Abstract
Scope
Three fluorescence biosensors were developed based on a 3T3-L1 preadipocyte line that stably expressed Nfkb-RE/GFP, Fabp4-P/CFP, and Nrf2-P/YFP fluorescent reporters. We hypothesized that nutraceuticals’ inflammatory, adipogenic, and antioxidant status will be identified based on the change in fluorescence in reporter adipocytes. We validated these assays with activators of NFκB, FABP4-regulating PPARγ, NFR2 and, thereafter, tested known and unknown properties of mangosteens (MG), the xanthone metabolites in mangosteen fruit.
Methods and results
We validated inflammatory and adipogenic properties of α-MG using a Nfkb-RE/GFP biosensor assay. Next, we identified unique properties of γ-MG, a minor mangosteen xanthone. γ-MG suppressed adipogenesis and adiponectin, but inhibited the Nfkb-RE/GFP reporter and secretion of inflammatory MCP-1 as compared to the control adipocytes. We found that the inhibition of adipogenesis and Nfkb-mediated inflammation depends on a dose-dependent reduction of Nrf2 promoter activity by α-MG. The Nrf2 inhibition resulted in the reduced Pparg expression. α-MG did not directly influence Pparg activity in Fabp4-P/CFP adipocytes.
Conclusion
α-MG-mediated antioxidant response via Nrf2 is a mechanism preventing adipogenesis and inflammation in adipocytes. Combined application of high-throughput biosensors could provide an effective platform for the identification of nutraceuticals and the mechanism of their actions in adipocytes and, potentially, in obese patients.
Keywords: Inflammation, Mangostin/Nrf2, Nuclear receptors, Obesity
1 Introduction
In Europe, 4.0% to 28.3% of men and 6.2% to 36.5% of women are obese, and a higher prevalence of obesity was found in both Eastern Europe and Mediterranean countries as compared to Western and Northern Europe [1]. Also in the United States, more than 90 million Americans are facing obesity [2]. The development of obesity is associated with chronic inflammation in adipose tissue and occurs in both adipocytes and resident immune cells [3]. It has been shown that adipose tissue is not only the major site for energy storage, but also has endocrine function in the control of immune and metabolic responses in different organs [4]. Visceral fat developing around internal organs is associated with insulin resistance and chronic inflammation that can adversely affect many degenerative diseases, including cancer, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease [5, 6]. Endocrine effects of adipose tissue are mediated by signaling molecules known as adipokines (e.g. adiponectin and leptin), and pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) [7] and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1)) [8]. Obesity is associated with elevated expression of MCP-1 in insulin-resistant 3T3-L1 adipocytes, in the adipose tissue of mice [8] and humans [9], which is thought to participate in macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue [10]. It is expected that some nutrients can decrease the progression of metabolic disorders associated with obesity by altering anti- and pro-inflammatory cytokines in adipocytes and/or inhibiting adipogenesis. However, varieties of nutrient responses disrupt the discovery of their therapeutic efficiency and primary mechanisms in the regulation of inflammation.
Recently, many phytonutrients were investigated for their potential therapeutic properties [11]. Garcinia mangostana L. (mangosteen), a tropical fruit originated from Southeast Asia, has been used in traditional therapy in the treatment of skin infection and dysentery for decades. These properties are ascribed to antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory activities of mangostin, which becomes a popular botanical supplement in recent years [12]. α-MG and γ-MG are two major xanthone derivatives isolated from the hull (pericarp) of mangosteen [13]. α-MG is a major xanthone capable to decrease adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by inhibiting fatty acid synthase [14]. It was also reported that both α-MG and γ-MG attenuated the expression of inflammatory genes, e.g. TNF-α, interleukin-6, and MCP-1 in human adipocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [15]. Less is known about the efficacy of γ-MG in the NF-κBlinked regulation of inflammatory and adipogenic processes and how antioxidant properties of xanthones influence adipogenesis.
The cumulative inflammatory signals could be measured through the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). NF-κB regulates many cytokines (e.g. MCP-1) by directly binding to the Nfkb response element (Nfkb-RE) in their promoters [16]. Previous reports demonstrated that adipogenesis changed the amount and composition of Rel proteins from the NF-κB complex. NF-κB proteins p65 (RelA), p68 (RelB), and inhibitor of κB (IκB) were up-regulated during adipogenesis resulting in overall activation of NF-κB [17]. Increased expression of p65 and p68 during adipogenesis may augment the sensitivity of adipocytes vs. preadipocytes to inflammatory stimuli. NF-κB is also regulated by nuclear factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a master regulator of transcription in adipogenesis [18]. Activated PPARγ induces its target genes (e.g. fatty acid binding protein 4 (Fabp4) [19]) and can bind to p65 in the nucleus thereby preventing the activation of Nfkb-RE during inflammation [20]. Studies also demonstrated that NF-κB inhibited Pparg expression and reduced obesity without impairing insulin sensitivity [21]. An antioxidant transcription factor, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2), is expressed in adipocytes and is an important inducer of Pparg expression and adipogenesis [22], whereas in response to stressors and in differentiated adipocytes, Nrf2 may attenuate NF-κB signaling pathway [23]. Potentially, the activation of Nfkb-RE encompasses counteracting processes in adipogenesis and inflammation. However, it remains unclear whether Nfkb-RE activation can assess interrelated inflammation and differentiation processes in adipocytes and serve as a basis for a high-throughput screening platform for the identification of nutrients with anti-inflammatory effects in adipose tissues.
