Abstract
Innate immune cells are critically involved in ischemic complications of atherosclerosis. While new insight emerged on the origin and role of leukocytes in steady state, the knowledge about myeloid cell's sources, functions and fate after stroke is limited. In our review, we highlight open questions in this important area while examining potential parallels in the immune response after stroke and myocardial infarction. We stress the need to better understand systemic interactions between ischemic tissue, immunity and hematopoiesis, as turn over of leukocytes in inflammatory sites can be rapid, and cell production and supply may serve as future therapeutic targets to modulate inflammation in the vessel wall, the brain and heart.
Introduction
Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the USA, and the majority of strokes are due to thrombotic or embolic complications of atherosclerosis. One in four strokes are recurrent events1, highlighting that both primary and secondary prevention are currently insufficient2. While it is increasingly agreed upon that innate immune cells importantly contribute to atherosclerosis and its ischemic complications, the role of leukocytes, their subsets, sources and fates after stroke are incompletely understood. Ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction (MI) have in common that the sustained tissue injury is sterile and that it is caused by a lack of oxygen. Distinct differences include the phenotype of injured cells and tissues, and the nature and timing of signals from ischemic brain and heart. Because both MI and ischemic stroke are caused by atherosclerosis, we suspect that there are many similarities. Therefore, the comparison of the immune response to these two most deadly complications of vascular disease may be useful. In our minireview, we highlight open questions regarding the systemic innate immune response after stroke, relating them to recent insight obtained after myocardial infarction (MI).
Local response in ischemic tissue and the role of monocyte subsets
Parabiosis experiments revealed that in the steady state, microglia primarily derive from local progenitors rather than from circulating leukocytes3. In response to stroke, microglia are rapidly activated and develop a pro-inflammatory phenotype4. Once brain tissue is compromised due to ischemia, the injury also triggers a systemic inflammatory response that contributes to lesion maturation and the removal of dead or dying cells5, 6. In patients7, 8 and mice9, 10 with stroke, acutely elevated blood counts of innate immune cells such as neutrophils and monocytes parallel data obtained after MI (reviewed in reference11). These blood leukocytes are recruited in large numbers to the ischemic brain, where they have a critical role in wound healing, but may also contribute to reperfusion injury5, 12. As seen in MI11, the ischemic brain first recruits neutrophils and later monocytes4. However, in contrast to the ischemic heart, microglia substantially contribute to the cellular inflammatory response in the brain4. Limited data are available on the role of monocyte subsets in inflammation, healing and resolution of inflammation after ischemic brain injury. In the infarcted mouse heart13, inflammatory Ly6Chigh monocytes are recruited first via CCL2/CCR2 and dominate the first 3 days after injury. Ly6Chigh monocytes are sources of inflammatory cytokines and pursue proteolytic and phagocytic removal of necrotic tissue. Likely, these cells give rise to M1 macrophages with similar pro-inflammatory functions. Starting on day 4 after MI, an inflammation resolution phenotype emerges, as Ly6Clow monocytes/macrophages are recruited via CX3CR1 to orchestrate tissue repair. These cells regulate angiogenesis and extracellular matrix production, but also continue phagocytosis of tissue debris. Blocking either monocytic phase impairs infarct healing and promotes heart failure in mice13. Several lines of evidence suggest analogous roles for monocyte and macrophage subsets after stroke. A parallel temporal pattern of inflammatory and pro-resolution macrophage phenotype occurs in murine brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion14. Contrasting MI data, a study14 reports that Ly6Clow cells are not recruited separately via CX3CR1 but rather derive from CCR2+ Ly6Chigh monocytes. Monocyte depletion increases hemorrhagic conversion of ischemic stroke, likely due to delayed myeloid cell repair functions14. On the other hand, deletion of CCR2 or its CCL2 ligand in mice results in smaller brain infarcts, together with decreased infiltration of monocyte/macrophages and pro-inflammatory cytokine production15, 16. These data point to potentially harmful as well as helpful functions of monocytes and macrophages after stroke, highlighting the necessity to better understand the role of subsets, timing, inflammation resolution and magnitude of innate immune responses in the injured brain.
