Abstract
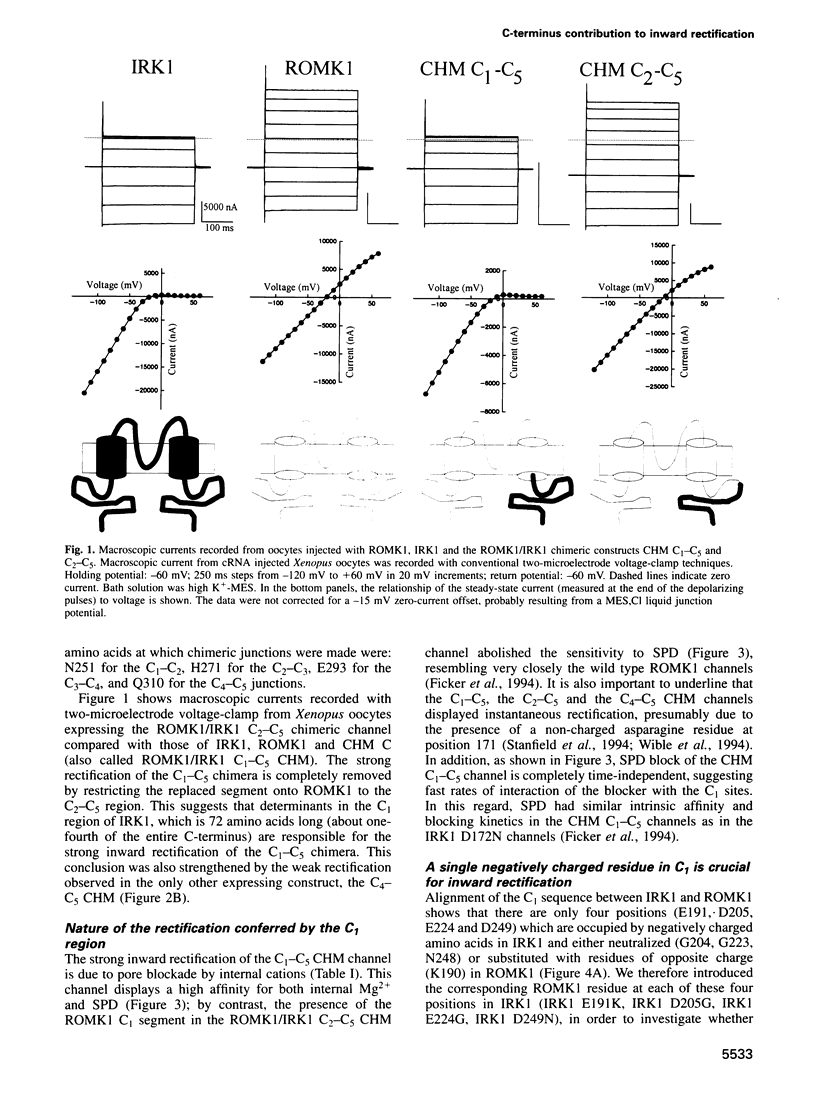
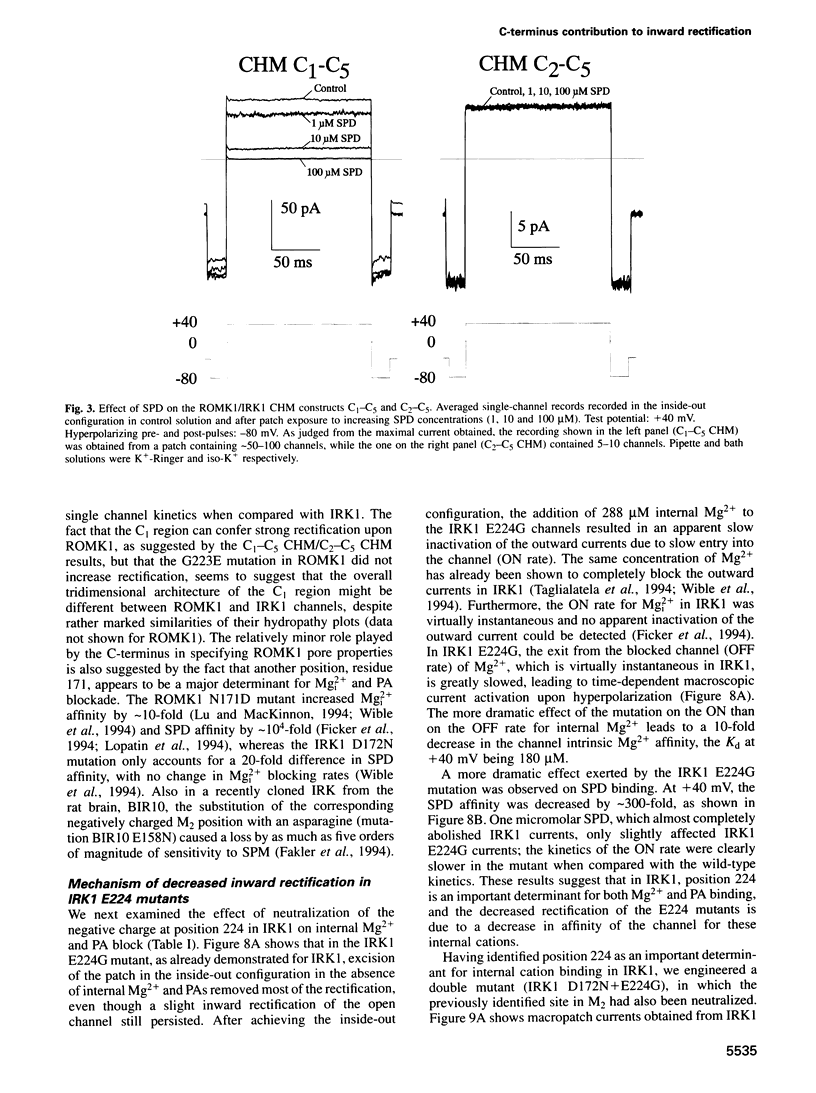
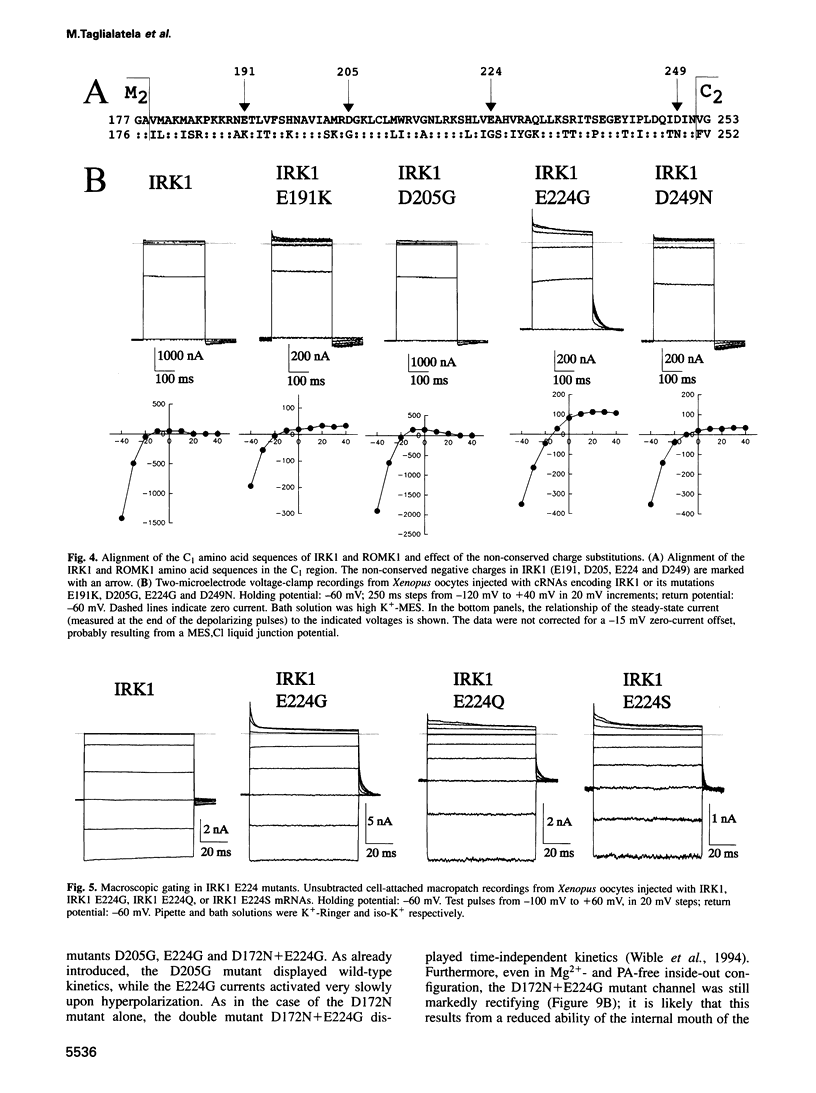
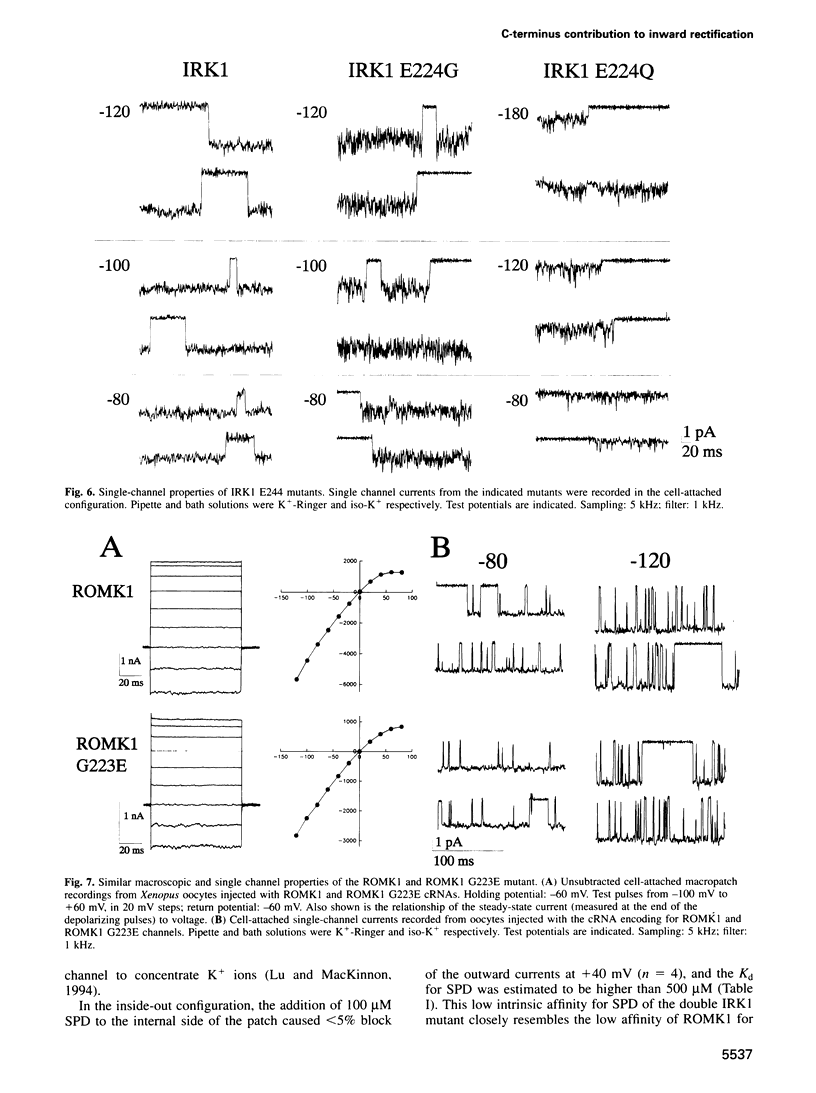
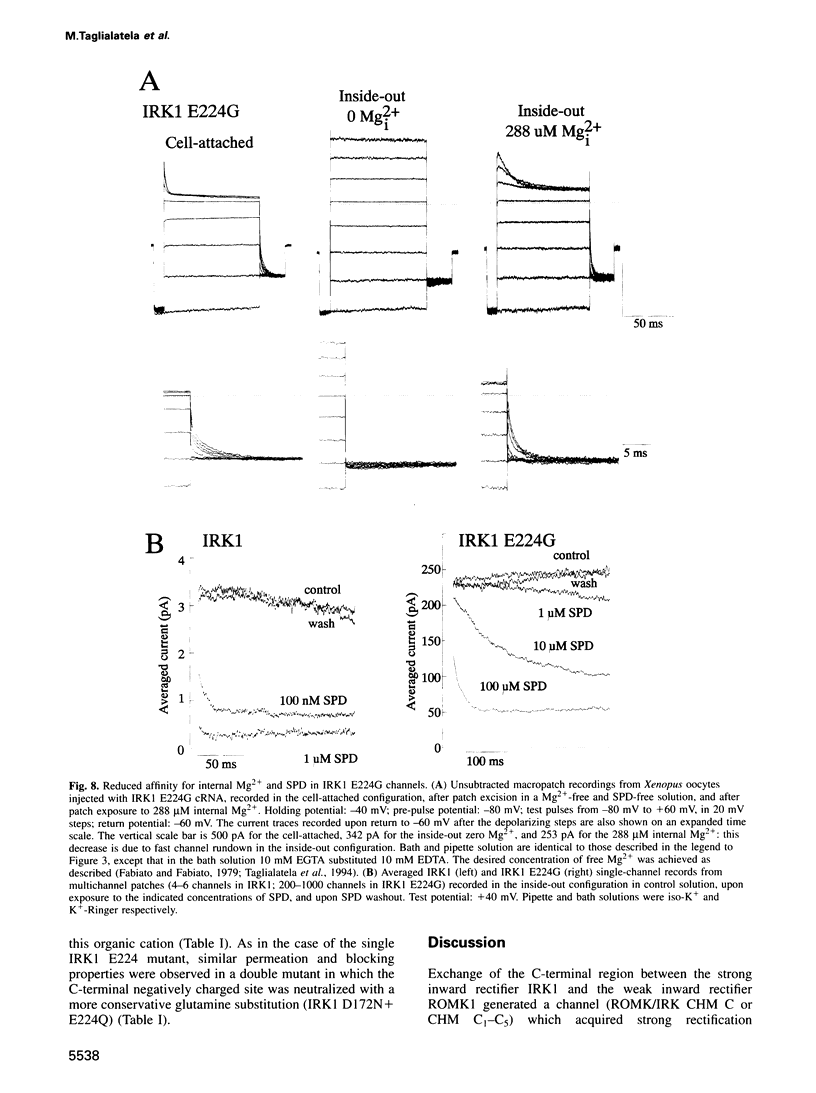
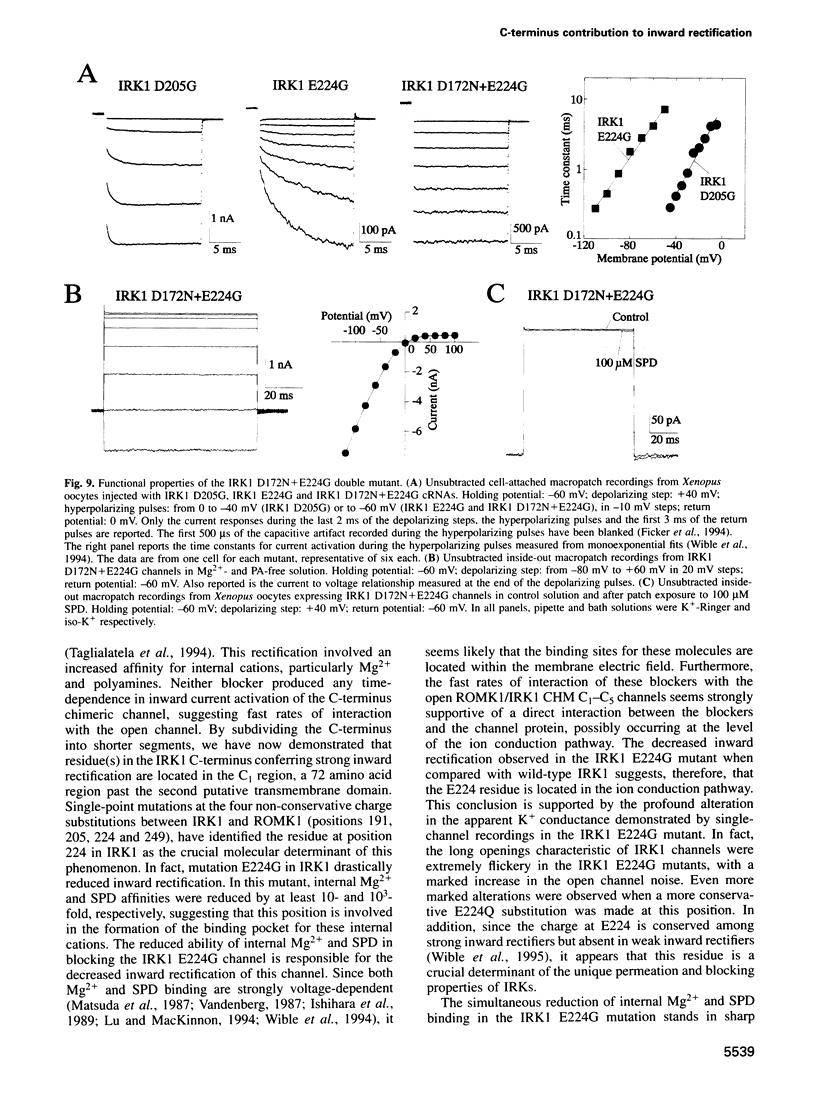
Critical loci for ion conduction in inward rectifier K+ channels are only now being discovered. The C-terminal region of IRK1 plays a crucial role in Mg2+i blockade and single-channel K+ conductance. A negatively charged aspartate in the putative second transmembrane domain (position 172) is essential for time-dependent block by the cytoplasmic polyamines spermine and spermidine. We have now localized the C-terminus effect in IRK1 to a single, negatively charged residue (E224). Mutation of E224 to G, Q and S drastically reduced rectification. Furthermore, the IRK1 E224G mutation decreased block by Mg2+i and spermidine and, like the E224Q mutation, caused a dramatic reduction in the apparent single-channel K+ conductance. The double mutation IRK1 D172N+ E224G was markedly insensitive to spermidine block, displaying an affinity similar to ROMK1. The results are compatible with a model in which the negatively