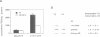Abstract
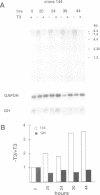
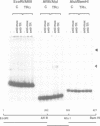
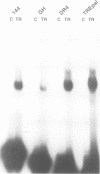
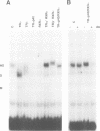
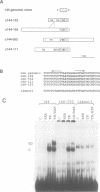
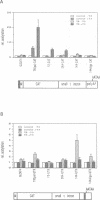
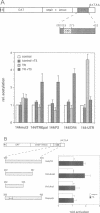
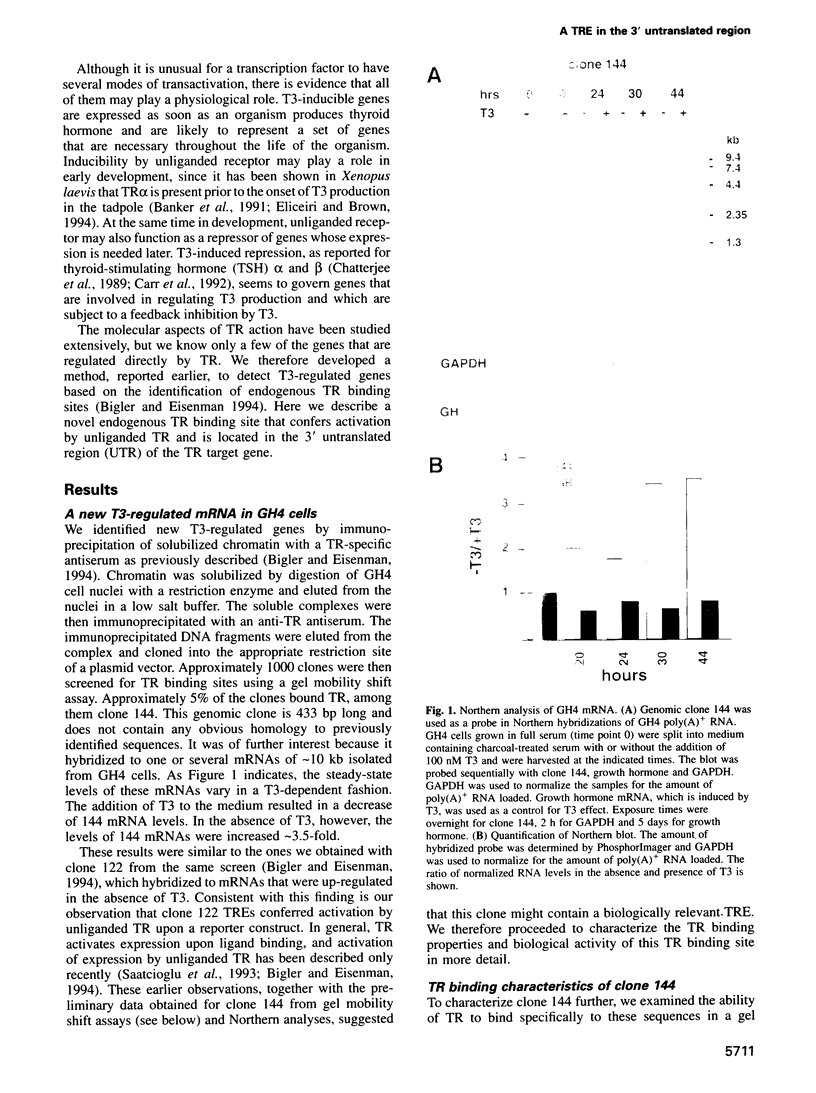
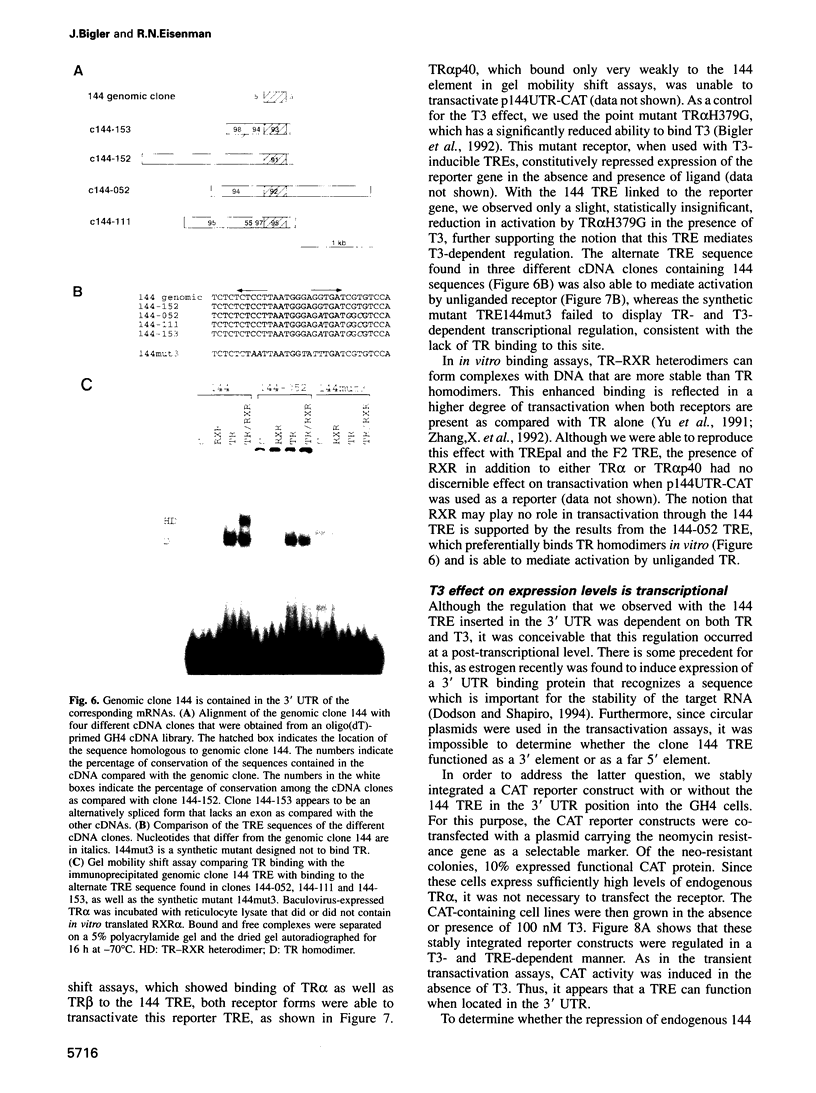
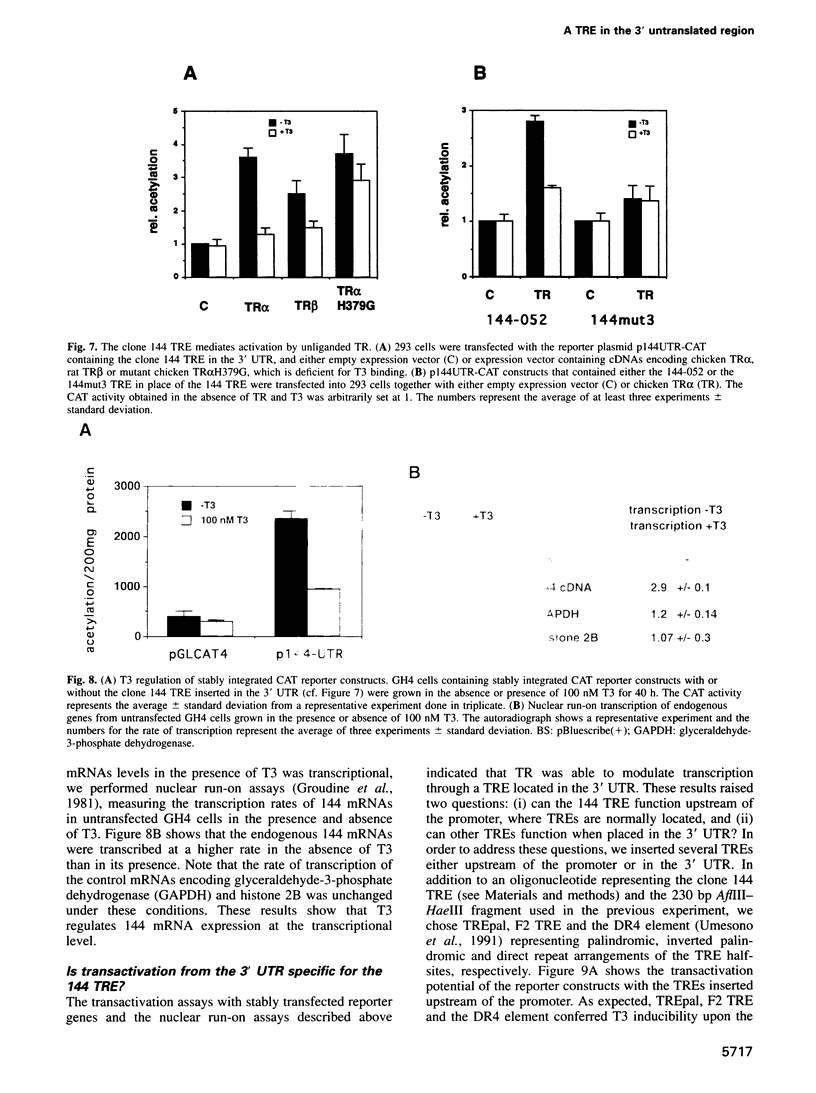
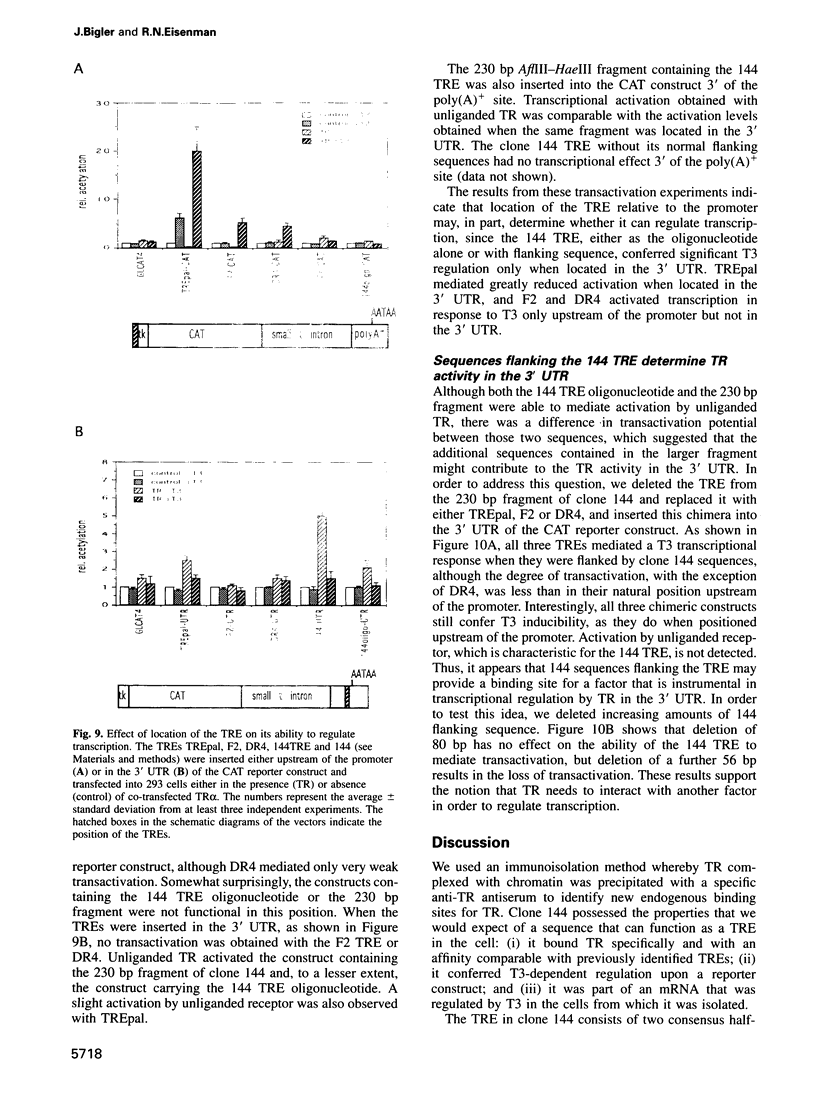
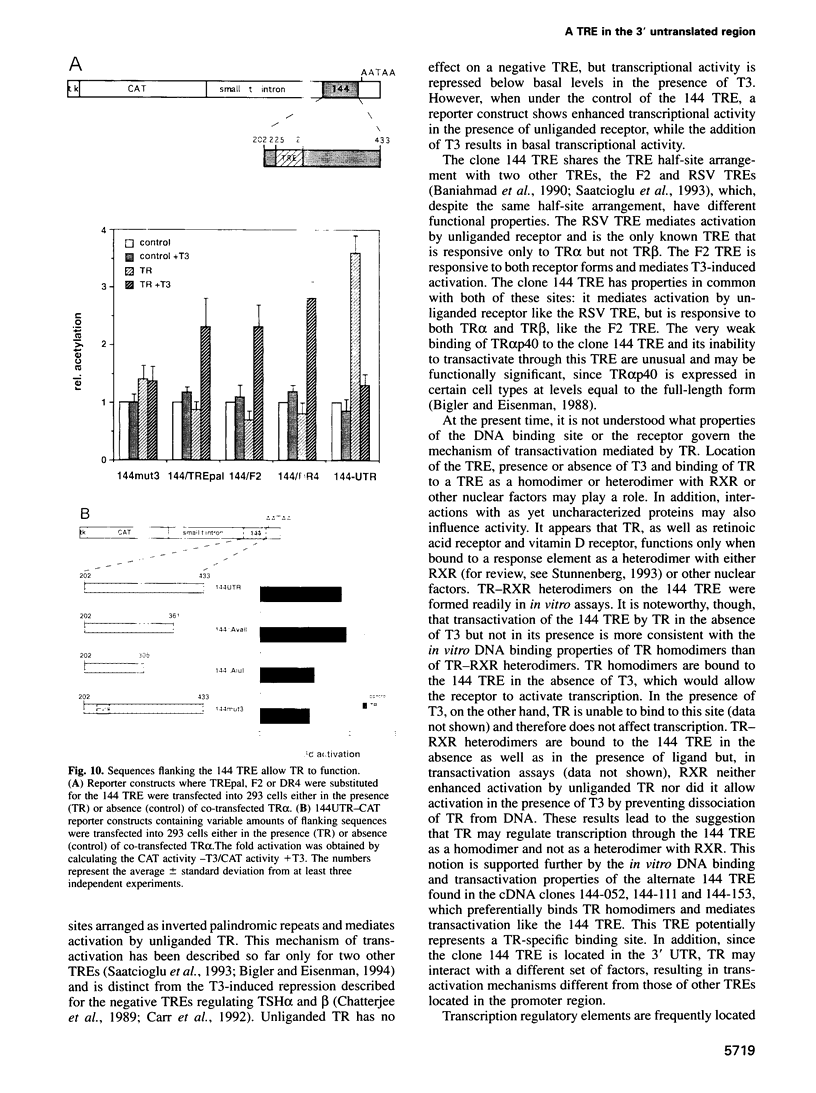
We describe a novel thyroid hormone response element (TRE)-containing sequence, clone 144, isolated by immunoprecipitation of nuclear thyroid hormone receptor (TR)-DNA complexes from the rat pituitary tumor cell line GH4. These cells express several mRNAs of approximately 10 kb that hybridize to the TRE-containing genomic clone 144. These mRNAs are up-regulated at the transcriptional level in the absence of thyroid hormone (T3) and repressed in its presence. The sequence protected from DNase I digestion by TR in clone 144 contains two consensus TRE half-sites arranged as inverted palindromes. The clone 144 TRE is located in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of several related mRNAs. A reporter construct transfected into 293 cells was responsive to TR regulation when the clone 144 TRE was inserted in the 3' UTR but not when inserted upstream of the promoter. As found for the endogenous 144 mRNAs, the 144 TRE reporter construct is activated by TR in the absence of T3, but not in its presence. Deletion analysis showed that clone 144 sequences flanking the TRE were necessary for TR-mediated regulation, suggesting that the mechanism by which TR regulates transcription through a TRE in the 3' UTR is different from that through the TREs located in the promoter region.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M. L., Nordström K., Demczuk S., Harbers M., Vennström B. Thyroid hormone alters the DNA binding properties of chicken thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4803–4810. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater J. A., Wisdom R., Verma I. M. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:519–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker D. E., Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. The thyroid hormone receptor gene (c-erbA alpha) is expressed in advance of thyroid gland maturation during the early embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5079–5089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. Isolation of a thyroid hormone-responsive gene by immunoprecipitation of thyroid hormone receptor-DNA complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7621–7632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. c-erbA encodes multiple proteins in chicken erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4155–4161. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Hokanson W., Eisenman R. N. Thyroid hormone receptor transcriptional activity is potentially autoregulated by truncated forms of the receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2406–2417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Myc and Max associate in vivo. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–80. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Dunn M. K., Harney J. W., Gulick T., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D. Thyroid hormone aporeceptor represses T3-inducible promoters and blocks activity of the retinoic acid receptor. New Biol. 1989 Dec;1(3):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Harney J. W., Koenig R. J., Moore D. D. Functional characterization of the rat growth hormone promoter elements required for induction by thyroid hormone with and without a co-transfected beta type thyroid hormone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):178–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A nuclear factor that enhances binding of thyroid hormone receptors to thyroid hormone response elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2500–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C., Bendik I., Wyss A., Meier E., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., Hunziker W. Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):657–660. doi: 10.1038/361657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr F. E., Kaseem L. L., Wong N. C. Thyroid hormone inhibits thyrotropin gene expression via a position-independent negative L-triiodothyronine-responsive element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18689–18694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee V. K., Lee J. K., Rentoumis A., Jameson J. L. Negative regulation of the thyroid-stimulating hormone alpha gene by thyroid hormone: receptor interaction adjacent to the TATA box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9114–9118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Smit-McBride Z., Lewis S., Sharif M., Privalsky M. L. Nuclear hormone receptors involved in neoplasia: erb A exhibits a novel DNA sequence specificity determined by amino acids outside of the zinc-finger domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2366–2376. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Krnacik M. J., Schmidhauser C., Yang C. L., Bissell M. J., Rosen J. M. High-level expression of the rat whey acidic protein gene is mediated by elements in the promoter and 3' untranslated region. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):905–914. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker C. J., Parker R. Mechanisms of mRNA degradation in eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Aug;19(8):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson R. E., Shapiro D. J. An estrogen-inducible protein binds specifically to a sequence in the 3' untranslated region of estrogen-stabilized vitellogenin mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3130–3138. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue M., Ernst H., Wentworth B., Nadal-Ginard B., Rosenthal N. A muscle-specific enhancer is located at the 3' end of the myosin light-chain 1/3 gene locus. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1779–1790. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri B. P., Brown D. D. Quantitation of endogenous thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta during embryogenesis and metamorphosis in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24459–24465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Casanova J., Raaka B. M., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. Half-site spacing and orientation determines whether thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors and related factors bind to DNA response elements as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):429–442. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Arce V., Perez Fernandez R. DNA sequences that act as high affinity targets for the vitamin D3 receptor in the absence of the retinoid X receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Mar;8(3):265–273. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.3.8015545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Multiple cell type-specific proteins differentially regulate target sequence recognition by the alpha retinoic acid receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Franco R., Weinberger C., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. A c-erb-A binding site in rat growth hormone gene mediates trans-activation by thyroid hormone. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):738–741. doi: 10.1038/329738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Orimo A., Hosoi T., Kondo S., Toyoshima H., Kondo T., Ikegami A., Ouchi Y., Orimo H., Muramatsu M. Genomic binding-site cloning reveals an estrogen-responsive gene that encodes a RING finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11117–11121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V., Kemmer K., Shakhov A., Jongeneel V., Beutler B. Constitutive activity of the tumor necrosis factor promoter is canceled by the 3' untranslated region in nonmacrophage cell lines; a trans-dominant factor overcomes this suppressive effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):673–677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston A. W., Gudas L. J. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive enhancer 3' of the murine homeobox gene Hox-1.6. Mech Dev. 1992 Sep;38(3):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90055-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Thanos D., Brickman J. M., Ma J., Maniatis T., Ptashne M. An HMG-like protein that can switch a transcriptional activator to a repressor. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):175–179. doi: 10.1038/371175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao J., Ozono K., Sone T., McDonnell D. P., Pike J. W. Vitamin D receptor interaction with specific DNA requires a nuclear protein and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9751–9755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Suzuki S., DeGroot L. J. High affinity and specificity of dimeric binding of thyroid hormone receptors to DNA and their ligand-dependent dissociation. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Feb;7(2):224–231. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.2.8469235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Towle H. C. Identification of nuclear factors that enhance binding of the thyroid hormone receptor to a thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1434–1442. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-9-1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Zilz N. D., McCreary N. L., MacDonald M. J., Towle H. C. Isolation and characterization of rat cDNA clones for two distinct thyroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12770–12777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Matthews M. A., Yucel J., Walls L., Golde W. T., Dynan W. S., Wachsman W. Interaction of host cell proteins with the human T-cell leukemia virus type I transcriptional control region. II. A comprehensive map of protein-binding sites facilitates construction of a simple chimeric promoter responsive to the viral tax2 gene product. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8237–8242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Conboy M. J., Rando T. A., Blau H. M. Tumor suppression by RNA from the 3' untranslated region of alpha-tropomyosin. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1107–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90320-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saatcioglu F., Deng T., Karin M. A novel cis element mediating ligand-independent activation by c-ErbA: implications for hormonal regulation. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1095–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90319-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. A major thyroid hormone response element in the third intron of the rat growth hormone gene. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):887–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Toft D. O. Steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jan;7(1):4–11. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.1.8446107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stunnenberg H. G. Mechanisms of transactivation by retinoic acid receptors. Bioessays. 1993 May;15(5):309–315. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazawa R., Yamamoto K., Suzuki K., Hirokawa K., Hirosawa S., Aoki N. Presence of functional cyclic AMP responsive element in the 3'-untranslated region of the human thrombomodulin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1391–1397. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tini M., Otulakowski G., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C., Giguère V. An everted repeat mediates retinoic acid induction of the gamma F-crystallin gene: evidence of a direct role for retinoids in lens development. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):295–307. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Stamler S. J., Engel J. D. Erythroid-specific transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is directed by a 3' enhancer. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):827–830. doi: 10.1038/328827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström G. M., Sjöberg M., Andersson M., Nordström K., Vennström B. Binding characteristics of the thyroid hormone receptor homo- and heterodimers to consensus AGGTCA repeat motifs. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1013–1022. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1324417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Darling D. S., Carter R. L., Forgione M., Umeda P. K., Chin W. W. Triiodothyronine (T3) decreases binding to DNA by T3-receptor homodimers but not receptor-auxiliary protein heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3565–3568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Sugawara A., Chin W. W. Triiodothyronine (T3) differentially affects T3-receptor/retinoic acid receptor and T3-receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23248–23252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Brooks R. L., Silversides D. W., West B. L., Leidig F., Baxter J. D., Eberhardt N. L. Negative thyroid hormone control of human growth hormone gene expression is mediated by 3'-untranslated/3'-flanking DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15056–15063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]