Pre-existing chronic inflammation exaggerates local cellular response
In atherosclerotic plaques, leukocytes contribute decisively to growth, inflammation, instability and rupture. In patients, ischemia often results from artery-occluding atherosclerotic plaque and thus occurs in a setting of chronic inflammation that generated the vulnerable, ruptured plaque in the first place. The immune response to ischemic heart and brain in the setting of atherosclerosis may be fundamentally different — we hypothesize exaggerated — when compared to external wounding after trauma in an otherwise healthy person. Excessive levels of circulating inflammatory monocytes hamper resolution of inflammation, impair infarct healing and cause heart failure in ApoE−/− mice after coronary ligation17. Thus, pre-existing chronic inflammation alters critical signals compared to a healthy steady state, and the raised systemic immune activity associated with atherosclerosis may impair the resolution of inflammation after ischemic brain injury. If stroke results from atherosclerosis, inflammation resolution in the ischemic brain may be disturbed, and harmful functions of inflammatory leukocytes may impair outcome. This hypothesis should be tested experimentally. Of note, increased leukocyte and monocyte counts in the blood correlate with post-MI heart failure progression in clinical studies18, and the blood level of the CD14highCD16− monocyte subset is associated with poor outcome and increased mortality in patients with stroke19.
Rapid cell turnover in ischemic tissue motivates study of leukocyte supply
In sites of acute inflammation, the turn over of innate immune cells, especially neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, may be surprisingly rapid. Fate-mapping studies determined that even 5 days after ischemic myocardial injury, myeloid cells are recruited in high numbers to the healing tissue, accounting for their relatively short infarct residence time of only 20 hours20. Similar numbers are not available for stroke; however, the leukocyte turnover may also be rapid. It will be important to understand local cell kinetics in the brain acutely after stroke, as high leukocyte turnover and ongoing recruitment necessitate increased leukocyte supply and production, all of which could be targeted therapeutically.
The splenic monocyte reservoir after MI and stroke
An interesting feature shared by ischemic brain and heart injury is a transient decrease in spleen size, likely reflecting the organ's release of leukocytes21, 22. Studies in animals splenectomized prior to ischemic insult of the brain or heart showed a decreased infiltration of innate immune cells into inflamed tissues20, 23. More recently, a lower number of splenic monocytes was described in an autopsy study of patients with acute MI24. A decrease in spleen size has been documented in patients with acute stroke25. Contrary to the systemically increased levels of innate immune cells, post-stroke inflammation is accompanied by a severe loss of lymphocytes in blood and spleen. Lymphopenia after stroke most likely results from lymphocyte apoptosis, which may contribute to the reduction in spleen's size9 and possibly to compromised immunity.
Accelerated hematopoiesis increases leukocyte production
Because the heightened demand for leukocytes in the ischemic lesion quickly exhausts ready-made cells in the body's reservoirs (i.e. blood, bone marrow and spleen), the hematopoietic system likely increases cell production. In mice with MI, we observed transfer of leukocyte progenitors from the bone marrow to the spleen, and splenic monocyte production20, 26 (Figure). Despite the health burden caused by stroke and MI, surprisingly little is known about how the bone marrow compartment reacts to ischemic injury, and how it is alerted after MI or stroke. The widespread systemic inflammatory response in both patients7 and animal models27 argues for an activation of the hematopoietic system after stroke. The recently reported increased hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell activation in mice and in patients with MI26 is likely generalizable although its impact on the brain, heart and vasculature are probably organ and tissue specific. Future studies will investigate hematopoietic stem cell behavior and their progeny's fate after ischemic brain injury, and examine the pathways that regulate bone marrow activity after stroke.
