Abstract
Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases (PPIases) are enzymes that catalyse protein folding both in vitro and in vivo. We isolated a peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) which is specifically associated with the 50S subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. This association was abolished by adding at least 1.5 M LiCl. Sequencing the N-terminal amino acids in addition to three proteolytic fragments totalling 62 amino acids revealed that this PPIase is identical to the E.coli trigger factor. A comparison of the amino acid sequence of trigger factor with those of other PPIase families shows little similarities, suggesting that trigger factor may represent an additional family of PPIases. Trigger factor was purified to homogeneity on a preparative scale from E.coli and its enzymatic properties were studied. In its activity towards oligopeptide substrates, the trigger factor resembles the FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs). Additionally, the pattern of subsite specificities with respect to the amino acid preceding proline in Suc-Ala-Xaa-Pro-Phe-4-nitroanilides is reminiscent of FKBPs. However, the PPIase activity of the trigger factor was not inhibited by either FK506 or by cyclosporin A at concentrations up to 100 microM. In vitro, the trigger factor catalysed the proline-limited refolding of a variant of RNase T1 much better than all other PPIases that have been examined so far.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Halvorson H. R., Brennan M. Consideration of the Possibility that the slow step in protein denaturation reactions is due to cis-trans isomerism of proline residues. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4953–4963. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90177-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton L. A., Davis J. M., Macdonald J. R., Bächinger H. P. Structural and functional characterization of Escherichia coli peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):927–934. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Brundage L., Rice M., Wickner W. ProOmpA spontaneously folds in a membrane assembly competent state which trigger factor stabilizes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1831–1835. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Guthrie B., Lecker S., Lill R., Wickner W. ProOmpA is stabilized for membrane translocation by either purified E. coli trigger factor or canine signal recognition particle. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1003–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90115-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Wickner W. Trigger factor: a soluble protein that folds pro-OmpA into a membrane-assembly-competent form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov A. N., Baldwin T. O. Contribution of cotranslational folding to the rate of formation of native protein structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Bang H., Ludwig B., Mann K., Hacker J. Mip protein of Legionella pneumophila exhibits peptidyl-prolyl-cis/trans isomerase (PPlase) activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1375–1383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Bang H., Mech C. Nachweis einer Enzymkatalyse für die cis-trans-Isomerisierung der Peptidbindung in prolinhaltigen Peptiden. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1984;43(10):1101–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman J., Nimmesgern E., Ohtsuka K., Hartl F. U. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):111–117. doi: 10.1038/370111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A. Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerases: immunophilins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):689–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Mutation data matrix and its uses. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:333–351. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie B., Wickner W. Trigger factor depletion or overproduction causes defective cell division but does not block protein export. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5555–5562. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5555-5562.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. K., Stein R. L. Substrate specificities of the peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase activities of cyclophilin and FK-506 binding protein: evidence for the existence of a family of distinct enzymes. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 24;29(16):3813–3816. doi: 10.1021/bi00468a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayano T., Takahashi N., Kato S., Maki N., Suzuki M. Two distinct forms of peptidylprolyl-cis-trans-isomerase are expressed separately in periplasmic and cytoplasmic compartments of Escherichia coli cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3041–3048. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
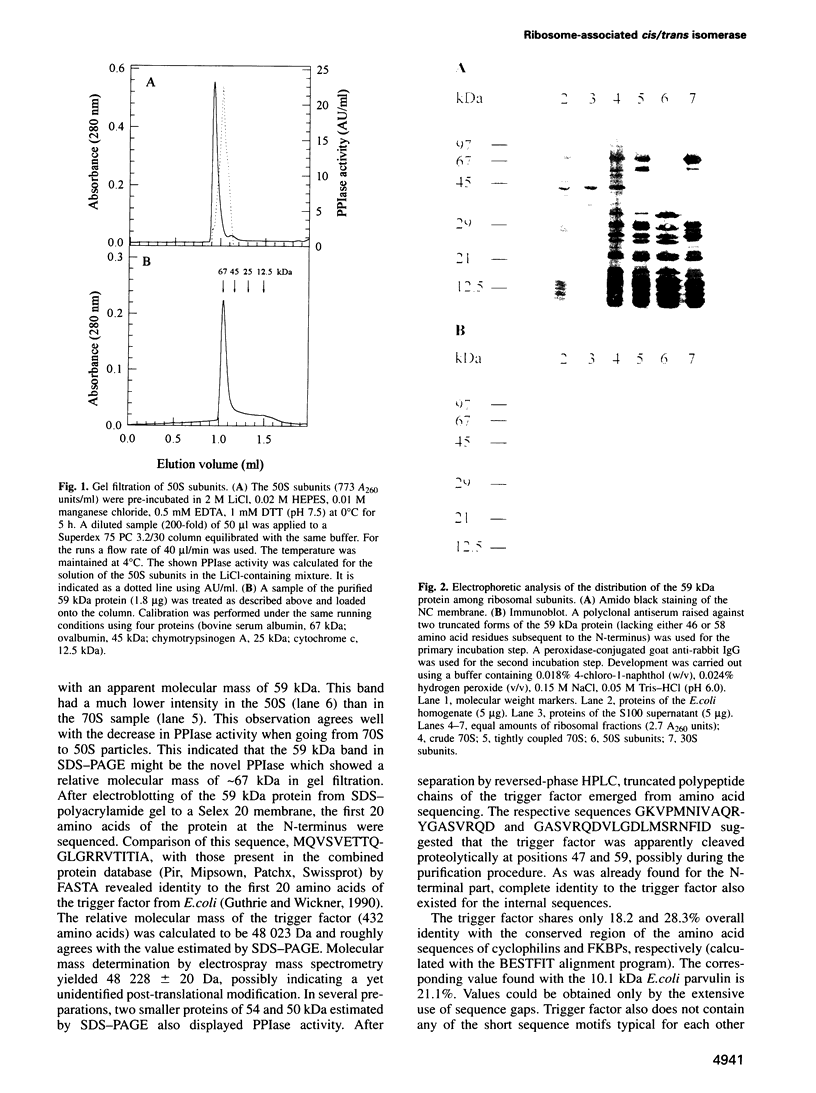
- Homann H. E., Nierhaus K. H. Ribosomal proteins. Protein compositions of biosynthetic precursors and artifical subparticles from ribosomal subunits in Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 28;20(2):249–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. What does protein refolding in vitro tell us about protein folding in the cell? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Mar 29;339(1289):287–295. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern G., Kern D., Schmid F. X., Fischer G. A kinetic analysis of the folding of human carbonic anhydrase II and its catalysis by cyclophilin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):740–745. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefhaber T., Grunert H. P., Hahn U., Schmid F. X. Folding of RNase T1 is decelerated by a specific tertiary contact in a folding intermediate. Proteins. 1992 Feb;12(2):171–179. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse M., Brunke M., Escher A., Szalay A. A., Tropschug M., Zimmermann R. Enzyme assembly after de novo synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysate involves molecular chaperones and immunophilins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2588–2594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlicki W., Odom O. W., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Chaperone-dependent folding and activation of ribosome-bound nascent rhodanese. Analysis by fluorescence. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 2;244(3):319–331. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K., Schmid F. X., Fischer G. Catalysis of protein folding by prolyl isomerase. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):268–270. doi: 10.1038/329268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S., Lill R., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Kumamoto C. A., Wickner W. Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli--SecB, trigger factor and GroEL--form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2703–2709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Crooke E., Guthrie B., Wickner W. The "trigger factor cycle" includes ribosomes, presecretory proteins, and the plasma membrane. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1013–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim V. I., Spirin A. S. Stereochemical analysis of ribosomal transpeptidation. Conformation of nascent peptide. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Walsh C. T. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans-isomerase from Escherichia coli: a periplasmic homolog of cyclophilin that is not inhibited by cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4028–4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Cyclosporin A inhibits an initial step in folding of transferrin within the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14835–14838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig B., Rahfeld J., Schmidt B., Mann K., Wintermeyer E., Fischer G., Hacker J. Characterization of Mip proteins of Legionella pneumophila. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 May 1;118(1-2):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur M. W., Thornton J. M. Influence of proline residues on protein conformation. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):397–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90721-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matouschek A., Rospert S., Schmid K., Glick B. S., Schatz G. Cyclophilin catalyzes protein folding in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mücke M., Schmid F. X. Folding mechanism of ribonuclease T1 in the absence of the disulfide bonds. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 6;33(48):14608–14619. doi: 10.1021/bi00252a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl A., Keller U. FK-506-binding proteins from streptomycetes producing immunosuppressive macrolactones of the FK-506 type. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5888–5894. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5888-5894.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahfeld J. U., Rücknagel K. P., Schelbert B., Ludwig B., Hacker J., Mann K., Fischer G. Confirmation of the existence of a third family among peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases. Amino acid sequence and recombinant production of parvulin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 26;352(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00932-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahfeld J. U., Schierhorn A., Mann K., Fischer G. A novel peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassow J., Mohrs K., Koidl S., Barthelmess I. B., Pfanner N., Tropschug M. Cyclophilin 20 is involved in mitochondrial protein folding in cooperation with molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp60. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2654–2662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinberger H. J., Geigenmüller U., Wedde M., Nierhaus K. H. Parameters for the preparation of Escherichia coli ribosomes and ribosomal subunits active in tRNA binding. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:658–670. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Sofia H. J., Koonin E. V., Plunkett G., 3rd, Lazar S., Rouviere P. E. A new family of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jan;20(1):12–14. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. Peptides of L-and D-alanine. Synthesis and optical rotations. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3362–3370. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X. Fast-folding and slow-folding forms of unfolded proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;131:70–82. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)31035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X., Mayr L. M., Mücke M., Schönbrunner E. R. Prolyl isomerases: role in protein folding. Adv Protein Chem. 1993;44:25–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60563-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X. Proline isomerization during refolding of ribonuclease A is accelerated by the presence of folding intermediates. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X. Prolyl isomerase: enzymatic catalysis of slow protein-folding reactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:123–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B., Rahfeld J., Schierhorn A., Ludwig B., Hacker J., Fischer G. A homodimer represents an active species of the peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase FKBP25mem from Legionella pneumophila. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 26;352(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00970-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönbrunner E. R., Mayer S., Tropschug M., Fischer G., Takahashi N., Schmid F. X. Catalysis of protein folding by cyclophilins from different species. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3630–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. E., Sarkar A., Wampler J. E. Occurrence and role of cis peptide bonds in protein structures. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90159-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Texter F. L., Spencer D. B., Rosenstein R., Matthews C. R. Intramolecular catalysis of a proline isomerization reaction in the folding of dihydrofolate reductase. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 30;31(25):5687–5691. doi: 10.1021/bi00140a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trandinh C. C., Pao G. M., Saier M. H., Jr Structural and evolutionary relationships among the immunophilins: two ubiquitous families of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3410–3420. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1464374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tropschug M., Wachter E., Mayer S., Schönbrunner E. R., Schmid F. X. Isolation and sequence of an FK506-binding protein from N. crassa which catalyses protein folding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):674–677. doi: 10.1038/346674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann B., Sakai H., Davis T. A., Wiedmann M. A protein complex required for signal-sequence-specific sorting and translocation. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):434–440. doi: 10.1038/370434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]