Abstract
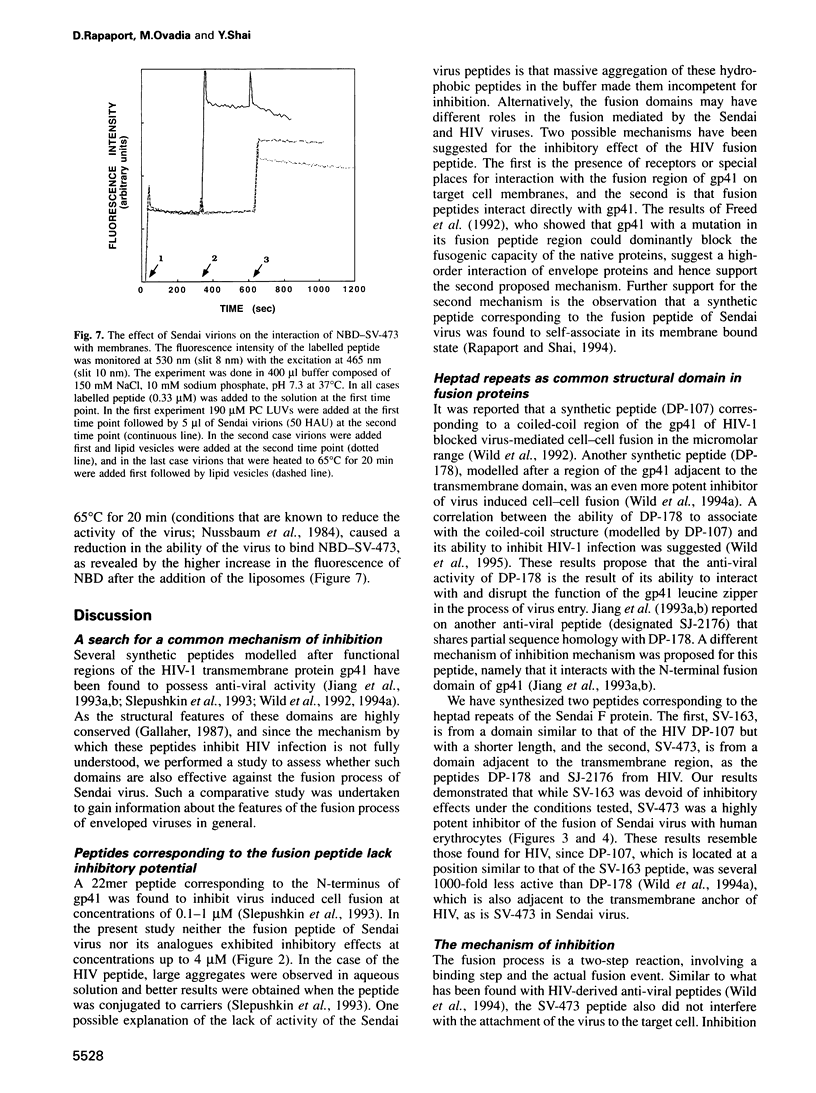
A series of peptides derived from three domains within the fusion protein of Sendai virus was synthesized and examined for their potential to inhibit the fusion of the virus with human red blood cells. These domains include the 'fusion peptide' and two heptad repeats, one adjacent to the fusion peptide (SV-163) and the other to the transmembrane domain (SV-473). Of all the peptides tested, only SV-473 was highly inhibitive. Using fluorescently-labelled peptides, the mechanism through which the SV-473 peptide inhibits the haemolytic activity of the virus was investigated. The results suggest that interactions of the active peptide with virion elements and lipid membranes are involved. Since it has recently been found that synthetic peptides corresponding to putative coiled-coil domains of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 transmembrane protein gp41 are potent inhibitors of HIV, we discuss the general property of virus-derived coiled-coil peptides as inhibitors of viral infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Rose K., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus fusion protein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):317–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkow G., Ovadia M. Inhibition of Sendai virus by various snake venom. Life Sci. 1992;51(16):1261–1267. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90015-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch M. L., Earl P. L., Fargnoli K., Picciafuoco S., Giombini F., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G. Identification of the fusion peptide of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.2541505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R., Malvoisin E., Beauverger P., Wild F. A leucine zipper structure present in the measles virus fusion protein is not required for its tetramerization but is essential for fusion. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1703–1707. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough P. A., Hughson F. M., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):37–43. doi: 10.1038/371037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. M., Kim P. S. A spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Pringle C. R., Easton A. J. Sequence analysis of the gene encoding the fusion glycoprotein of pneumonia virus of mice suggests possible conserved secondary structure elements in paramyxovirus fusion glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1717–1724. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay A., London E. Parallax method for direct measurement of membrane penetration depth utilizing fluorescence quenching by spin-labeled phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):39–45. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Delwart E. L., Buchschacher G. L., Jr, Panganiban A. T. A mutation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein gp41 dominantly interferes with fusion and infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):70–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Myers D. J., Risser R. Characterization of the fusion domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein gp41. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey S., Tamm L. K. Membrane insertion and lateral diffusion of fluorescence-labelled cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV signal peptide in charged and uncharged phospholipid bilayers. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):713–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2720713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit E., Bach D., Kerr I. D., Sansom M. S., Chejanovsky N., Shai Y. The alpha-5 segment of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin: in vitro activity, ion channel formation and molecular modelling. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 15;304(Pt 3):895–902. doi: 10.1042/bj3040895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Doms R. W., York D., White J. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: site-specific mutagenesis of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Klappe K. Sendai virus-erythrocyte membrane interaction: quantitative and kinetic analysis of viral binding, dissociation, and fusion. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):87–95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.87-95.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Membrane fusion of enveloped viruses: especially a matter of proteins. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Apr;22(2):121–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00762943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. M., Lamb R. A. Studies on the fusion peptide of a paramyxovirus fusion glycoprotein: roles of conserved residues in cell fusion. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2443–2455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2443-2455.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S., Lin K., Strick N., Neurath A. R. HIV-1 inhibition by a peptide. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):113–113. doi: 10.1038/365113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S., Lin K., Strick N., Neurath A. R. Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by a fusion domain binding peptide from the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein GP41. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Sep 15;195(2):533–538. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., Danieli T., White J. M. Lipid-anchored influenza hemagglutinin promotes hemifusion, not complete fusion. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A. Paramyxovirus fusion: a hypothesis for changes. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):1–11. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehete P. N., Arlinghaus R. B., Sastry K. J. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and syncytium formation in human cells by V3 loop synthetic peptides from gp120. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6841–6846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6841-6846.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick S. L., Hoekstra D. Membrane penetration of Sendai virus glycoproteins during the early stages of fusion with liposomes as determined by hydrophobic photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7433–7437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum O., Zakai N., Loyter A. Membrane-bound antiviral antibodies as receptors for Sendai virions in receptor-depleted erythrocytes. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):185–197. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peretz H., Toister Z., Laster Y., Loyter A. Fusion of intact human erythrocytes and erythrocyte ghosts. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):1–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouny Y., Rapaport D., Mor A., Nicolas P., Shai Y. Interaction of antimicrobial dermaseptin and its fluorescently labeled analogues with phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12416–12423. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport D., Shai Y. Interaction of fluorescently labeled analogues of the amino-terminal fusion peptide of Sendai virus with phospholipid membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15124–15131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport D., Shai Y. Interaction of fluorescently labeled pardaxin and its analogues with lipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23769–23775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Studies with cross-linking reagents on the oligomeric form of the paramyxovirus fusion protein. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):160–168. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergel-Germano T., McQuain C., Morrison T. Mutations in the fusion peptide and heptad repeat regions of the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein block fusion. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7654–7658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7654-7658.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai Y., Bach D., Yanovsky A. Channel formation properties of synthetic pardaxin and analogues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20202–20209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepushkin V. A., Kornilaeva G. V., Andreev S. M., Sidorova M. V., Petrukhina A. O., Matsevich G. R., Raduk S. V., Grigoriev V. B., Makarova T. V., Lukashov V. V. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) penetration into target cells by synthetic peptides mimicking the N-terminus of the HIV-1 transmembrane glycoprotein. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):294–301. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Nir S., Wilschut J. Membrane fusion activity of influenza virus. Effects of gangliosides and negatively charged phospholipids in target liposomes. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1698–1704. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C. T., Shugars D. C., Greenwell T. K., McDanal C. B., Matthews T. J. Peptides corresponding to a predictive alpha-helical domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 are potent inhibitors of virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9770–9774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C., Dubay J. W., Greenwell T., Baird T., Jr, Oas T. G., McDanal C., Hunter E., Matthews T. Propensity for a leucine zipper-like domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 to form oligomers correlates with a role in virus-induced fusion rather than assembly of the glycoprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12676–12680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C., Greenwell T., Shugars D., Rimsky-Clarke L., Matthews T. The inhibitory activity of an HIV type 1 peptide correlates with its ability to interact with a leucine zipper structure. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995 Mar;11(3):323–325. doi: 10.1089/aid.1995.11.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild C., Oas T., McDanal C., Bolognesi D., Matthews T. A synthetic peptide inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus replication: correlation between solution structure and viral inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10537–10541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. G., King D. S., Shin Y. K. Insertion of a coiled-coil peptide from influenza virus hemagglutinin into membranes. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):274–276. doi: 10.1126/science.7939662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]