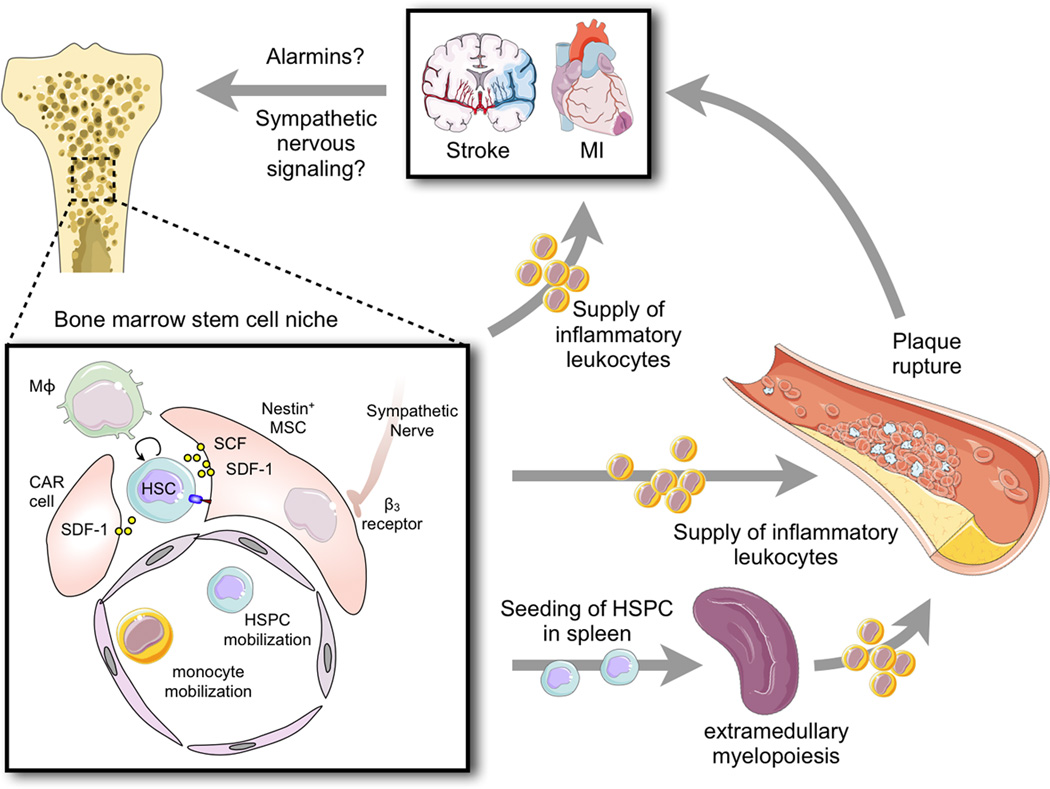
Figure 1. Putative organ networks after myocardial infarction and stroke.
The cartoon illustrates events after ischemic injury of either the brain or the heart that lead to accelerated disease progression in atherosclerotic plaque (some events are experimentally proven in mice, others are still hypothetical). The enlarged inset depicts processes in the bone marrow microenvironment after MI. Here, niche cells provide signals that regulate hematopoietic stem cell activity, retention and leukocyte production. After MI, increased sympathetic nervous signaling releases noradrenaline in the bone marrow niche, which binds to β3 adrenoreceptors on niche cells. These withdraw the soluble factor SDF-1 which results in increased hematopoietic progenitor cell activity and emigration to extramedullary sites. Similar processes may be active after stroke. Increased production of leukocytes then feeds an expanded pool of circulating monocytes which are recruited to the injured brain or myocardial infarct, but also to atherosclerotic plaque in higher numbers, accelerating plaque growth and vulnerability. This feedback loop may cause the high clinical reoccurrence rates of MI and stroke. HSC: hematopoietic stem cell. HSPC: hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. CAR: CXCL12 abundant reticular cell, Mϕ: macrophage.
Danger signals alerting immune and hematopoietic system after stroke and MI
Long-range signals transfer information from the site of injury to the site of innate immune cell production. These could be transmitted in the bloodstream in form of intracellular danger signals released from dying cells in the wound, acting as receptor ligands on progenitor cells or on the hematopoietic niche (Figure). Alternatively, signals could be delivered via extravascular routes through the fibers of the sympathetic nervous system. Noradrenaline, released from sympathetic nerves in the bone marrow after MI, binds to β3 adrenergic receptors expressed on mesenchymal stromal cells, providing the microenvironmental cues in hematopoietic tissue after myocardial infarction26. Identifying and inhibiting those signals may help to curtail leukocyte overproduction and -supply, as both are likely rate-limiting inflammation in the brain, the heart and the artery wall.
Increased leukocyte production may cause recurrent stroke and MI
The cells that are produced in response to ischemia not only travel to the injury site but may be diverted to atherosclerotic lesions in the arterial wall. Similar cell types, especially neutrophils and inflammatory monocytes, are early responders after MI and stroke as well as major instigators of inflammatory atherosclerosis. In parallel to the high re-occurrence rates in patients with ischemic complications of atherosclerosis, we observed that MI as well as stroke accelerates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE−/− mice26. If we improve our understanding of the putative crosstalk between the immune and hematopoietic systems with injured brain and heart (Figure), we may expand our clinical ability to prevent recurrent ischemia. The development of new therapeutic strategies modulating the hematopoietic system with translatable pharmacological interventions may present a crucial step towards secondary prevention of stroke and MI. On this path, it will likely be helpful to compare the systemic immune response after MI and stroke, and to determine the prevailing parallels and differences.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by an American Heart Association postdoctoral fellowship to Gabriel Courties (13POST16580004) and grants from the and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (R01-HL114477, R01-HL095629). The figure was prepared using Servier Medical Art.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: none.
