if the substrate was prenicked, if the flanking DNA was very short or if the two flanking strands were non-complementary. The presence of a single nucleotide beyond the Mu genome end on the non-cut strand was critical for transpososome stability. Donor cleavage additionally required at least two flanking nucleotides on the strand to be cleaved. The flanking DNA double helix was destabilized, implying distortion of the DNA near the active site. Although donor cleavage required Mg2+, strand transfer took place in the presence of Ca2+ as well, suggesting a conformational difference in the active site for the two chemical steps.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adzuma K., Mizuuchi K. Interaction of proteins located at a distance along DNA: mechanism of target immunity in the Mu DNA strand-transfer reaction. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adzuma K., Mizuuchi K. Steady-state kinetic analysis of ATP hydrolysis by the B protein of bacteriophage mu. Involvement of protein oligomerization in the ATPase cycle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6159–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adzuma K., Mizuuchi K. Target immunity of Mu transposition reflects a differential distribution of Mu B protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90387-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison R. G., Chaconas G. Role of the A protein-binding sites in the in vitro transposition of mu DNA. A complex circuit of interactions involving the mu ends and the transpositional enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19963–19970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton R., Gamas P., Craig N. L. Tn7 transposition in vitro proceeds through an excised transposon intermediate generated by staggered breaks in DNA. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90388-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Kremenstova E., Luo L. Complete transposition requires four active monomers in the mu transposase tetramer. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 15;8(20):2416–2428. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.20.2416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Luo L. Identification of residues in the Mu transposase essential for catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6654–6658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Mizuuchi K. DNA-promoted assembly of the active tetramer of the Mu transposase. Genes Dev. 1992 Nov;6(11):2221–2232. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.11.2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. MuB protein allosterically activates strand transfer by the transposase of phage Mu. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1003–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90552-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Mizuuchi M., Savilahti H., Mizuuchi K. Division of labor among monomers within the Mu transposase tetramer. Cell. 1993 Aug 27;74(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90519-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Excision of Tn10 from the donor site during transposition occurs by flush double-strand cleavages at the transposon termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4648–4652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O. Integration of retroviral DNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Integration of human immunodeficiency virus DNA: adduct interference analysis of required DNA sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3458–3462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., Gloor G., Miller J. L. Amplification and purification of the bacteriophage Mu encoded B transposition protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Mizuuchi K. A defined system for the DNA strand-transfer reaction at the initiation of bacteriophage Mu transposition: protein and DNA substrate requirements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7570–7574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Mechanism of transposition of bacteriophage Mu: structure of a transposition intermediate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):867–876. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Role of DNA topology in Mu transposition: mechanism of sensing the relative orientation of two DNA segments. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Transposition of Mu DNA: joining of Mu to target DNA can be uncoupled from cleavage at the ends of Mu. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90645-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Site-specific recognition of the bacteriophage Mu ends by the Mu A protein. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger D. J., Boeke J. D. A specific terminal structure is required for Ty1 transposition. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):324–330. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P. Genetics of retroviral integration. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:527–544. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Kinetic and structural analysis of a cleaved donor intermediate and a strand transfer intermediate in Tn10 transposition. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90218-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Chaconas G. Mechanistic aspects of DNA transposition. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Oct;2(5):698–704. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman P. D., Rio D. C. P element transposition in vitro proceeds by a cut-and-paste mechanism and uses GTP as a cofactor. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90116-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., Zou A. H., Jayaram M., Getzoff E., Harshey R. DNA-protein complexes during attachment-site synapsis in Mu DNA transposition. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1585–1591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie B. D., Chan B. S., Allison R. G., Chaconas G. Structural aspects of a higher order nucleoprotein complex: induction of an altered DNA structure at the Mu-host junction of the Mu type 1 transpososome. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3051–3059. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung P. C., Teplow D. B., Harshey R. M. Interaction of distinct domains in Mu transposase with Mu DNA ends and an internal transpositional enhancer. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):656–658. doi: 10.1038/338656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. B protein of bacteriophage mu is an ATPase that preferentially stimulates intermolecular DNA strand transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):699–703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Adzuma K. Inversion of the phosphate chirality at the target site of Mu DNA strand transfer: evidence for a one-step transesterification mechanism. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90145-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Mechanism of transposition of bacteriophage Mu: polarity of the strand transfer reaction at the initiation of transposition. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K. Transpositional recombination: mechanistic insights from studies of mu and other elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1011–1051. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Baker T. A., Mizuuchi K. Assembly of the active form of the transposase-Mu DNA complex: a critical control point in Mu transposition. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90104-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Baker T. A., Mizuuchi K. DNase protection analysis of the stable synaptic complexes involved in Mu transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9031–9035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Efficient Mu transposition requires interaction of transposase with a DNA sequence at the Mu operator: implications for regulation. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90854-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi M., Mizuuchi K. Target site selection in transposition of phage Mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:515–523. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namgoong S. Y., Jayaram M., Kim K., Harshey R. M. DNA-protein cooperativity in the assembly and stabilization of mu strand transfer complex. Relevance of DNA phasing and att site cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):514–527. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P., Mizuuchi K. Structure of the bacteriophage Mu transposase core: a common structural motif for DNA transposition and retroviral integration. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Buch S. J., Chaconas G. Transpososomes: stable protein-DNA complexes involved in the in vitro transposition of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Chaconas G. A protein factor which reduces the negative supercoiling requirement in the Mu DNA strand transfer reaction is Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):3028–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Chaconas G. The Mu transpositional enhancer can function in trans: requirement of the enhancer for synapsis but not strand cleavage. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90081-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Lavoie B. D., Chaconas G. Action at a distance in Mu DNA transposition: an enhancer-like element is the site of action of supercoiling relief activity by integration host factor (IHF). EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3483–3489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Plasterk R. H. Human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein requires a subterminal position of its viral DNA recognition sequence for efficient cleavage. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4636–4644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4636-4644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor--operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6961–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Chaconas G. Flanking host sequences can exert an inhibitory effect on the cleavage step of the in vitro mu DNA strand transfer reaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9552–9558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Luenen H. G., Colloms S. D., Plasterk R. H. The mechanism of transposition of Tc3 in C. elegans. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]