To compare inflammatory and adipogenic nutrient properties, we developed a biosensor Nfkb-RE preadipocyte cell line. Since the activation of PPARγ in adipocytes can be monitored by activation of Fabp4 (aP2) promoter [24], we used Fabp4-P/CFP as biosensor for the transcription status of PPARγ. To explore early differentiation events and antioxidant status we also developed the Nrf2-P/YFP preadipocyte cell line. We hypothesize that the combined application of Nfkb-RE/GFP, Fabp4-P/CFP, and Nrf2-P/YFP promoter biosensors enables an effective screening of MG effects and their anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in adipocytes. We applied these assays to study MG xanthones for both the validation of our assays with their established effects and the elucidation of their unknown properties on NRF2 in adipogenesis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents and supplies
We bought reagents from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and cell culture media from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA) unless otherwise indicated. Vectors were purchased: Cignal Lenti NFκB Reporter (GFP) Kit from SABiociences/Qiagen (Valencia, CA); mCherry constitutive expression vector from Genecopoeia (Rockville, MD), human Fabp4 promoter vector with eCFP reporter from Genecopoeia (Rockville, MD), and human Nrf2 promoter vector with eYFP reporter in from Genecopoeia (Rockville, MD). Rosiglitazone (BRL 49653, denote as BRL) was purchased from Enzo Life Sciences (Farmingdale, NY). All-trans retinoic acid isomer, which was stored under an argon atmosphere and protected from light, was used in our studies. α-MG [1, 3, 6-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-2, 8-bis (3-methyl-2-butenyl)-9H-xanthen-9-one] and γ-MG [1,3,6,7-Tetrahydroxy-2, 8-bis (3-methyl-2-butenyl)-9H-xanthen-9-one] were purified (≥98% as assessed by NMR spectroscopy) as described before [25].
2.2 Preparation of MG-enriched fetal bovine serum (FBS)
6mg α-MG or γ-MG (purity ≥95%) was added to 10mL FBS in 35mL glass vial. The mixture was incubated in shaking water bath (85rpm, 37°C for 48h) under a nitrogen atmosphere. The homogenated solution was filtered through a 0.22μm sterile filter. The filtrate was FBS enriched with α-MG or γ-MG (α- or γ-MG-FBS). The final concentrations of α-MG and γ-MG were 2298 ± 126 and 1951 ± 120 μmoL/L FBS. They were determined by HPLC-DAD analysis after MG-FBS extraction with diethyl ether [25].
2.3 Production of mCherry, Fabp4-P and Nrf2-P lenti-viral titers
Lenti-viral titers were produced using Lenti-Pac™ Lentiviral Packaging Kits (GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD). 1.3–1.5 × 106 of the HEK293Ta Lentiviral Packaging cells (GeneCopoeia, Rockville, MD) were plated in a 10-cm dish two days before transfection in DMEM (10mL), which was supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS. 2.5μg of shDNA clone (mCherry, Fabp4-P, or Nrf2-P), 5μL Lenti-Pac FIV mix and 15μL of EndoFectin-Lenti were diluted into 200μL Opti-MEM® I (Invitrogen) in a sterile polypropylene tube. The DNA-EndoFectin-Lenti complex was incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes and then added directly to the dish. Cells were incubated in a CO2 incubator at 37°C 8–14h. TiterBoost reagent (0.2%) was added to the culture medium. Pseudovirus-containing culture medium was collected 48h post transfection after being centrifuged at 2000rpm for 15min. The vector-containing supernatants were used for the transfection.
2.4 Nfkb-RE/GFP cell line derivation
Murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes capable of differentiation [26] were used for the derivation of three reporter cell lines. 80% confluent murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in P60 dish were transfected with 20μL Nfkb-RE/GFP lentiviral reporter vector (0.8 × 107 TU/ml; SABiociences/Qiagen) in the presence of 2.5μL Polybrene transfection reagent (Millipore; Billerica, MA) in 2.5mL Opti-MEM. After 3h, cells were supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated calf serum (CS). Stable clones were selected with puromycin (1.0mg/mL; Invitrogen). Selected cells were grown in a 6-well plate until 80% confluent. Then they were transfected with 1mL vector-containing supernatant, 0.5mL Opti-MEM and 0.5μL Polybrene (Millipore, Billerica, MA). After 3h, cells were supplemented with 10% CS. 24h post-transfection cells were replaced with standard culture medium (DMEM containing 10% CS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin) [27]. At 90% confluence, cells were plated into 96-well plate to achieve a density of single cell per well. Clones were tested with 20ng/mL LPS. Cells in each well were split in two wells when they were confluent. One well was for the control cells treated with standard culture media, and the other well was stimulated with 20ng/mL LPS. 24h after stimulation, fluorescence was measured in transfected cells after removal of culture media and double wash with PBS. After removal of the final wash solution from cells, an appropriate volume (i.e. 120μL for 24-well plate, 150μL for P60 dish) of RIPA buffer (Boston BioProducts, Ashland, MA) containing complete protease inhibitor (Roche Diagnostics Corporation, Indianapolis, IN) was added to each well. Cells were incubated on ice for 15min, and then plate was scratched using a tip to lyse residual cells. 80μL of cell lysate for each well was transferred to a black 96-well plate (Fisher Scientific Company, Hanover, IL) to measure fluorescence. GFP was measured at wavelengths Ex/Em 485/528, and mCherry at Ex/Em 587/640. Fluorescence was measured sequentially in same lysates using Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT). We calculated the ratio of GFP to mCherry (GFP/mCherry) control fluorescence for each well. Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocyte line was selected from a clone demonstrating the highest GFP/mCherry ratio in response to 20ng/mL LPS. Fluorescence measurements in stimulated Nfkb-RE/mGFP preadipocyte and adipocytes were performed using the same procedure.