References
- 1.Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2012;125(1):e2–e220. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31823ac046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C. The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron. 2010;67(2):181–198. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science. 2010;330(6005):841–845. doi: 10.1126/science.1194637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schilling M, Besselmann M, Leonhard C, Mueller M, Ringelstein EB, Kiefer R. Microglial activation precedes and predominates over macrophage infiltration in transient focal cerebral ischemia: a study in green fluorescent protein transgenic bone marrow chimeric mice. Exp Neurol. 2003;183(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(03)00082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kamel H, Iadecola C. Brain-immune interactions and ischemic stroke: clinical implications. Arch Neurol. 2012;69(5):576–581. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.del Zoppo GJ, Becker KJ, Hallenbeck JM. Inflammation after stroke: is it harmful? Arch Neurol. 2001;58(4):669–672. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.4.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Emsley HC, Smith CJ, Gavin CM, et al. An early and sustained peripheral inflammatory response in acute ischaemic stroke: relationships with infection and atherosclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2003;139(1–2):93–101. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(03)00134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vogelgesang A, Grunwald U, Langner S, et al. Analysis of lymphocyte subsets in patients with stroke and their influence on infection after stroke. Stroke. 2008;39(1):237–241. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.493635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, et al. Splenic atrophy in experimental stroke is accompanied by increased regulatory T cells and circulating macrophages. J Immunol. 2006;176(11):6523–6531. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liesz A, Hagmann S, Zschoche C, et al. The spectrum of systemic immune alterations after murine focal ischemia: immunodepression versus immunomodulation. Stroke. 2009;40(8):2849–2858. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.549618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M. Leukocyte behavior in atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure. Science. 2013;339(6116):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.1230719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eltzschig HK, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1391–1401. doi: 10.1038/nm.2507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nahrendorf M, Swirski FK, Aikawa E, et al. The healing myocardium sequentially mobilizes two monocyte subsets with divergent and complementary functions. J Exp Med. 2007;204(12):3037–3047. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gliem M, Mausberg AK, Lee JI, et al. Macrophages prevent hemorrhagic infarct transformation in murine stroke models. Ann Neurol. 2012;71(6):743–752. doi: 10.1002/ana.23529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dimitrijevic OB, Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV. Absence of the chemokine receptor CCR2 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Stroke. 2007;38(4):1345–1353. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000259709.16654.8f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hughes PM, Allegrini PR, Rudin M, Perry VH, Mir AK, Wiessner C. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 deficiency is protective in a murine stroke model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22(3):308–317. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200203000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Panizzi P, Swirski FK, Figueiredo JL, et al. Impaired infarct healing in atherosclerotic mice with Ly-6C(hi) monocytosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(15):1629–1638. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Engstrom G, Melander O, Hedblad B. Leukocyte count and incidence of hospitalizations due to heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2009;2(3):217–222. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.827071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Urra X, Villamor N, Amaro S, et al. Monocyte subtypes predict clinical course and prognosis in human stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(5):994–1002. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Leuschner F, Rauch PJ, Ueno T, et al. Rapid monocyte kinetics in acute myocardial infarction are sustained by extramedullary monocytopoiesis. J Exp Med. 2012;209(1):123–137. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Seifert HA, Hall AA, Chapman CB, Collier LA, Willing AE, Pennypacker KR. A transient decrease in spleen size following stroke corresponds to splenocyte release into systemic circulation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012;7(4):1017–1024. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9406-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Etzrodt M, et al. Identification of splenic reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites. Science. 2009;325(5940):612–616. doi: 10.1126/science.1175202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ajmo CTJ, Vernon DO, Collier L, et al. The spleen contributes to stroke-induced neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86(10):2227–2234. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van der Laan AM, Ter Horst EN, Delewi R, et al. Monocyte subset accumulation in the human heart following acute myocardial infarction and the role of the spleen as monocyte reservoir. Eur Heart J. 2013 doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht331. ePub. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sahota P, Vahidy F, Nguyen C, et al. Changes in spleen size in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a pilot observational study. Int J Stroke. 2013;8(2):60–67. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dutta P, Courties G, Wei Y, et al. Myocardial infarction accelerates atherosclerosis. Nature. 2012;487(7407):325–329. doi: 10.1038/nature11260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Offner H, Subramanian S, Parker SM, Afentoulis ME, Vandenbark AA, Hurn PD. Experimental stroke induces massive, rapid activation of the peripheral immune system. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26(5):654–665. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]