charged residue at position 224, E224, is a major determinant of pore properties in IRK1. By means of a specific interaction with the negatively charged residue at position 172, D172, E224 contributes to the formation of the binding pocket for Mg2+ and polyamines, a characteristic of strong inward rectifiers.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dascal N., Schreibmayer W., Lim N. F., Wang W., Chavkin C., DiMagno L., Labarca C., Kieffer B. L., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Trollinger D. Atrial G protein-activated K+ channel: expression cloning and molecular properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10235–10239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Bond C., Glowatzki E., König C., Adelman J. P., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. A structural determinant of differential sensitivity of cloned inward rectifier K+ channels to intracellular spermine. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakler B., Brändle U., Glowatzki E., Weidemann S., Zenner H. P., Ruppersberg J. P. Strong voltage-dependent inward rectification of inward rectifier K+ channels is caused by intracellular spermine. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90459-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficker E., Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Henley C. M., Brown A. M. Spermine and spermidine as gating molecules for inward rectifier K+ channels. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1068–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7973666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W. Giant excised cardiac sarcolemmal membrane patches: sodium and sodium-calcium exchange currents. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Nov;415(2):247–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00370601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara K., Mitsuiye T., Noma A., Takano M. The Mg2+ block and intrinsic gating underlying inward rectification of the K+ current in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:297–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., DeBiasi M., Hartmann H. A., Brown A. M. A single nonpolar residue in the deep pore of related K+ channels acts as a K+:Rb+ conductance switch. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):136–144. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81800-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Baldwin T. J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):127–133. doi: 10.1038/362127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin A. N., Makhina E. N., Nichols C. G. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):366–369. doi: 10.1038/372366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., MacKinnon R. Electrostatic tuning of Mg2+ affinity in an inward-rectifier K+ channel. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):243–246. doi: 10.1038/371243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Saigusa A., Irisawa H. Ohmic conductance through the inwardly rectifying K channel and blocking by internal Mg2+. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):156–159. doi: 10.1038/325156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. R., DeCoursey T. E. Intrinsic gating of inward rectifier in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells in the presence or absence of internal Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jul;96(1):109–133. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Caporaso R., Brown A. M. Specification of pore properties by the carboxyl terminus of inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Science. 1994 May 6;264(5160):844–847. doi: 10.1126/science.8171340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A. Inward rectification of a potassium channel in cardiac ventricular cells depends on internal magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wible B. A., De Biasi M., Majumder K., Taglialatela M., Brown A. M. Cloning and functional expression of an inwardly rectifying K+ channel from human atrium. Circ Res. 1995 Mar;76(3):343–350. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wible B. A., Taglialatela M., Ficker E., Brown A. M. Gating of inwardly rectifying K+ channels localized to a single negatively charged residue. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):246–249. doi: 10.1038/371246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Control of rectification and permeation by residues in two distinct domains in an inward rectifier K+ channel. Neuron. 1995 May;14(5):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



