Abstract
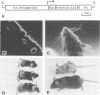
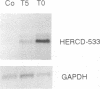
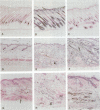
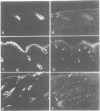
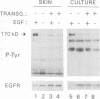
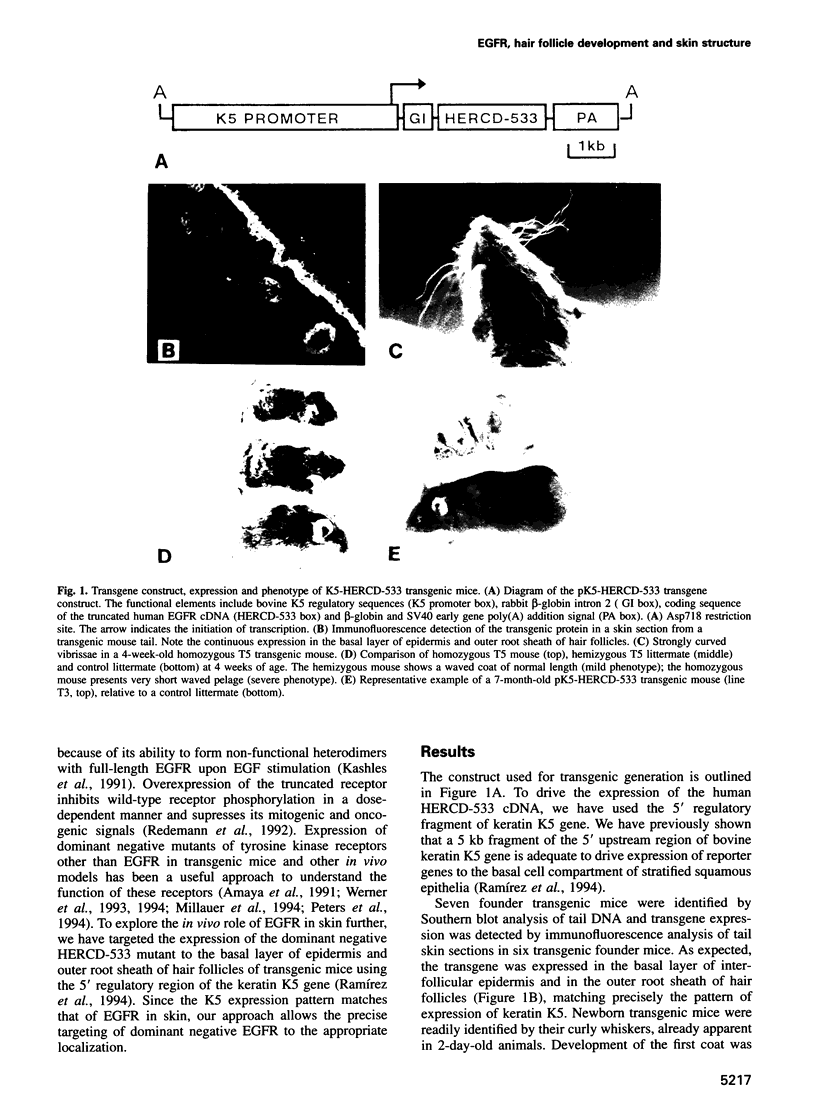
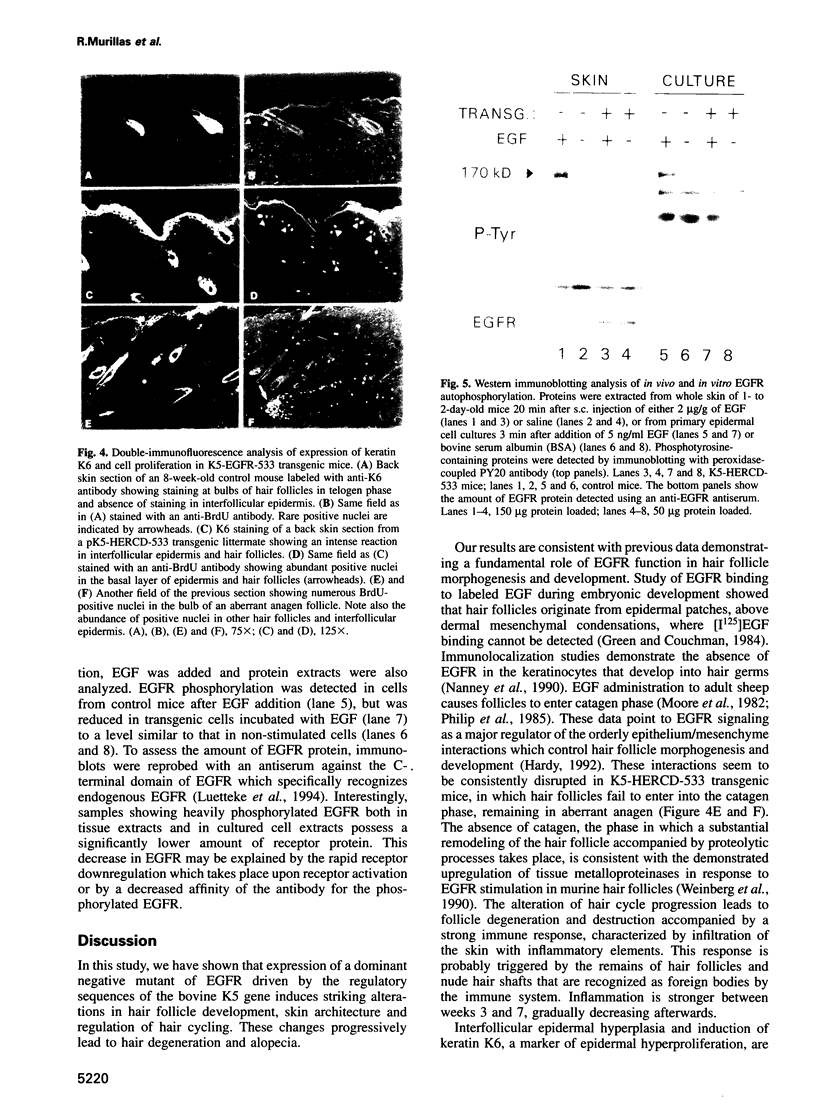
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a key regulator of keratinocyte biology. However, the physiological role of EGFR in vivo has not been well established. To analyze the role of EGFR in skin, we have generated transgenic mice expressing an EGFR dominant negative mutant in the basal layer of epidermis and outer root sheath of hair follicles. Mice expressing the mutant receptor display short and waved pelage hair and curly whiskers during the first weeks of age, but subsequently pelage and vibrissa hairs become progressively sparser and atrophic. Eventually, most mice present severe alopecia. Histological examination of the skin of transgenic mice shows striking alterations in the development of hair follicles, which fail to enter into catagen stage. These alterations eventually lead to necrosis and disappearance of the follicles, accompanied by strong infiltration of the skin with inflammatory elements. The interfollicular epidermis of these mice shows marked hyperplasia, expression of hyperproliferation-associated keratin K6 and increased 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine incorporation. EGFR function was inhibited in transgenic skin keratinocytes, since in vivo and in vitro autophosphorylation of EGFR was almost completely abolished on EGF stimulation. These results implicate EGFR in the control of hair cycle progression, and provide new information about its role in epidermal growth and differentiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. Expression of a dominant negative mutant of the FGF receptor disrupts mesoderm formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):257–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrandon Y., Green H. Cell migration is essential for sustained growth of keratinocyte colonies: the roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1131–1137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing M., Zentgraf H., Jorcano J. L. Differentially expressed bovine cytokeratin genes. Analysis of gene linkage and evolutionary conservation of 5'-upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):567–575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., ELLIOTT G. A. The stimulation of epidermal keratinization by a protein isolated from the submaxillary gland of the mouse. J Invest Dermatol. 1963 Jan;40:1–5. doi: 10.1038/jid.1963.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Derynck R., Wilcox J. N., Bringman T. S., Goustin A. S., Moses H. L., Pittelkow M. R. Production and auto-induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in human keratinocytes. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):817–820. doi: 10.1038/328817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Sipes N. J., Bascom C. C., Graves-Deal R., Pennington C. Y., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Growth modulation of mouse keratinocytes by transforming growth factors. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1596–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. The stimulation of epidermal proliferation by a specific protein (EGF). Dev Biol. 1965 Dec;12(3):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Goeddel D. V., Ullrich A., Gutterman J. U., Williams R. D., Bringman T. S., Berger W. H. Synthesis of messenger RNAs for transforming growth factors alpha and beta and the epidermal growth factor receptor by human tumors. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. W., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation in the neonatal mouse: association of a M(r) 55,000 substrate with the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8477–8481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendly B. M., Winget M., Hudziak R. M., Lipari M. T., Napier M. A., Ullrich A. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive to either the human epidermal growth factor receptor or HER2/neu gene product. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1550–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Basketter D. A., Couchman J. R., Rees D. A. Distribution and number of epidermal growth factor receptors in skin is related to epithelial cell growth. Dev Biol. 1983 Dec;100(2):506–512. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Couchman J. R. Distribution of epidermal growth factor receptors in rat tissues during embryonic skin development, hair formation, and the adult hair growth cycle. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Aug;83(2):118–123. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12263298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. H. The secret life of the hair follicle. Trends Genet. 1992 Feb;8(2):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90350-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Higashiyama S., Asada H., Hashimura E., Kobayashi T., Sudo K., Nakagawa T., Damm D., Yoshikawa K., Taniguchi N. Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor is an autocrine growth factor for human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20060–20066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetteke N. C., Phillips H. K., Qiu T. H., Copeland N. G., Earp H. S., Jenkins N. A., Lee D. C. The mouse waved-2 phenotype results from a point mutation in the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 15;8(4):399–413. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.4.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetteke N. C., Qiu T. H., Peiffer R. L., Oliver P., Smithies O., Lee D. C. TGF alpha deficiency results in hair follicle and eye abnormalities in targeted and waved-1 mice. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):263–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90228-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann G. B., Fowler K. J., Gabriel A., Nice E. C., Williams R. L., Dunn A. R. Mice with a null mutation of the TGF alpha gene have abnormal skin architecture, wavy hair, and curly whiskers and often develop corneal inflammation. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90227-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millauer B., Shawver L. K., Plate K. H., Risau W., Ullrich A. Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature. 1994 Feb 10;367(6463):576–579. doi: 10.1038/367576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modjtahedi H., Eccles S., Sandle J., Box G., Titley J., Dean C. Differentiation or immune destruction: two pathways for therapy of squamous cell carcinomas with antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1695–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Panaretto B. A., Carter N. B. Epidermal hyperplasia and wool follicle regression in sheep infused with epidermal growth factor. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Mar;84(3):172–175. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12264699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Panaretto B. A., Robertson D. Epidermal growth factor delays the development of the epidermis and hair follicles of mice during growth of the first coat. Anat Rec. 1983 Jan;205(1):47–55. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092050107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. P., Panaretto B. A., Robertson D. Inhibition of wool growth in merino sheep following administration of mouse epidermal growth factor and a derivative. Aust J Biol Sci. 1982;35(2):163–172. doi: 10.1071/bi9820163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney L. B., Magid M., Stoscheck C. M., King L. E., Jr Comparison of epidermal growth factor binding and receptor distribution in normal human epidermis and epidermal appendages. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Nov;83(5):385–393. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12264708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney L. B., Stoscheck C. M., King L. E., Jr, Underwood R. A., Holbrook K. A. Immunolocalization of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal developing human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6):742–748. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Schlessingert J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol. 1993 Jul 1;3(7):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90350-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters K., Werner S., Liao X., Wert S., Whitsett J., Williams L. Targeted expression of a dominant negative FGF receptor blocks branching morphogenesis and epithelial differentiation of the mouse lung. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3296–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Dougall W. C., Hellman M. E., Greene M. I. Kinase-deficient neu proteins suppress epidermal growth factor receptor function and abolish cell transformation. Oncogene. 1994 May;9(5):1507–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann N., Holzmann B., von Rüden T., Wagner E. F., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Anti-oncogenic activity of signalling-defective epidermal growth factor receptor mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):491–498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Fuchs E. Transgenic mice provide new insights into the role of TGF-alpha during epidermal development and differentiation. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):714–727. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg W. C., Brown P. D., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Yuspa S. H. Growth factors specifically alter hair follicle cell proliferation and collagenolytic activity alone or in combination. Differentiation. 1990 Dec;45(3):168–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Smola H., Liao X., Longaker M. T., Krieg T., Hofschneider P. H., Williams L. T. The function of KGF in morphogenesis of epithelium and reepithelialization of wounds. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.7973639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Weinberg W., Liao X., Peters K. G., Blessing M., Yuspa S. H., Weiner R. L., Williams L. T. Targeted expression of a dominant-negative FGF receptor mutant in the epidermis of transgenic mice reveals a role of FGF in keratinocyte organization and differentiation. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2635–2643. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe C., Müller W., Rüther U. Long-term consequences of interleukin-6 overexpression in transgenic mice. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;11(8):587–592. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kamata N., Kawano H., Shimizu S., Kuroki T., Toyoshima K., Rikimaru K., Nomura N., Ishizaki R., Pastan I. High incidence of amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in human squamous carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):414–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Cros D. L. Fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor in hair development. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Jul;101(1 Suppl):106S–113S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12363020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]