2.5 Fabp4-P/CFP and Nrf2-P/YFP cell lines derivation
80% confluent murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in 24-well plate were transfected with 400μL of the produced Fabp4-P/CFP or Nrf2-P/YFP lentiviral titer vector, 400μL of the produced mCherry lentiviral titer vector, and 2μL Polybrene (Millipore, Billerica, MA). After 3h, cells were supplemented with 10% CS. 24h post-transfection, the transfection culture medium was replaced with standard culture medium. Stable clones were selected with puromycin (1.0mg/mL; Invitrogen). Selected cells were grown until approximately 90% confluence. Cells were plated into 96-well plate to achieve a single cell per well density. Fabp4-P/CFP clones were tested with 1μM BRL. Nrf2-P/YFP Clones were tested with 100nM RA in media containing UV-treated FBS to eliminate effects of endogenous retinoids. Cells in each well were split in two wells when they were confluent. One control well was treated with standard culture media, and the other well was treated with 1μM BRL (or 100nM RA). 24h after stimulation, fluorescence was measured in Fabp4-P/CFP cells as described above. CFP was measured at wavelengths Ex/Em 426/460 and normalized by mCherry at Ex/Em 587/640. 48h after stimulation, fluorescence was measured in Nrf2-P/YFP cells as described above. YFP was at Ex/Em 500/530 and normalized by mCherry at Ex/Em 587/640. We calculated the ratio CFP/mCherry (or YFP/mCherry) for each well. The Fabp4-P/CFP preadipocyte line was selected from a clone demonstrating the highest CFP/mCherry ratio in response to 1μM BRL. Nrf2-P/YFP preadipocyte line was selected from a clone demonstrating the highest YFP/mCherry ratio in response to 100nM RA.
2.6 Cell differentiation
Cells were cultured and maintained in a standard culture medium. Differentiation was induced (d0) in confluent preadipocytes using differentiation media (differentiation media I) containing 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (0.5mM), dexamethasone (1μM), insulin (1.7μM), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin in DMEM. Differentiation media II contained 10% FBS, insulin (1.7μM), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin in DMEM was replaced every 48h post induction as before [27].
2.7 Semi-quantitative mRNA analysis
mRNA was isolated from adipocyte cultures according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen; Valencia, CA). cDNA was prepared from purified mRNA and analyzed using 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System, TaqMan fluorogenic detection system and validated primers (Applied Biosystems; Foster City, CA). Comparative real time PCR was performed in triplicate, including no-template controls. The mRNA expression of interested genes was normalized by 18S expression level using the comparative cycle threshold (Ct) method.
2.8 Triglyceride assay
L-Type Triglyceride M Kit (Wako Diagnostics; Richmond, VA) was performed using RIPA cell lysates according to manufacturer’s description. The absorbance (650 nm) was measured using Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Microplate Reader.
2.9 Protein assay
The protein content in RIPA cell lysates was measured using BCA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific; Rockford, IL). The absorbance (595 nm) was measured using Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Microplate Reader.
2.10 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
MCP1 concentrations in the media were collected from Nfkb-RE/GFP cells and analyzed using ELISA Kit (Invitrogen; Grand Island, NY) according to manufacturer’s instruction. The absorbance (450 nm) was measured using Synergy H1 Hybrid Multi-Mode Microplate Reader.
2.11 Statistical analysis
Data were shown as mean ± SD (or SEM) based on 3 to 4 independent experiments. Group comparisons were performed using Mann-Whitney U test. Significance was determined using Pearson correlation analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Nfkb-RE biosensor monitors the regulation of NF-κB during adipogenesis and inflammation
We developed an inflammatory biosensor cell line via the stable transfection of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes with lentiviral Nfkb-RE/GFP. Consequently, constitutively expressed vector containing mCherry fluorescent protein was transfected into these cells as an endogenous control accounting for cell proliferation and metabolic state. We selected the clone that had the highest GFP/mCherry ratio. This clone was termed Nfkb-RE/GFP.
We validated the sensitivity of the Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes to classical endogenous and exogenous inducers of NF-κB activation. We examined Nfkb-RE/GFP cells prior to and after differentiation. Differentiation was confirmed by a significantly greater expression of Pparg in differentiated (146%) vs. non-differentiated cells (100%) (Fig. 1a). The activation of NF-κB was also 50% higher in differentiated Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes compared to non-differentiated cells (Fig. 1b). These observations were in agreement with reports demonstrating higher expression of NF-κB subunits p65 and p68 and the activation of NF-κB during differentiation [17]. Next we stimulated NF-κB by its classical inducer LPS [28] in both Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes and differentiated Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes. The activation of NF-κB was only moderately elevated in non-differentiated preadipocytes stimulated with LPS (120%) vs. non-treated controls (100%), while in differentiated adipocytes LPS stimulation was significantly increased compared to non-stimulated adipocytes (273% vs. 148%, respectively) (Fig. 1b). The time course of the Nfkb-RE/GFP activation in the LPS-stimulated adipocytes is shown in the insert of Fig. 1b.
Figure 1. Differentiation increases Pparg expression and NF-κB activity in Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes.
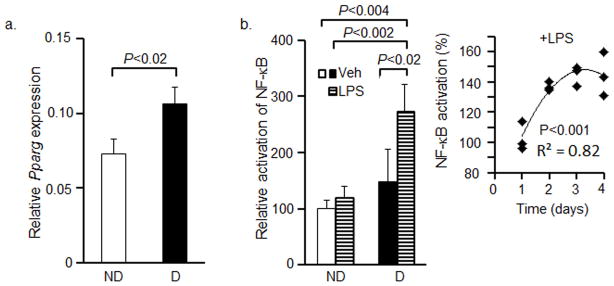
(a) Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes were differentiated for 8d. Expression of Pparg was measured in Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes (ND, white bar) and differentiated Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes (D, black bar) using TaqMan assay (Mann Whitney U test, n=3, mean±SD).
