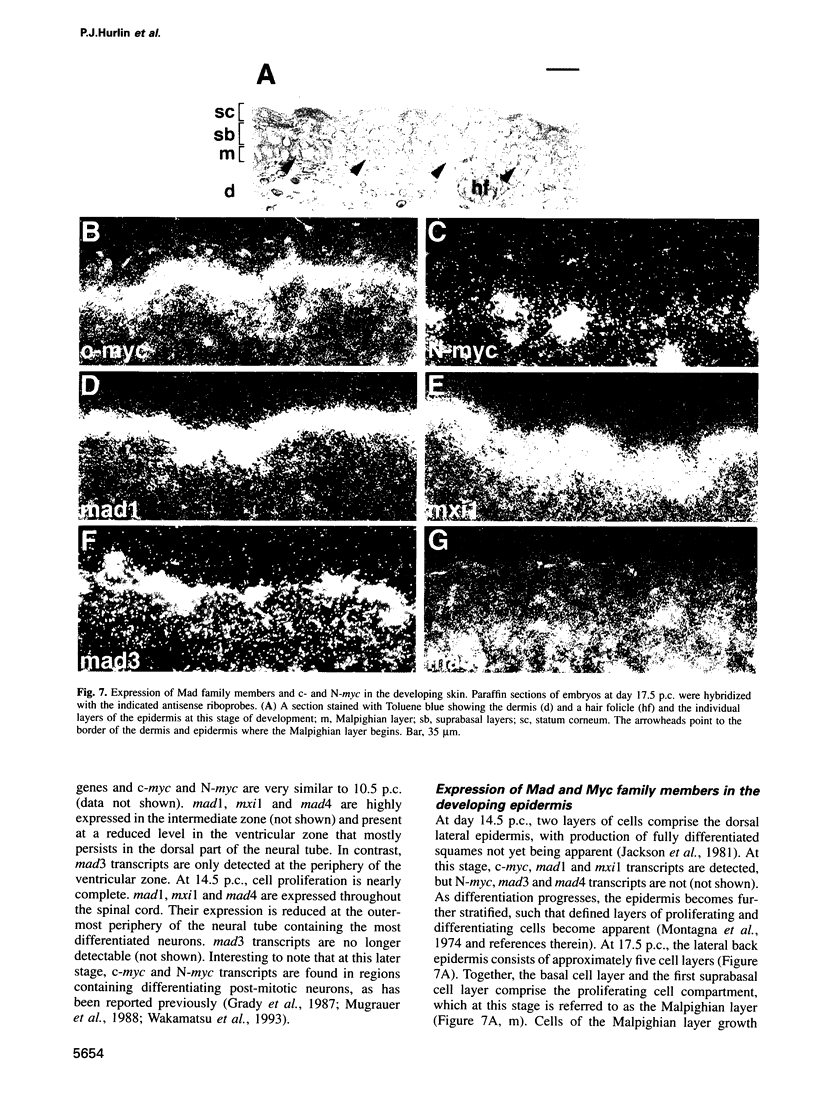
Abstract
The basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper (bHLHZip) protein Max associates with members of the Myc family, as well as with the related proteins Mad (Mad1) and Mxi1. Whereas both Myc:Max and Mad:Max heterodimers bind related E-box sequences, Myc:Max activates transcription and promotes proliferation while Mad:Max represses transcription and suppresses Myc dependent transformation. Here we report the identification and characterization of two novel Mad1- and Mxi1-related proteins, Mad3 and Mad4. Mad3 and Mad4 interact with both Max and mSin3 and repress transcription from a promoter containing CACGTG binding sites. Using a rat embryo fibroblast transformation assay, we show that both Mad3 and Mad4 inhibit c-Myc dependent cell transformation. An examination of the expression patterns of all mad genes during murine embryogenesis reveals that mad1, mad3 and mad4 are expressed primarily in growth-arrested differentiating cells. mxi1 is also expressed in differentiating cells, but is co-expressed with either c-myc, N-myc, or both in proliferating cells of the developing central nervous system and the epidermis. In the developing central nervous system and epidermis, downregulation of myc genes occurs concomitant with upregulation of mad family genes. These expression patterns, together with the demonstrated ability of Mad family proteins to interfere with the proliferation promoting activities of Myc, suggest that the regulated expression of Myc and Mad family proteins function in a concerted fashion to regulate cell growth in differentiating tissues.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Brooks M. W., Levy N., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Oncogenic activity of the c-Myc protein requires dimerization with Max. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90663-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Dalton S., Brooks M. W., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. Transcriptional activation by the human c-Myc oncoprotein in yeast requires interaction with Max. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):423–426. doi: 10.1038/359423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I., Land H. The c-Myc protein induces cell cycle progression and apoptosis through dimerization with Max. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5083–5087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin C., Wagner A. J., Hay N. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation by Myc and repression by Max. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham K. B., Givol D., Avivi A., Yayon A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Mapping of murine fibroblast growth factor receptors refines regions of homology between mouse and human chromosomes. Genomics. 1994 Jun;21(3):656–658. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Eisenman R. N. A switch from Myc:Max to Mad:Max heterocomplexes accompanies monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2110–2119. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Kretzner L., Eisenman R. N. Mad: a heterodimeric partner for Max that antagonizes Myc transcriptional activity. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Lawrence Q. A., Eisenman R. N. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Huang J., Ma A., Kretzner L., Alt F. W., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Binding of myc proteins to canonical and noncanonical DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5216–5224. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Friedrich G. A., Soriano P. Transcriptional enhancer factor 1 disruption by a retroviral gene trap leads to heart defects and embryonic lethality in mice. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2293–2301. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Cole M. D. Constitutive c-myc oncogene expression blocks mouse erythroleukaemia cell differentiation but not commitment. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):760–763. doi: 10.1038/320760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. W., Buchan H. L., Civin C. I., Kastan M. B. Altered cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution of the c-myc protein in differentiating ML-1 human myeloid leukemia cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 May;4(5):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Schreiber-Agus N., Alt F. W. myc family oncogenes in the development of normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:1–46. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle L. R., Yin X., Brothman A. R., Williams B. J., Atkin N. B., Prochownik E. V. Mutation of the MXI1 gene in prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):249–255. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoff S., Ayer D. E., Zervos A. S., Steingrímsson E., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Eisenman R. N., Brent R., Disteche C. M. Mapping of two genes encoding members of a distinct subfamily of MAX interacting proteins: MAD to human chromosome 2 and mouse chromosome 6, and MXI1 to human chromosome 10 and mouse chromosome 19. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):665–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder P. A., Bell S. M., Knowles M. A. Deletion of two regions on chromosome 4 in bladder carcinoma: definition of a critical 750kB region at 4p16.3. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3433–3436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone G., Tatò F., Alemà S. Distinctive effects of the viral oncogenes myc, erb, fps, and src on the differentiation program of quail myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):426–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O. Enforced expression of the c-myc oncogene inhibits cell differentiation by precluding entry into a distinct predifferentiation state in G0/G1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1614–1624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Mocarski E. S. Translational control of cytomegalovirus gene expression is mediated by upstream AUG codons. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3334–3340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3334-3340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Schwab M., Rosenau W. Expression of N-myc and c-src during the development of fetal human brain. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 1;47(11):2931–2936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Cechova K., Tassi V., Dalla-Favera R. Opposite regulation of gene transcription and cell proliferation by c-Myc and Max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2935–2939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington E. A., Bennett M. R., Fanidi A., Evan G. I. c-Myc-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts is inhibited by specific cytokines. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3286–3295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Sternglanz R., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H. Identification of a new family of tissue-specific basic helix-loop-helix proteins with a two-hybrid system. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3813–3822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Winter S., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. II. Epithelial differentiation and intermediate-sized filaments in early postimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. HLH proteins, fly neurogenesis, and vertebrate myogenesis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90525-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskinen P. J., Ayer D. E., Eisenman R. N. Repression of Myc-Ras cotransformation by Mad is mediated by multiple protein-protein interactions. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Jun;6(6):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskinen P. J., Västrik I., Mäkelä T. P., Eisenman R. N., Alitalo K. Max activity is affected by phosphorylation at two NH2-terminal sites. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Mar;5(3):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max proteins possess distinct transcriptional activities. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):426–429. doi: 10.1038/359426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahoz E. G., Xu L., Schreiber-Agus N., DePinho R. A. Suppression of Myc, but not E1a, transformation activity by Max-associated proteins, Mad and Mxi1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5503–5507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. G., Pettersson M., Oberg F., Nilsson K., Lüscher B. Expression of mad, mxi1, max and c-myc during induced differentiation of hematopoietic cells: opposite regulation of mad and c-myc. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1247–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A., Münsterberg A. Wiring diagrams: regulatory circuits and the control of skeletal myogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. H., Nerlov C., Prendergast G., MacGregor D., Ziff E. B. c-Myc represses transcription in vivo by a novel mechanism dependent on the initiator element and Myc box II. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):4070–4079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman G. J., Harris A. W., Bath M. L., Eisenman R. N., Adams J. M. Overexpressed max is not oncogenic and attenuates myc-induced lymphoproliferation and lymphomagenesis in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 2;10(5):1013–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mano H., Mano K., Tang B., Koehler M., Yi T., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Ihle J. N. Expression of a novel form of Tec kinase in hematopoietic cells and mapping of the gene to chromosome 5 near Kit. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):417–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugrauer G., Alt F. W., Ekblom P. N-myc proto-oncogene expression during organogenesis in the developing mouse as revealed by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1325–1335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Koskinen P. J., Västrik I., Alitalo K. Alternative forms of Max as enhancers or suppressors of Myc-ras cotransformation. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):373–377. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Partanen J., Schwab M., Alitalo K. Plasmid pLTRpoly: a versatile high-efficiency mammalian expression vector. Gene. 1992 Sep 10;118(2):293–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
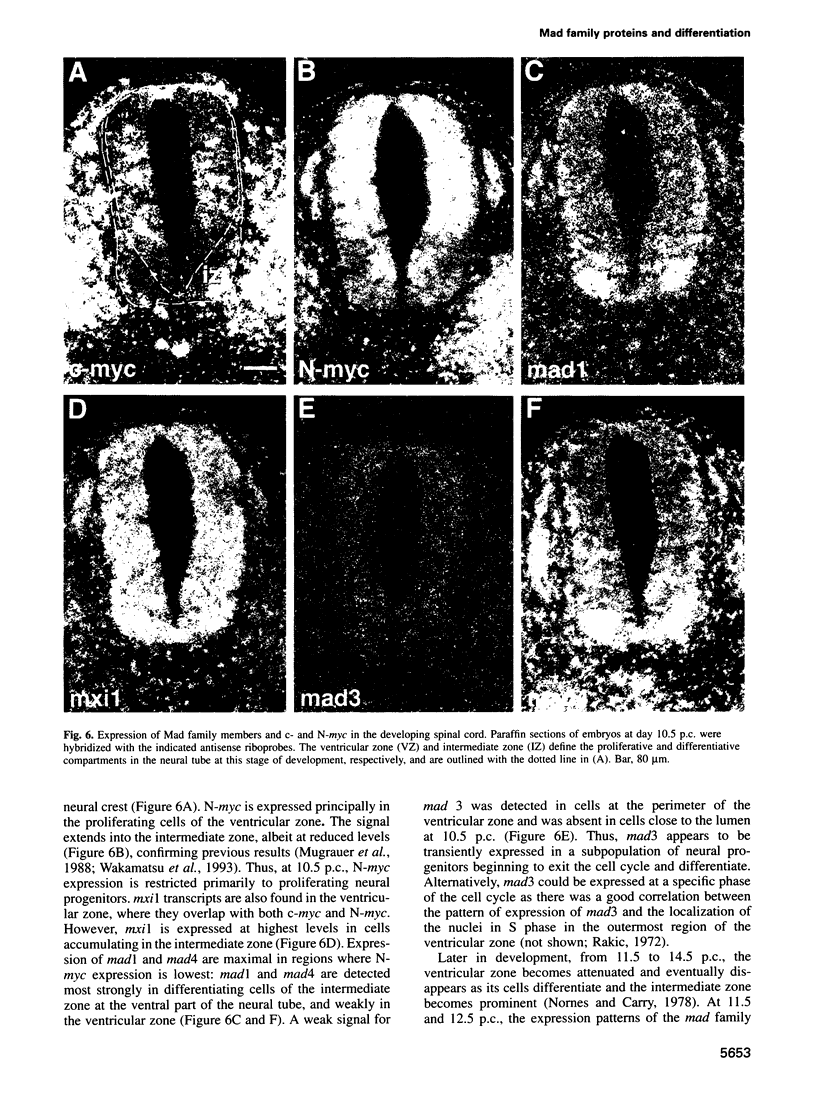
- Nornes H. O., Carry M. Neurogenesis in spinal cord of mouse: an autoradiographic analysis. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 22;159(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quéva C., Ness S. A., Grässer F. A., Graf T., Vandenbunder B., Stéhelin D. Expression patterns of c-myb and of v-myb induced myeloid-1 (mim-1) gene during the development of the chick embryo. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):125–133. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol. 1972 May;145(1):61–83. doi: 10.1002/cne.901450105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Carruthers C., Gutjahr T., Roeder R. G. Direct role for Myc in transcription initiation mediated by interactions with TFII-I. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):359–361. doi: 10.1038/365359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber-Agus N., Chin L., Chen K., Torres R., Rao G., Guida P., Skoultchi A. I., DePinho R. A. An amino-terminal domain of Mxi1 mediates anti-Myc oncogenic activity and interacts with a homolog of the yeast transcriptional repressor SIN3. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):777–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Groudine M. Control of c-myc regulation in normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Västrik I., Kaipainen A., Penttilä T. L., Lymboussakis A., Alitalo R., Parvinen M., Alitalo K. Expression of the mad gene during cell differentiation in vivo and its inhibition of cell growth in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(6):1197–1208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.6.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu Y., Watanabe Y., Shimono A., Kondoh H. Transition of localization of the N-Myc protein from nucleus to cytoplasm in differentiating neurons. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90236-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. The MyoD family and myogenesis: redundancy, networks, and thresholds. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1241–1244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Chen Y., Gilbert D. J., Moore K. J., Yu L., Simon M. I., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Identification, chromosomal location, and genome organization of mammalian G-protein-coupled receptors. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):175–184. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]