Abstract
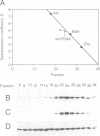
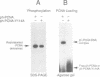
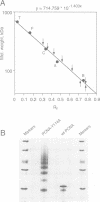
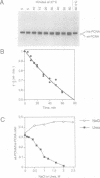
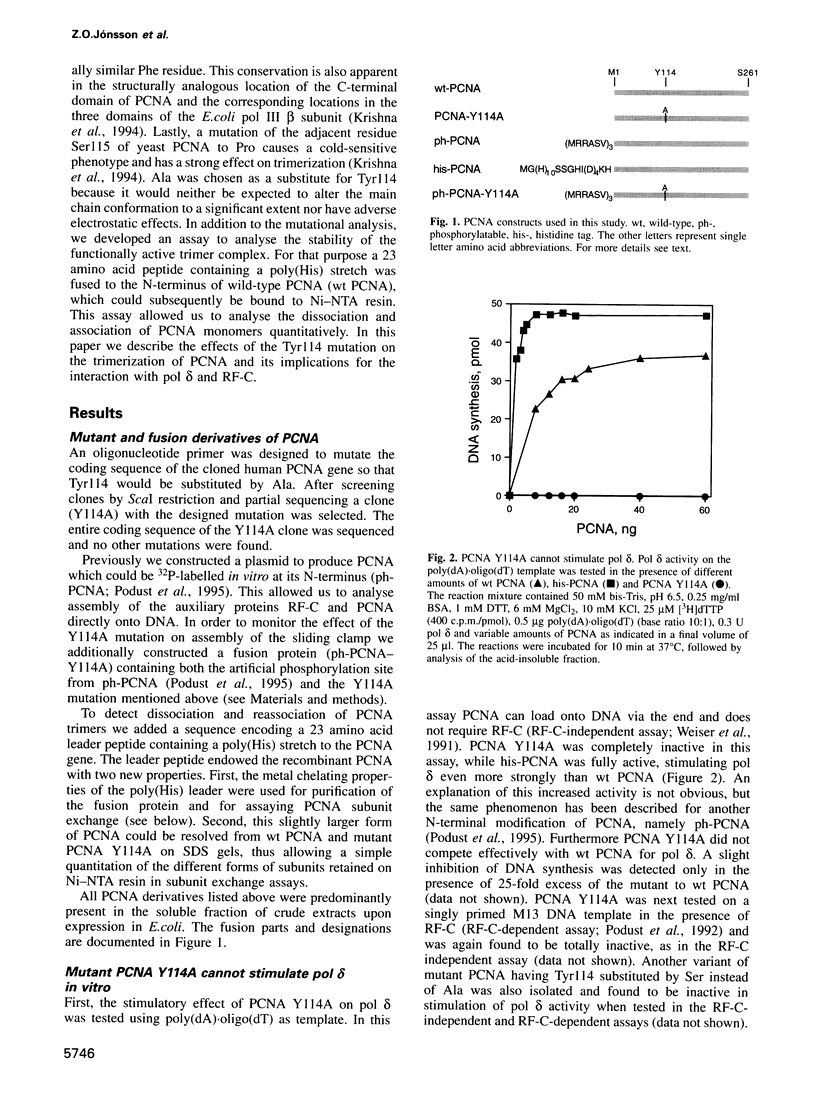
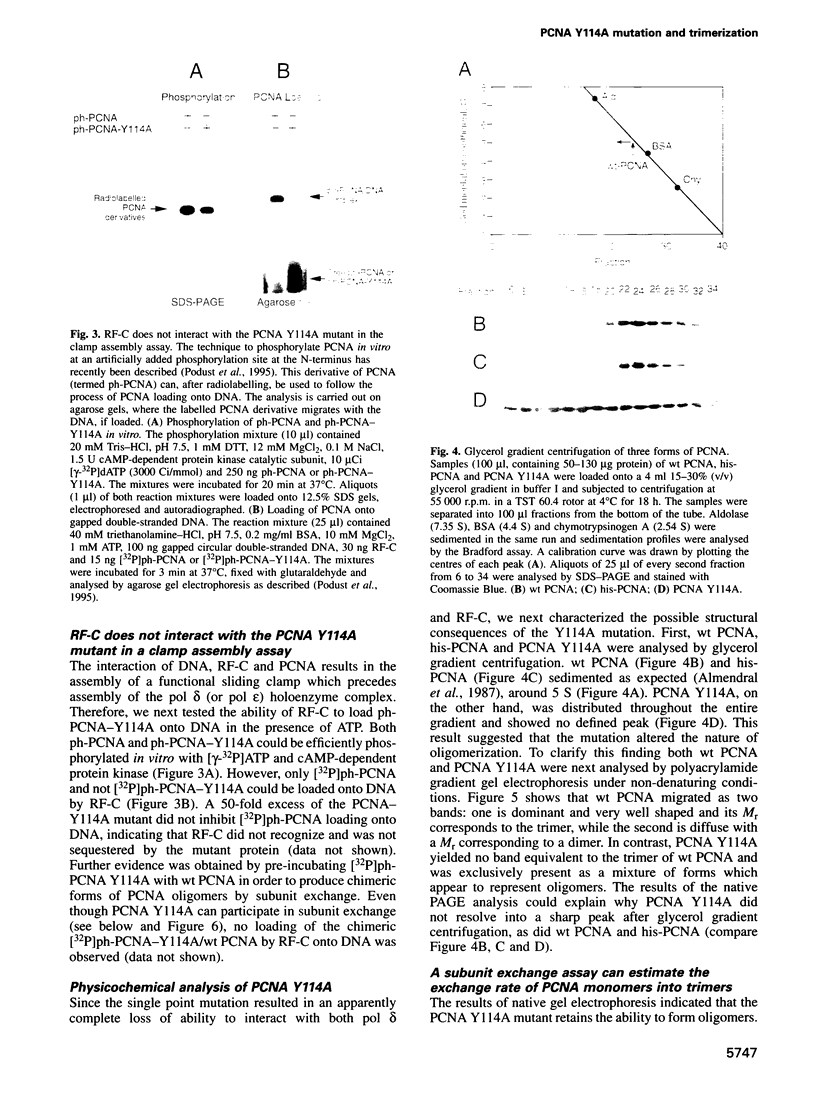
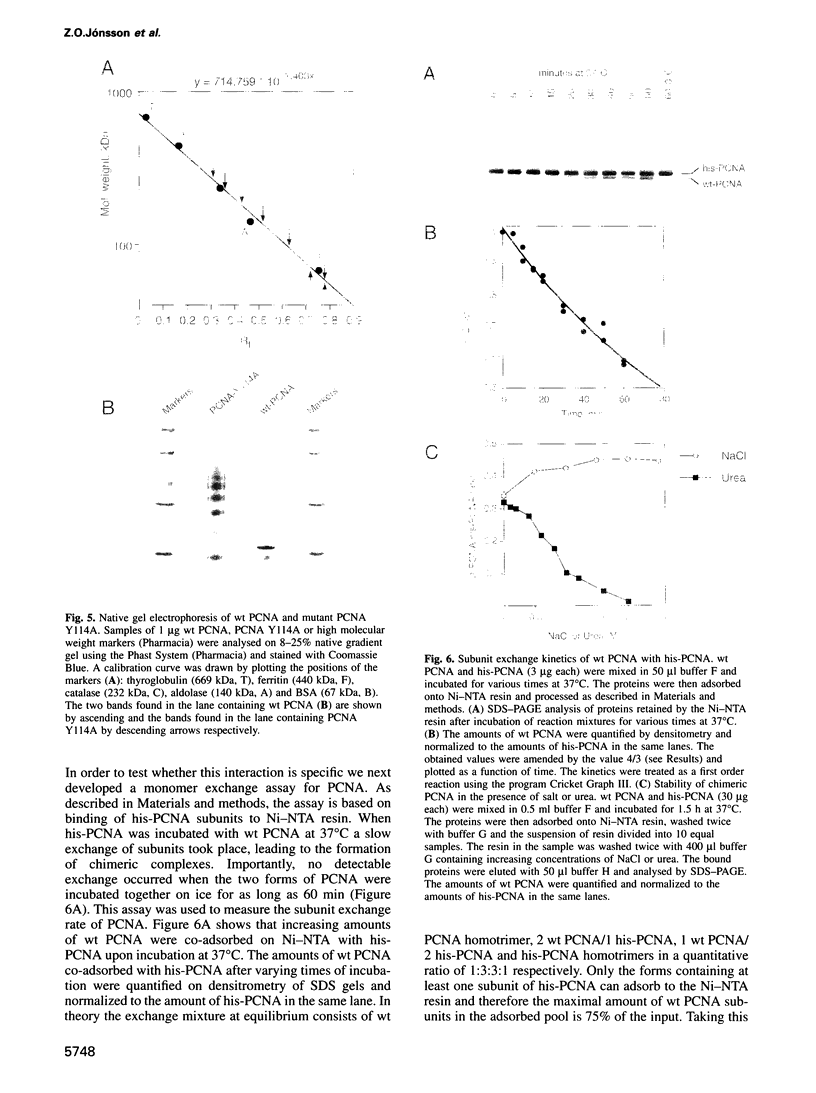
In order to study the effect of trimerization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) on its interaction with DNA polymerase (pol) delta and its loading onto DNA by replication factor C (RF-C) we have mutated a single tyrosine residue located at the subunit interface (Tyr114) to alanine. This mutation (Y114A) had a profound effect on PCNA, since it completely abolished trimer formation as seen by glycerol gradient sedimentation and native gel electrophoresis. Furthermore, the mutant protein was unable to stimulate DNA synthesis by pol delta and did not compete effectively with wild-type PCNA for pol delta, although it was able to oligomerize and could to some extent interact with subunits of functionally active PCNA. We thus conclude that PCNA molecules that are not part of a circular trimeric complex cannot interact with the pol delta core. furthermore, the mutant protein could not be loaded onto DNA by RF-C and did not compete with wild-type PCNA for loading onto DNA, indicating that PCNA trimerization may also be a prerequisite for its recognition by RF-C. The adverse effects caused by this single mutation suggest that trimerization of PCNA is essential for the monomers to keep their overall structure and that the structural changes imposed by trimerization are important for interaction with other proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand S. R., Bernstein R. M., Mathews M. B. Trimeric structure of human proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Implications for enzymatic function and autoantibody recognition. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 1;153(7):3070–3078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. A search for differential polypeptide synthesis throughout the cell cycle of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgers P. M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae replication factor C. II. Formation and activity of complexes with the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and with DNA polymerases delta and epsilon. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22698–22706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fien K., Stillman B. Identification of replication factor C from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a component of the leading-strand DNA replication complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):155–163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Rozas H., Kelman Z., Dean F. B., Pan Z. Q., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., O'Donnell M., Hurwitz J. Cdk-interacting protein 1 directly binds with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and inhibits DNA replication catalyzed by the DNA polymerase delta holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8655–8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. S., Banga S. S., Grigliatti T. A., Boyd J. B. Mutagen sensitivity and suppression of position-effect variegation result from mutations in mus209, the Drosophila gene encoding PCNA. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1450–1459. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong X. P., Onrust R., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. Three-dimensional structure of the beta subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: a sliding DNA clamp. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90445-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna T. S., Kong X. P., Gary S., Burgers P. M., Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the eukaryotic DNA polymerase processivity factor PCNA. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1233–1243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of elongation of primed DNA by DNA polymerase delta, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and activator 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5672–5676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka S., Yamaguchi M., Matsukage A. D-type cyclin-binding regions of proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11030–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlear M. A., Howell E. A., Espenshade K. K., Holm C. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (pol30) mutations suppress cdc44 mutations and identify potential regions of interaction between the two encoded proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4390–4397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust L. M., Podust V. N., Floth C., Hübscher U. Assembly of DNA polymerase delta and epsilon holoenzymes depends on the geometry of the DNA template. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2970–2975. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust L. M., Podust V. N., Sogo J. M., Hübscher U. Mammalian DNA polymerase auxiliary proteins: analysis of replication factor C-catalyzed proliferating cell nuclear antigen loading onto circular double-stranded DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3072–3081. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podust V. N., Georgaki A., Strack B., Hübscher U. Calf thymus RF-C as an essential component for DNA polymerase delta and epsilon holoenzymes function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4159–4165. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji K. K., Kenny M. K., Wood R. D. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for DNA excision repair. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90416-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Chen I. T., Zhan Q., Bae I., Chen C. Y., Gilmer T. M., Kastan M. B., O'Connor P. M., Fornace A. J., Jr Interaction of the p53-regulated protein Gadd45 with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Science. 1994 Nov 25;266(5189):1376–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.7973727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Smart machines at the DNA replication fork. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):725–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Castillo C., So A. G., Downey K. M. An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12310–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):574–578. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser T., Gassmann M., Thömmes P., Ferrari E., Hafkemeyer P., Hübscher U. Biochemical and functional comparison of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10420–10428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Zhang H., Beach D. D type cyclins associate with multiple protein kinases and the DNA replication and repair factor PCNA. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90518-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Xiong Y., Beach D. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen and p21 are components of multiple cell cycle kinase complexes. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Sep;4(9):897–906. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.9.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]