(b) Nfkb-RE/GFP pre-adipocytes (ND, white bar) were differentiated for 4d (D, black bar), then they were stimulated with 10ng/mL LPS for 24h (LPS, horizontal line bars). GFP/mCherry ratio was obtained from total cell lysates in RIPA buffer. Data are shown as relative activation of NF-κB in non-differentiated Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes (100%) compared to Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes in the presence and absence of LPS (Mann Whitney U test, n=4, mean±SD). The time-dependent induction of Nfkb-RE/GFP in LPS-treated adipocytes is shown in the Insert. For time-dependent experiment, differentiation was induced in preadipocytes. 24h before adipocyte harvest, the medium was replaced with DMEM containing 10ng/mL LPS, insulin, 1% FBS DMEM (i.e. modified second differentiation medium). Data are shown as normalized Nfkb-RE/GFP activation to that seen at day 1 (average, 100%). Statistic analysis was examined by Pearson correlation test.
3.2 Nfkb-RE biosensor detects the dual role of rosiglitazone in the activation of NF-κB during adipogenesis
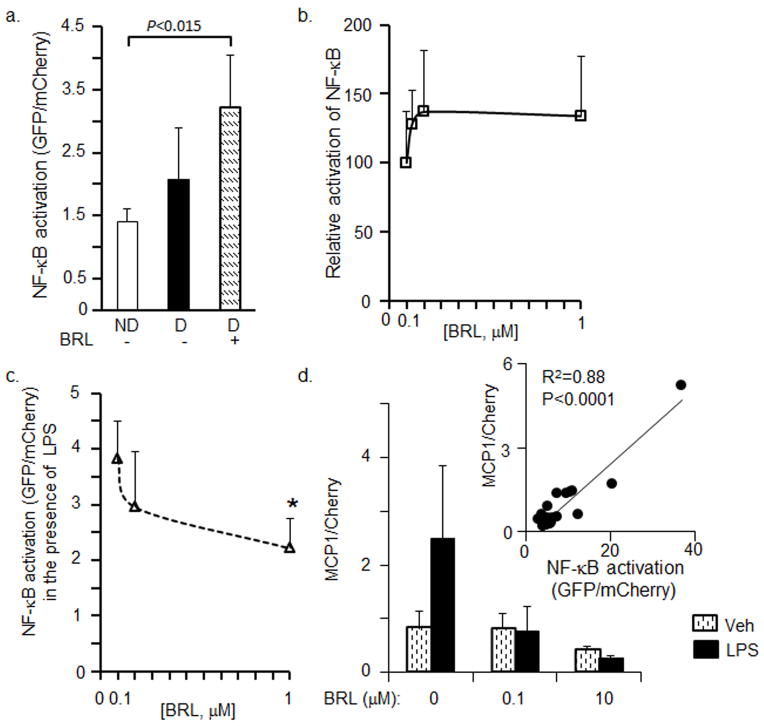
Rosiglitazone (BRL) is an agonist of PPARγ that induces adipogenesis [29], as well as a suppressor of NF-κB activation [30]. We examined Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes before and after differentiation in the presence and absence of BRL. Correspondent to the level of differentiation, e.g. preadipocytes<adipocytes<BRL-treated adipocytes, NF-κB was activated from 100% in non-differentiated cells to 154% in differentiated, and 230% in BRL-treated adipocytes suggesting moderate activation of NF-κB during adipogenesis (Fig. 2a,b). Consistent with its anti-inflammatory role, in the presence of LPS, BRL significantly suppressed the induction of NF-κB activation caused by LPS in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2c). We also examined the production of a classical NF-κB target MCP-1 [16] in these experiments (Fig. 2c). MCP-1 levels correlated with Nfkb-RE activation in these experiments (Fig. 2c, insert). Thus, Nfkb-RE biosensor detected both adipogenesis- and inflammation-related activation of NF-κB. Given the NF-κB activation in adipocytes we continued to test effects of antioxidants in the differentiated Nfkb-RE adipocytes.
Figure 2. Rosiglitazone regulates NF-κB activity in Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes in LPS-dependent manner.
(a) Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes (ND, white bar) were differentiated for 4d (D, black bar) and stimulated with and without 100nM BRL for 24h (hatched bar). The GFP/mCherry ratio was obtained from total cell lysates in RIPA buffer (Mann Whitney U test, n=3 or 4, mean±SD).
(b) Relative activation of NF-κB in Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes differentiated for 4 days and stimulated with different concentration of BRL. Data are shown as relative activation of NF-κB in Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes (ND, GFP/mCherry ratio 100%) compared to adipocytes treated with BRL (Mann Whitney U test, n=4 or 8, mean±SD)
(c) Relative activation of NF-κB in Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes differentiated for 4d and simultaneously stimulated with different concentration of BRL and 10ng/mL LPS for 24h (dashed line). Data are shown as GFP/mCherry ratios. An asterisk (P<0.01), signifies a significant difference between differentiated Nfkb-RE/GFP stimulated with BRL and LPS vs. LPS-stimulated control (Mann Whitney U test, n=4, mean±SD).
(d) MCP-1 levels in adipocyte treated with and without LPS. Experiments were performed as in b and c. Differentiated for 3d adipocytes were pre-treated for 10 min with BRL, then LPS (10 ng/mL) was added for 24 h. Stimulation media contained 1%FBS. Media and cell lysates were collected for the measurement of MCP-1 protein level by ELISA and Nfkb-RE/GFP/mCherry fluorescence ratio, respectively. Insert shows the correlation between MCP-1 protein levels and Nfkb-RE/GFP fluorescence normalized by mCherry. Pearson correlation test.
