Abstract
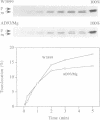
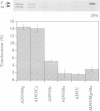
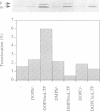
The construction of a mutant Escherichia coli strain which cannot synthesize phosphatidylethanolamine provides a tool to study the involvement of non-bilayer lipids in membrane function. This strain produces phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin (CL) as major membrane constituents and requires millimolar concentrations of divalent cations for growth. In this strain, the lipid phase behaviour is tightly regulated by adjustment of the level of CL which favours a nonbilayer organization in the presence of specific divalent cations. We have used an in vitro system of inverted membrane vesicles to study the involvement of non-bilayer lipids in protein translocation in the secretion pathway. In this system, protein translocation is very low in the absence of divalent cations but can be enhanced by inclusion of Mg2+, Ca2+ or Sr2+ but not by Ba2+ which is unable to sustain growth of the mutant strain and cannot induce a non-bilayer phase in E. coli CL dispersions. Alternatively, translocation in cation depleted vesicles could be increased by incorporation of the non-bilayer lipid DOPE (18:1) but not by DMPE (14:0) or DOPC (18:1), both of which are bilayer lipids under physiological conditions. We conclude that non-bilayer lipids are essential for efficient protein transport across the plasma membrane of E. coli.
Full text
PDF
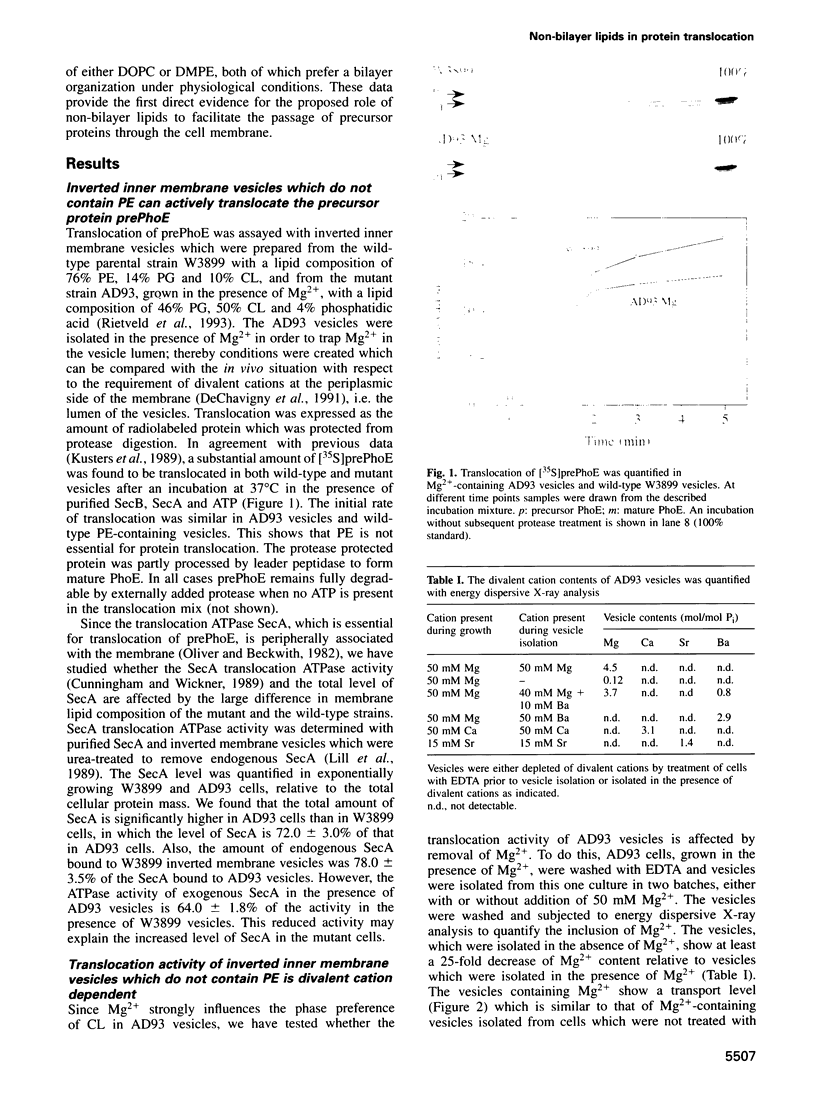




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apell H. J., Bersch B. Oxonol VI as an optical indicator for membrane potentials in lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 16;903(3):480–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkowitz R. A., Bassilana M. Protein translocation in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 9;1197(3):311–343. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
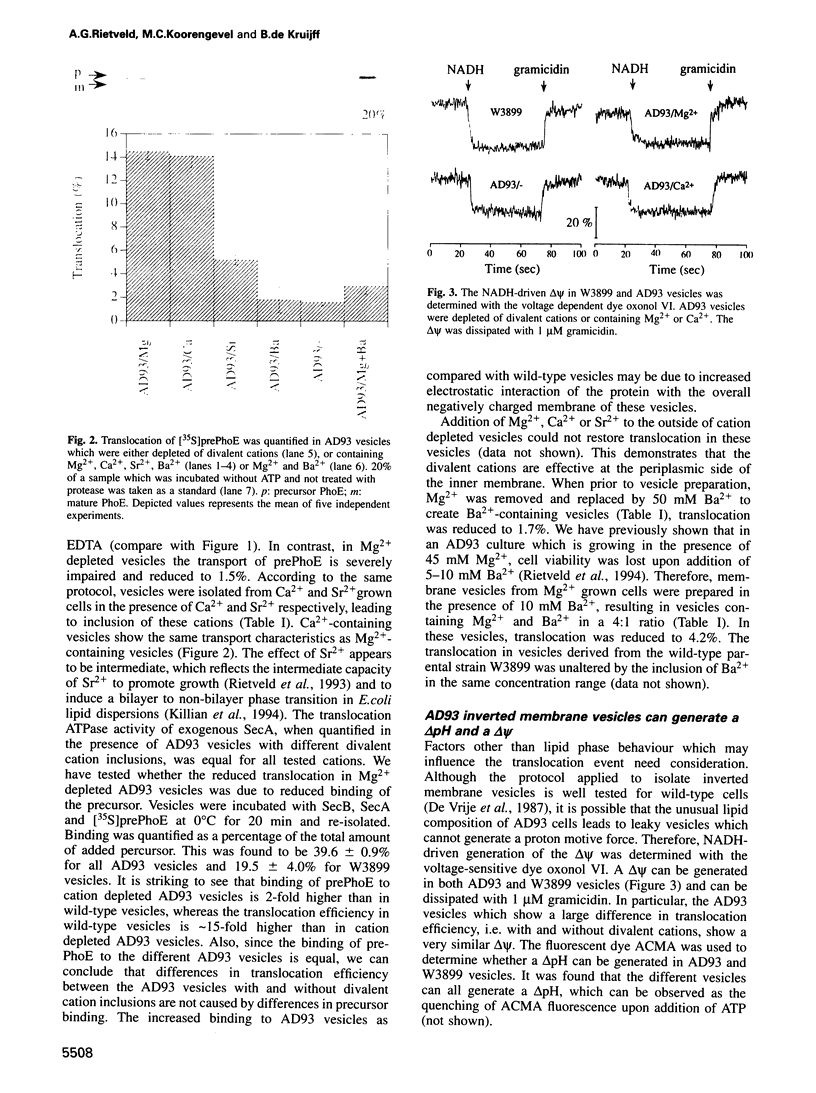
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg A. M., Demel R. A., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Penetration of the signal sequence of Escherichia coli PhoE protein into phospholipid model membranes leads to lipid-specific changes in signal peptide structure and alterations of lipid organization. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5678–5685. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breukink E., Demel R. A., de Korte-Kool G., de Kruijff B. SecA insertion into phospholipids is stimulated by negatively charged lipids and inhibited by ATP: a monolayer study. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 4;31(4):1119–1124. doi: 10.1021/bi00119a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. The enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine and purification by CM-cellulose column chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 20;488(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. The polymorphic phase behaviour of phosphatidylethanolamines of natural and synthetic origin. A 31P NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Lill R., Crooke E., Rice M., Moore K., Wickner W., Oliver D. SecA protein, a peripheral protein of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane, is essential for the functional binding and translocation of proOmpA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):955–959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham K., Wickner W. Specific recognition of the leader region of precursor proteins is required for the activation of translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8630–8634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vrije T., Tommassen J., De Kruijff B. Optimal posttranslational translocation of the precursor of PhoE protein across Escherichia coli membrane vesicles requires both ATP and the protonmotive force. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChavigny A., Heacock P. N., Dowhan W. Sequence and inactivation of the pss gene of Escherichia coli. Phosphatidylethanolamine may not be essential for cell viability. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5323–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
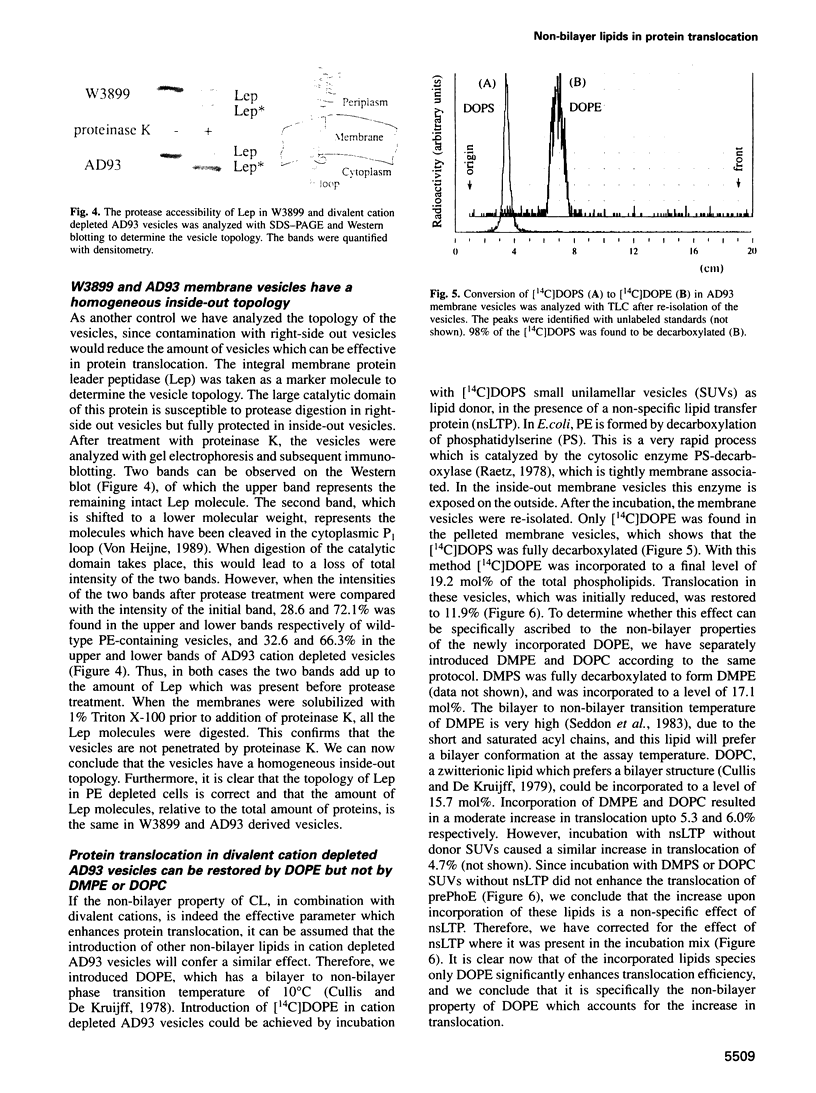
- Demel R. A., Goormaghtigh E., de Kruijff B. Lipid and peptide specificities in signal peptide--lipid interactions in model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 24;1027(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. B., Sprecher H. Unidimensional thin-layer chromatography of phospholipids on boric acid-impregnated plates. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):660–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller B. L., Movva N. R., Wickner W. Both ATP and the electrochemical potential are required for optimal assembly of pro-OmpA into Escherichia coli inner membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4219–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Wickner W. SecA protein needs both acidic phospholipids and SecY/E protein for functional high-affinity binding to the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24596–24600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. L., Bezrukov S. M., Gruner S. M., Tate M. W., Vodyanoy I., Parsegian V. A. Probability of alamethicin conductance states varies with nonlamellar tendency of bilayer phospholipids. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81040-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., Fabrie C. H., Baart W., Morein S., de Kruijff B. Effects of temperature variation and phenethyl alcohol addition on acyl chain order and lipid organization in Escherichia coli derived membrane systems. A 2H- and 31P-NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 13;1105(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90202-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., Keller R. C., Struyvé M., de Kroon A. I., Tommassen J., de Kruijff B. Tryptophan fluorescence study on the interaction of the signal peptide of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein PhoE with model membranes. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8131–8137. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., Koorengevel M. C., Bouwstra J. A., Gooris G., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Effect of divalent cations on lipid organization of cardiolipin isolated from Escherichia coli strain AH930. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 19;1189(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., de Jong A. M., Bijvelt J., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Induction of non-bilayer lipid structures by functional signal peptides. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):815–819. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Rajapandi T., Oliver D. SecA protein is exposed to the periplasmic surface of the E. coli inner membrane in its active state. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):845–853. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90602-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klionsky D. J., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. In vivo evidence for the role of the epsilon subunit as an inhibitor of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1055–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1055-1060.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters R., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Negatively charged phospholipids restore prePhoE translocation across phosphatidylglycerol-depleted Escherichia coli inner membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8659–8662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters R., Huijbregts R., de Kruijff B. Elevated cytosolic concentrations of SecA compensate for a protein translocation defect in Escherichia coli cells with reduced levels of negatively charged phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 10;308(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81060-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusters R., de Vrije T., Breukink E., de Kruijff B. SecB protein stabilizes a translocation-competent state of purified prePhoE protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20827–20830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecker S., Lill R., Ziegelhoffer T., Georgopoulos C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Kumamoto C. A., Wickner W. Three pure chaperone proteins of Escherichia coli--SecB, trigger factor and GroEL--form soluble complexes with precursor proteins in vitro. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2703–2709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Cunningham K., Brundage L. A., Ito K., Oliver D., Wickner W. SecA protein hydrolyzes ATP and is an essential component of the protein translocation ATPase of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill R., Dowhan W., Wickner W. The ATPase activity of SecA is regulated by acidic phospholipids, SecY, and the leader and mature domains of precursor proteins. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90742-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martoglio B., Hofmann M. W., Brunner J., Dobberstein B. The protein-conducting channel in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum is open laterally toward the lipid bilayer. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mileykovskaya E. I., Dowhan W. Alterations in the electron transfer chain in mutant strains of Escherichia coli lacking phosphatidylethanolamine. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24824–24831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. In vitro translocation of bacterial proteins across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7421–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Toivio-Kinnucan M., Racker E. Effect of lipid composition on the calcium/adenosine 5'-triphosphate coupling ratio of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):130–135. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesmeyanova M. A. On the possible participation of acid phospholipids in the translocation of secreted proteins through the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 7;142(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phoenix D. A., Kusters R., Hikita C., Mizushima S., de Kruijff B. OmpF-Lpp signal sequence mutants with varying charge hydrophobicity ratios provide evidence for a phosphatidylglycerol-signal sequence interaction during protein translocation across the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17069–17073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phoenix D. A., de Wolf F. A., Rutger, Staffhorst W. H., Hikita C., Mizushima S., de Kruijff B. Phosphatidylglycerol dependent protein translocation across the Escherichia coli inner membrane is inhibited by the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin. Evidence for an electrostatic interaction between the signal sequence and phosphatidylglycerol. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 7;324(1):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogliano J. A., Beckwith J. SecD and SecF facilitate protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):554–561. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorthuis B. J., Wirtz K. W. Nonspecific lipid transfer protein from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:592–596. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The complete general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):50–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.50-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Enzymology, genetics, and regulation of membrane phospholipid synthesis in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Sep;42(3):614–659. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.3.614-659.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld A. G., Chupin V. V., Koorengevel M. C., Wienk H. L., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Regulation of lipid polymorphism is essential for the viability of phosphatidylethanolamine-deficient Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28670–28675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld A. G., Killian J. A., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Polymorphic regulation of membrane phospholipid composition in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12427–12433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Cevc G., Marsh D. Calorimetric studies of the gel-fluid (L beta-L alpha) and lamellar-inverted hexagonal (L alpha-HII) phase transitions in dialkyl- and diacylphosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Blobel G. A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani K., Shiozuka K., Tokuda H., Mizushima S. In vitro analysis of the process of translocation of OmpA across the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. A translocation intermediate accumulates transiently in the absence of the proton motive force. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18582–18588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko I., De Kruijff B., Verkleij A. J. Polymorphic phase behaviour of cardiolipin from bovine heart and from Bacillus subtilis as detected by 31P-NMR and freeze-fracture techniques. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+ and temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 22;684(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B. Polymorphic regulation of membrane lipid composition. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):587–588. doi: 10.1038/329587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vrije T., de Swart R. L., Dowhan W., Tommassen J., de Kruijff B. Phosphatidylglycerol is involved in protein translocation across Escherichia coli inner membranes. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):173–175. doi: 10.1038/334173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):456–458. doi: 10.1038/341456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]