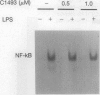
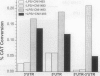
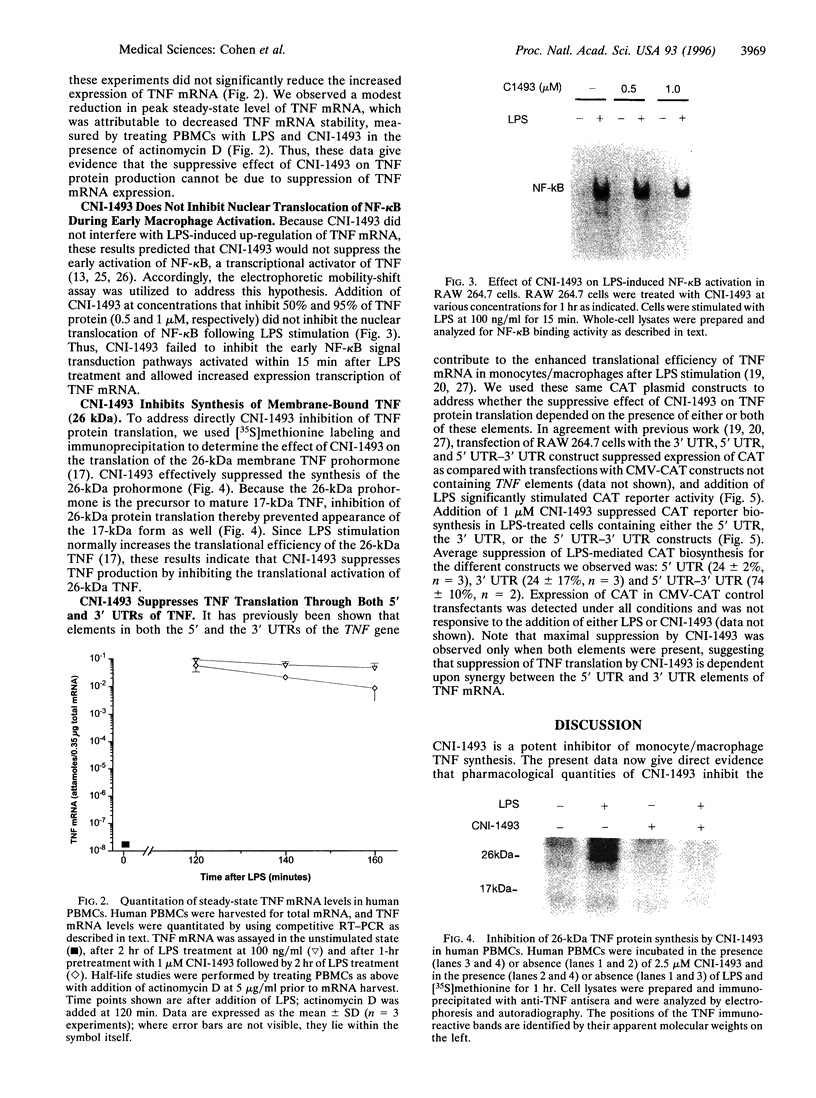
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) mediates a wide variety of disease states including septic shock, acute and chronic inflammation, and cachexia. Recently, a multivalent guanylhydrazone (CNI-1493) developed as an inhibitor of macrophage activation was shown to suppress TNF production and protect against tissue inflammation and endotoxin lethality [Bianchi, M., Ulrich, P., Bloom, O., Meistrell, M., Zimmerman, G. A., Schmidtmayerova, H., Bukrinsky, M., Donnelley, T., Bucala, R., Sherry, B., Manogue, K. R., Tortolani, A. J., Cerami, A. & Tracey, K. J. (1995) Mol. Med. 1, 254-266, and Bianchi, M., Bloom, O., Raabe, T., Cohen, P. S., Chesney, J., Sherry, B., Schmidtmayerova, H., Zhang, X., Bukrinsky, M., Ulrich, P., Cerami, A. & Tracey, J. (1996) J. Exp. Med., in press]. We have now elucidated the mechanism by which CNI-1493 inhibits macrophage TNF synthesis and show here that it acts through suppression of TNF translation efficiency. CNI-1493 blocked neither the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced increases in the expression of TNF mRNA nor the translocation of nuclear factor NF-kappa B to the nucleus in macrophages activated by 15 min of LPS stimulation, indicating that CNI-1493 does not interfere with early NF-kappa B-mediated transcriptional regulation of TNF. However, synthesis of the 26-kDa membrane form of TNF was effectively blocked by CNI-1493. Further evidence for the translational suppression of TNF is given by experiments using chloram-phenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) constructs containing elements of the TNF gene that are involved in TNF translational regulation. Both the 5' and 3' untranslated regions of the TNF gene were required to elicit maximal translational suppression by CNI-1493. Identification of the molecular target through which CNI-1493 inhibits TNF translation should provide insight into the regulation of macrophage activation and mechanisms of inflammation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Tkacenko V., Milsark I., Krochin N., Cerami A. Effect of gamma interferon on cachectin expression by mononuclear phagocytes. Reversal of the lpsd (endotoxin resistance) phenotype. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1791–1796. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., Ulrich P., Bloom O., Meistrell M., 3rd, Zimmerman G. A., Schmidtmayerova H., Bukrinsky M., Donnelley T., Bucala R., Sherry B. An inhibitor of macrophage arginine transport and nitric oxide production (CNI-1493) prevents acute inflammation and endotoxin lethality. Mol Med. 1995 Mar;1(3):254–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coso O. A., Chiariello M., Yu J. C., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind J. S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y., Zhang B., Lotz M. Protein tyrosine kinase activation is required for lipopolysaccharide induction of cytokines in human blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6692–6700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Whitehurst C. E., Thompson P., Beutler B. Lipopolysaccharide signals activation of tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis through the ras/raf-1/MEK/MAPK pathway. Mol Med. 1994 Nov;1(1):93–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Doyle C., Maniatis T. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation by virus and lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9769–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton J., McMahon M., DeFranco A. L. Activation of Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase in murine macrophages partially mimics lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling events. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):147–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Beutler B. The essential role of the UA-rich sequence in endotoxin-induced cachectin/TNF synthesis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1990 May-Jun;1(2):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Brown T., Beutler B. Endotoxin-responsive sequences control cachectin/tumor necrosis factor biosynthesis at the translational level. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):465–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Huez G., Beutler B. Interactive effects of the tumor necrosis factor promoter and 3'-untranslated regions. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1843–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Thompson P., Beutler B. Dexamethasone and pentoxifylline inhibit endotoxin-induced cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis at separate points in the signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):391–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Mukaida N., Kuno K., Rice N., Okamoto S., Matsushima K. Establishment of lipopolysaccharide-dependent nuclear factor kappa B activation in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):4158–4164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jue D. M., Sherry B., Luedke C., Manogue K. R., Cerami A. Processing of newly synthesized cachectin/tumor necrosis factor in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8371–8377. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Sedivy J. M. Raf-1 protein kinase activates the NF-kappa B transcription factor by dissociating the cytoplasmic NF-kappa B-I kappa B complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Claret F. X., Abo A., Karin M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1147–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradines-Figueres A., Raetz C. R. Processing and secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha in endotoxin-treated Mono Mac 6 cells are dependent on phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23261–23268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Beyaert R., Vandevoorde V., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3095–3104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede N. S., Tsytsykova A. V., Chatila T., Goldfeld A. E., Geha R. S. Transcriptional activation of the human TNF-alpha promoter by superantigen in human monocytic cells: role of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 15;155(2):902–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]