3.3 α-MG and γ-MG inhibit adipogenesis and inflammation in Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes
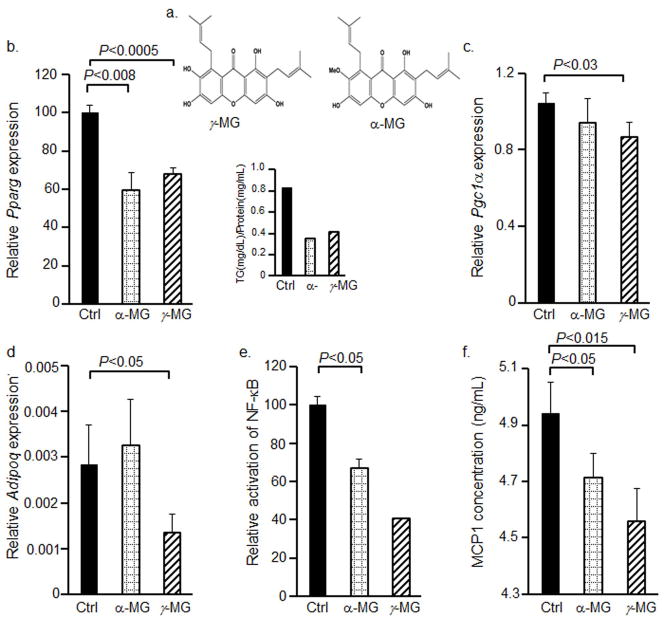
To access whether the sensitivity of Nfkb-RE assay is sufficient to measure anti-inflammatory effects of antioxidants, we selected mangostin xanthones. The structural difference between α-MG and γ-MG is the methoxyl group at the No.7 carbon atom (Fig. 3a). In consonance with previous reports [14, 15], Pparg expression was significantly reduced (by 40%) in the presence of 10μM α-MG in Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes (Fig. 3b). γ-MG also suppressed Pparg expression by 30% compared to control group (Fig. 3b). The ratio of triglyceride to protein concentrations was also correspondently reduced in both α-MG and γ-MG-treated adipocytes (Fig. 3b, insert). However, γ-MG also had specific properties. γ-MG treated adipocytes expressed less Pgc1α and adiponectin (Adipoq) compared to adipocytes treated with α-MG (Fig. 3c,d). Despite of the decrease in anti-inflammatory adiponectin expression, both α-MG and γ-MG suppressed the activation of inflammation to a similar extent. This was indicated by Nfkb-RE activation (Fig. 3e) and validated by the production of MCP-1 (Fig. 3f) from these cells. Mcp1 is an established NF-κB target gene [31]. The concentration of MCP-1 protein in the media was significantly lower in both γ-MG and α-MG-treated cells as compared to vehicle-stimulated Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes. Our results are in agreement with γ-MG and α-MG’s inhibition of adipocytes stimulated by LPS. Although γ-MG showed a potent anti-inflammatory and anti-obesogenic effect, it also reduced adiponectin, a major insulin-sensitizing adipokine in adipocytes [32]. Therefore after the validation of our assays, we applied them for the identification of a potential mechanism for anti-inflammatory and anti-adipogenic effects of α-MG.
Figure 3. α-MG and γ-MG inhibit the levels of Pparg and other adipogenic and inflammatory markers.
(a) The chemical structure of α-MG and γ-MG.
(b–f) Nfkb-RE/GFP preadipocytes were differentiated in P60 dishes (n=4 per each condition) for 7d in differentiation media I and II containing 10μM α-MG and10μM γ-MG replaced every 48h. The mRNA expressions of Pparg (b), Pgc1α (c), and Adipoq (d) were measured in non-stimulated (Ctrl, black bars), α-MG- (dotted grid bars) and γ-MG-stimulated (upward hatched bars) Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes using TaqMan assay (Mann Whitney U test, n=3, mean±SD). Whereas 3 sets of cell were harvested for mRNA, one set was harvested in RIPA buffer for the triglyceride measurements. Triglyceride/protein was measured in duplicate per each condition (b insert).
(e) The GFP/mCherry ratios obtained from total cell lysates in RIPA buffer are shown as relative activation of NF-κB in Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes in standard differentiation media (Ctrl, black bars) (n=5, mean±SEM additional experiments were performed in differentiated cells stimulated with and without 10μM α-MG) differentiation media containing 10μM α-MG (α-MG, dotted grid bars), and differentiation media containing 10μM γ-MG (upward diagonal bars) (same sample as in b, insert).
(f) The protein expression of MCP1 was measured in differentiation media from non-stimulated (Ctrl, black bars), α-MG- (dotted grid bars) and γ-MG-stimulated Nfkb-RE/GFP adipocytes described in (b–f) using ELISA assay (Mann Whitney U test, n=3, mean±SD).
