Abstract
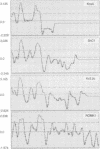
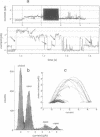
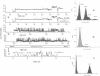
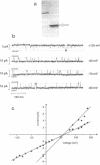
We report the identification, functional expression, purification, reconstitution and electrophysiological characterization of an up to now unique prokaryotic potassium ion channel (KcsA). It has a rectifying current-voltage relationship and displays subconductance states, the largest of which amounts to A approximately equal to 90 pS. The channel is blocked by Cs- ions and gating requires the presence of Mg2+ ions. The kcsA gene has been identified in the gram-positive soil bacterium Streptomyces lividans. It encodes a predicted 17.6 kDa protein with two potential membrane-spanning helices linked by a central domain which shares a high degree of similarity with the H5 segment conserved among eukaryotic ion channels. Multiple alignments of deduced amino acids suggest that the novel channel has the closest kinship to the S5, H5 and S6 regions of voltage-gated K+ channel families, mainly to the subfamily represented by the Shaker protein from Drosophila melanogaster. Moreover, KcsA is most distantly related to eukaryotic inwardly rectifying channels with two putative predicted transmembrane segments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Huprikar S. S., Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J., Gaber R. F. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson N. S., Robertson G. A., Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):551–555. doi: 10.1126/science.1857984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Functional bases for interpreting amino acid sequences of voltage-dependent K+ channels. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:173–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. L., Aldrich R. W., Yellen G. Tetraethylammonium blockade distinguishes two inactivation mechanisms in voltage-activated K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5092–5095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Keller B. U. A membrane fusion strategy for single-channel recordings of membranes usually non-accessible to patch-clamp pipette electrodes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80442-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich W., Betzler M., Schrempf H. An amplifiable and deletable chloramphenicol-resistance determinant of Streptomyces lividans 1326 encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2789–2797. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe A., Schröter K. H., Ruppersberg J. P., Stocker M., Drewes T., Beckh S., Pongs O. Cloning and expression of a human voltage-gated potassium channel. A novel member of the RCK potassium channel family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1749–1756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Potassium channels and their evolving gates. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):119–122. doi: 10.1038/371119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Hedrich R., Vaz W. L., Criado M. Single channel recordings of reconstituted ion channel proteins: an improved technique. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jan;411(1):94–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00581652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler A., Dittrich W., Betzler M., Schrempf H. Cloning and analysis of a deletable tetracycline-resistance determinant of Streptomyces lividans 1326. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1103–1109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luneau C., Wiedmann R., Smith J. S., Williams J. B. Shaw-like rat brain potassium channel cDNA's with divergent 3' ends. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P., RUDIN D. O., TIEN H. T., WESCOTT W. C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:979–980. doi: 10.1038/194979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R. An Escherichia coli homologue of eukaryotic potassium channel proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3510–3514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrou S., Ordway R. W., Kirber M. T., Dopico A. M., Hamilton J. A., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Direct effects of fatty acids and other charged lipids on ion channel activity in smooth muscle cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1995 Feb-Mar;52(2-3):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(95)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigac J., Vujaklija D., Toman Z., Gamulin V., Schrempf H. Structural instability of a bifunctional plasmid pZG1 and single-stranded DNA formation in Streptomyces. Plasmid. 1988 May;19(3):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Kecskemethy N., Müller R., Krah-Jentgens I., Baumann A., Kiltz H. H., Canal I., Llamazares S., Ferrus A. Shaker encodes a family of putative potassium channel proteins in the nervous system of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1087–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O. Structure-function studies on the pore of potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1993 Oct;136(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00241484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehberg B., Urban B. W., Duch D. S. The membrane lipid cholesterol modulates anesthetic actions on a human brain ion channel. Anesthesiology. 1995 Mar;82(3):749–758. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199503000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L., Baker K., Butler A., Covarrubias M., Pak M. D., Wei A. An essential 'set' of K+ channels conserved in flies, mice and humans. Trends Neurosci. 1992 May;15(5):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtman D. P., Schroeder J. I., Lucas W. J., Anderson J. A., Gaber R. F. Expression of an inward-rectifying potassium channel by the Arabidopsis KAT1 cDNA. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1654–1658. doi: 10.1126/science.8966547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. I., Ward J. M., Gassmann W. Perspectives on the physiology and structure of inward-rectifying K+ channels in higher plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:441–471. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Bonneaud N., Minet M., Lacroute F., Salmon J. M., Gaymard F., Grignon C. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1585180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong M., Chandy K. G., Gutman G. A. Molecular evolution of voltage-sensitive ion channel genes: on the origins of electrical excitability. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):221–242. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Takahashi K., Ikeda M., Hayakawa H., Ogawa A., Kawaguchi Y., Sakai O. Cloning of a pH-sensitive K+ channel possessing two transmembrane segments. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):642–645. doi: 10.1038/367642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Caporaso R., Brown A. M. Specification of pore properties by the carboxyl terminus of inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Science. 1994 May 6;264(5160):844–847. doi: 10.1126/science.8171340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]