3.4 α-MG inhibits Nrf2 promoter activation in adipocytes
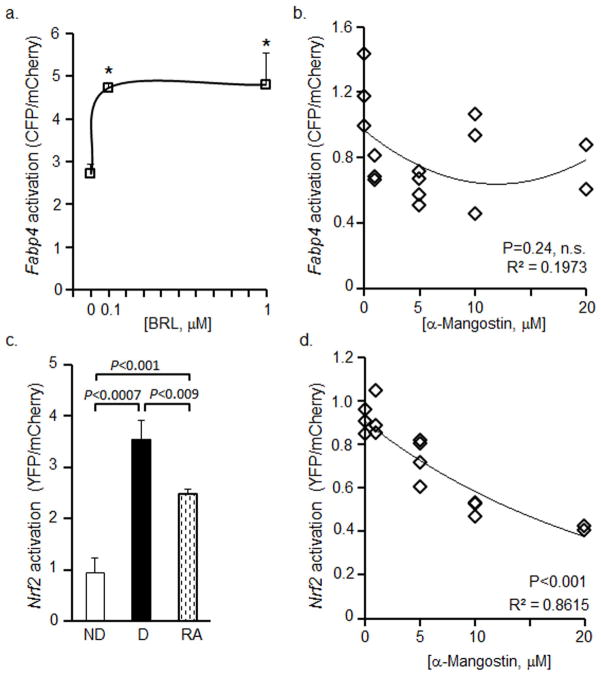
Adipogenesis depends on inductions of Pparg expression and its activity [18]. To test the activity of PPARγ we developed Fabp4-P/CFP adipogenic biosensor cell line using similar approach as with Nfkb-RE/GFP. We validated the sensitivity of Fabp4-P/CFP activation in response to classical synthetic PPARγ ligand BRL. The activation of FABP4 was significantly induced in Fabp4-P/CFP adipocytes in the presence of both 100nM and 1μM BRL (Fig. 4a). In contrast, stimulation of differentiated adipocytes with a range of α-MG (1–20μM) did not influence the activation of FABP4 (Fig. 4b).
Figure 4. α-MG does not regulate the Fabp4 promoter, but inhibits the activation of Nrf2 promoter in adipocytes.
(a) Fabp4-P/CFP preadipocytes were differentiated for 5d and stimulated with different BRL concentration in differentiation media II for 24h. The CFP/mCherry ratio was obtained from total cell lysates in RIPA buffer. Data are shown as CFP/mCherry ratios. An asterisk indicates a significant difference between non-stimulated and BRL-stimulated controls (P<0.01, Mann Whitney U test, n=3 or 4, mean±SD).
(b) Fabp4-P/CFP preadipocytes were differentiated for 8d containing different concentrations of α-MG that were replaced every 48h. Data are shown as CFP/mCherry ratios (Pearson correlation test, n.s.- not significant).
(c) Nrf2-P/YFP preadipocytes (ND, white bars), and preadipocytes were differentiated for 4d. Cells were stimulated with (RA 100nM, diagonal bar) and without RA (D, black bar) in DMEM medium containing 10% CS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin, and 3% UV-treated FBS for 48 h. The YFP/mCherry ratio was measured in total RIPA cell lysates. Data are shown as YFP/mCherry ratios (Mann Whitney U test, n=3, mean±SD).
(d) Nrf2-P/YFP preadipocytes were differentiated for 8d in differentiation media containing different concentrations of α-MG that were replaced every 48h. The YFP/mCherry ratio was obtained from total RIPA cell lysates. Data are shown as YFP/mCherry ratios (Pearson correlation test, P<0.001).
Next we examined transcriptional regulators of Pparg expression, which include an antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 [22]. We developed an additional Nrf2-P/YFP biosensor 3T3-L1 preadipocytes cell line as before. We validated the sensitivity of Nrf2P-YFP activation in response to classical inhibitor of Nrf2 activation, all-trans retinoic acid (RA) [33]. We examined Nrf2-P/YFP cells prior to differentiation and 4 days after differentiation. The activation of Nrf2 was significantly greater 277% in differentiated cells than non-differentiated cells (100%) (Fig. 4c). RA stimulation efficiently suppressed (−30%) the activation of Nrf2 compared to the differentiated Nrf2-P/YFP cells (Fig. 4c). α-MG stimulation of differentiated Nrf2-P/YFP adipocytes resulted in a significant inverse dose-dependent decrease in Nrf2 activation (Fig. 4d). This study supported the role of α-MG in the inhibition of Nrf2.
4 Discussion
Adipocyte differentiation is controlled by redox status, nutrient, endocrine, and genetic factors through a comprehensive network of transcription factors [34]. These converged signals in differentiated adipocytes are responsible for different susceptibility to inflammation, regulated predominantly by the NF-κB pathway [17]. These events are also controlled by the expression and activity of Pparg in response to the redox status in cells [18, 22]. Given the complexity of regulation, we developed three biosensors to study the action of NF-κB during adipogenesis. We anticipated that the combination of Nfkb-RE/GFP, Fabp4-P/CFP, and Nrf2-P/CFP biosensors could provide a high-throughput platform for the screening and discovery of anti-inflammatory and anti-obesogenic nutraceuticals. We validated our assays using an established anti-inflammatory xanthone α-MG and identified its novel mechanism of anti-adipogenic action. α-MG acted as an effective inhibitor of Nrf2 that blocked the expression of Pparg and subsequent adipogenesis and also reducing physiologic inflammatory response in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
We preformed thorough validation of biosensor clones using their known activators and inhibitors and compared these responses to the results obtained with the established methods, such as ELISA and quantitative PCR. An additional examination of biosensor activation during adipogenesis showed results that were consistent with the previously published reports [17, 18, 22]. In our experiments, mature adipocytes, as compared to preadipocytes, had mildly greater activity of NF-κB with or without LPS (Fig. 1b). All mature adipocytes had induced expression of Pparg (Fig. 1a). This biosensor system also detected counteracting processes, where BRL can induce adipogenesis as an agonist of PPARγ but suppress NF-κB [29, 30]. For example in our biosensor assay, BRL induced adipogenesis and, therefore, the activation of NF-κB, but inhibited the LPS-triggered inflammation in adipocytes in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2). Similar validation was undertaken with the Nrf2-P/YFP and Fabp4-P/CFP preadipocytes. The activity of these genes was increased during adipogenesis, where BRL activated Fabp4-P/CFP at concentrations that are known to induce PPARγ activation [29]. In our recent study, we also applied Nfkb-RE/GFP to evaluate inflammatory responses in adipocytes cultured in zinc deficient condition [35]. These results suggest that this Nfkb-RE/GFP and other biosensor preadipocyte lines offer a sensitive semi-quantitative high-throughput approach to assess antioxidant, adipogenesis, and NF-κB-related inflammatory responses.
Recent interest in polyphenolic xanthones, α-MG and γ-MG, arose from their traditional use as an anti-inflammatory remedy in the traditional medicine. Several groups showed that α-MG and γ-MG could also inhibit adipogenesis and inflammation in adipocytes stimulated with LPS [14, 15]. In consonance with these finding, our data showed that Pparg expression was significantly decreased by α-MG and γ-MG (Fig. 3b). The predominant xanthone α-MG appeared to have more beneficial effects in adipogenesis (Fig. 3c,d), because γ-MG treatment reduced the expression of Adipoq and Pgc1a. Indeed, adiponectin is a key regulator in glucose and lipid metabolism and its level declines in obese people [32]. Pgc1a stimulates biogenesis of mitochondria in adipocytes and has other beneficial anti-obesogenic effects in other tissue [36]. Nonetheless, both α-MG and γ-MG effectively suppressed the activation of NF-κB during adipogenesis, which was demonstrated by significantly reduced protein expression of MCP-1 (Fig. 3f). Our data suggested that α-MG and γ-MG could reduce adipogenesis and inflammation via different pathways. In our mechanistic studies we focused on the major xanthone α-MG demonstrating more beneficial effects on transcription of adiponectin than γ-MG in adipogenesis. However, future functional studies need to be performed to evaluate γ-MG effects on glucose metabolism.
The mechanism by which α-MG suppressed adipogenesis was explored using Fabp4-P/CFP and Nrf2-P/YFP biosensors. In Fabp4-P/CFP adipocytes, α-MG did not regulate the Fabp4 promoter, suggesting an indirect role of α-MG in Pparg inhibition (Fig. 4b). Our expression studies also showed that the major mechanism of α-MG-dependent adipogenesis was resulted from the inhibition of Pparg expression (Fig. 3b). Nrf2 is an important inducer of Pparg expression in vitro and in vivo [22]. The Nrf2 deficiency in adipocytes suppressed adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and the development of adipose tissue in the adipose tissue-specific knock out mouse model, where Nrf2 inhibited Pparg expression [22]. We have shown marked concentration-dependent inhibition of adipogenesis by α-MG (Fig. 4d). Our findings suggested that α-MG acted primarily on inhibition of the Nrf2 promoter (Fig. 4d), suppressing adipogenesis and adipogenesis-related NF-kB activation (Fig. 3). In the differentiated adipocytes, Nrf2 may play a different role, because Nrf2 signaling interferes with the NF-κB signaling pathway [23]. Nrf2 plays an important role in the plethora of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer and obesity [37, 38]. These diseases are associated with either constitutive Nrf2 activation or its suppression. Although more studies are needed to determine the specific site of α-MG-dependent regulation of Nrf2, this xanthone could be a potential nutraceutical for the treatment of disorders associated with constitutive Nrf2 activation. Thus, combined biosensor assay platform provides an opportunity for efficient screening of nutrients and their functions in inflammation and adipogenesis.
Figure 5. Hypothetical mechanism for α-MG effects in adipogenesis.
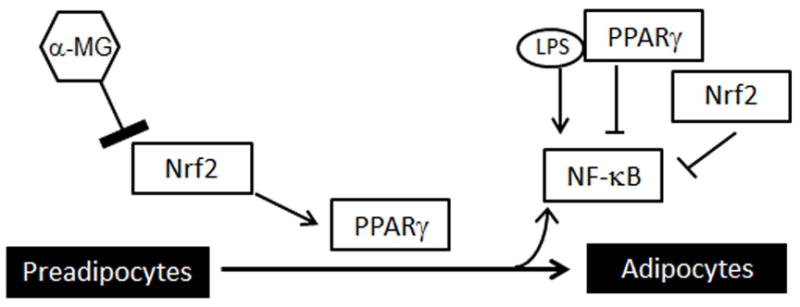
α-MG suppressed promoter activity in Nrf2. The deficient Nrf2 activity inhibits the expression of Pparg and differentiation in adipocytes. Inhibition of adipogenesis results in reduced activation of NF-κB.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the Nucleic Acid Shared Resource at The Ohio State University (OSU) for excellent technical and intellectual support. This research was supported by the Food Innovation Center, Office for International Affairs and Center for Advanced Functional Foods Research and Entrepreneurship at OSU, and Daskal Foundation (O.Z., Q. S., L.G., D.D.). The project described was supported by Award Number UL1RR025755 (O.Z.) from the National Center for Research Resources, funded by the Office of the Director, National Institutes of Health (OD) and supported by the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Abbreviations
- α-MG
α-mangostin
- BRL
rosiglitazone
- CFP
cyan fluorescent protein
- Fabp4-P
fatty acid binding protein 4 promoter
- γ-MG
γ-mangostin
- GFP
green fluorescent protein
- MCP1
monocyte chemotactic protein-1
- Nfkb-RE
nuclear factor κB response element
- Nrf2-P
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor promoter
- PPARγ
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- RA
retinoic acid
- YFP
yellow fluorescent protein
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Berghofer A, Pischon T, Reinhold T, Apovian CM, Sharma AM, et al. Obesity prevalence from a European perspective: a systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:200. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baker RG, Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-kappaB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 2011;13:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:2548–2556. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:579–591. doi: 10.1038/nrc1408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2005;96:939–949. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000163635.62927.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wisse BE. The inflammatory syndrome: the role of adipose tissue cytokines in metabolic disorders linked to obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:2792–2800. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000141966.69934.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sartipy P, Loskutoff DJ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in obesity and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:7265–7270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1133870100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dahlman I, Kaaman M, Olsson T, Tan GD, Bickerton AS, et al. A unique role of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 among chemokines in adipose tissue of obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:5834–5840. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-0369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kanda H, Tateya S, Tamori Y, Kotani K, Hiasa K, et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1494–1505. doi: 10.1172/JCI26498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhao J. Nutraceuticals, nutritional therapy, phytonutrients, and phytotherapy for improvement of human health: a perspective on plant biotechnology application. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2007;1:75–97. doi: 10.2174/187220807779813893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Obolskiy D, Pischel I, Siriwatanametanon N, Heinrich M. Garcinia mangostana L. : a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother Res. 2009;23:1047–1065. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wilawan Mahabusarakam PW, Taylor Walter C. Chemical Constituents of Garcinia mangostana. Journal of Natural Products. 1987;50:474–478. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Quan X, Wang Y, Ma X, Liang Y, Tian W, et al. alpha-Mangostin induces apoptosis and suppresses differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells via inhibiting fatty acid synthase. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bumrungpert A, Kalpravidh RW, Chitchumroonchokchai C, Chuang CC, West T, et al. Xanthones from mangosteen prevent lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in primary cultures of human adipocytes. J Nutr. 2009;139:1185–1191. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.106617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pamukcu B, Lip GY, Shantsila E. The nuclear factor--kappa B pathway in atherosclerosis: a potential therapeutic target for atherothrombotic vascular disease. Thromb Res. 2011;128:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Berg AH, Lin Y, Lisanti MP, Scherer PE. Adipocyte differentiation induces dynamic changes in NF-kappaB expression and activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;287:E1178–1188. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00002.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM. PPARgamma : a nuclear regulator of metabolism, differentiation, and cell growth. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:37731–37734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100034200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lefterova MI, Zhang Y, Steger DJ, Schupp M, Schug J, et al. PPARgamma and C/EBP factors orchestrate adipocyte biology via adjacent binding on a genome-wide scale. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2941–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.1709008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen F, Wang M, O’Connor JP, He M, Tripathi T, et al. Phosphorylation of PPARgamma via active ERK1/2 leads to its physical association with p65 and inhibition of NF-kappabeta. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:732–744. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tang T, Zhang J, Yin J, Staszkiewicz J, Gawronska-Kozak B, et al. Uncoupling of inflammation and insulin resistance by NF-kappaB in transgenic mice through elevated energy expenditure. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:4637–4644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pi J, Leung L, Xue P, Wang W, Hou Y, et al. Deficiency in the nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 transcription factor results in impaired adipogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:9292–9300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.093955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li W, Khor TO, Xu C, Shen G, Jeong WS, et al. Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76:1485–1489. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tontonoz P, Spiegelman BM. Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:289–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.061307.091829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chaivisuthangkura A, Malaikaew Y, Chaovanalikit A, Jaratrungtawee A, Panseeta P, Rataananukul P, Suksumrarm S. Prenylated Xanthone Composition of Garcinia mangostana (Mangosteen) Fruit Hull. Chromatographia. 2009;69:315–318. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Green H, Meuth M. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell. 1974;3:127–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yasmeen R, Reichert B, Deiuliis J, Yang F, Lynch A, et al. Autocrine function of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 as a determinant of diet- and sex-specific differences in visceral adiposity. Diabetes. 2013;62:124–136. doi: 10.2337/db11-1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Celec P. Nuclear factor kappa B--molecular biomedicine: the next generation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004;58:365–371. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2003.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Camp HS, Li O, Wise SC, Hong YH, Frankowski CL, et al. Differential activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by troglitazone and rosiglitazone. Diabetes. 2000;49:539–547. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mao JW, Tang HY, Wang YD. Influence of Rosiglitazone on the Expression of PPARgamma, NF-kappaB, and TNF-alpha in Rat Model of Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:845672. doi: 10.1155/2012/845672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ferrante AW., Jr Obesity-induced inflammation: a metabolic dialogue in the language of inflammation. J Intern Med. 2007;262:408–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hajer GR, van der Graaf Y, Olijhoek JK, Edlinger M, Visseren FL. Low plasma levels of adiponectin are associated with low risk for future cardiovascular events in patients with clinical evident vascular disease. Am Heart J. 2007;154:750, e751–757. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2007.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang XJ, Hayes JD, Henderson CJ, Wolf CR. Identification of retinoic acid as an inhibitor of transcription factor Nrf2 through activation of retinoic acid receptor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:19589–19594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709483104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yasmeen R, Jeyakumar SM, Reichert B, Yang F, Ziouzenkova O. The contribution of vitamin A to autocrine regulation of fat depots. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1821:190–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu MJ, Bao S, Bolin ER, Burris DL, Xu X, et al. Zinc Deficiency Augments Leptin Production and Exacerbates Macrophage Infiltration into Adipose Tissue in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J Nutr. 2013 doi: 10.3945/jn.113.175158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Medina-Gomez G, Gray S, Vidal-Puig A. Adipogenesis and lipotoxicity: role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and PPARgammacoactivator-1 (PGC1) Public Health Nutr. 2007;10:1132–1137. doi: 10.1017/S1368980007000614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Singh S, Vrishni S, Singh BK, Rahman I, Kakkar P. Nrf2-ARE stress response mechanism: a control point in oxidative stress-mediated dysfunctions and chronic inflammatory diseases. Free Radic Res. 2010;44:1267–1288. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2010.507670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schneider KS, Chan JY. Emerging role of nrf2 in adipocytes and adipose biology. Adv Nutr. 2013;4:62–66. doi: 10.3945/an.112.003103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]