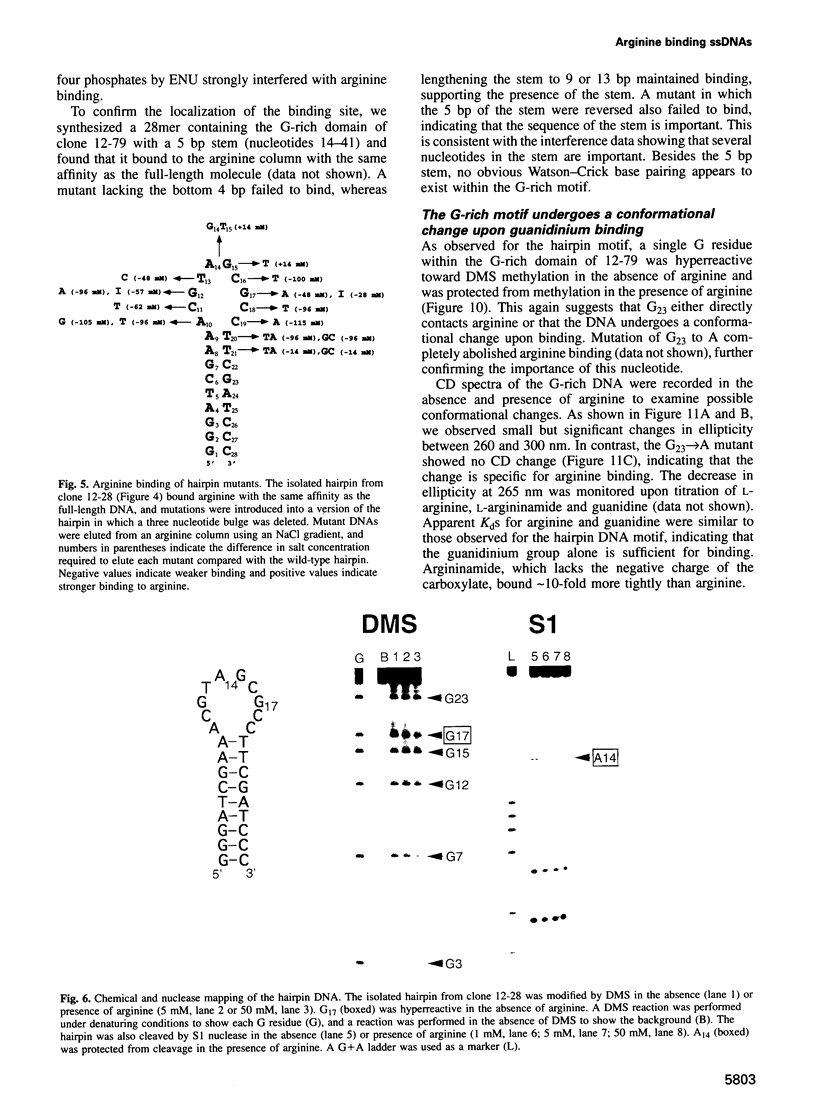
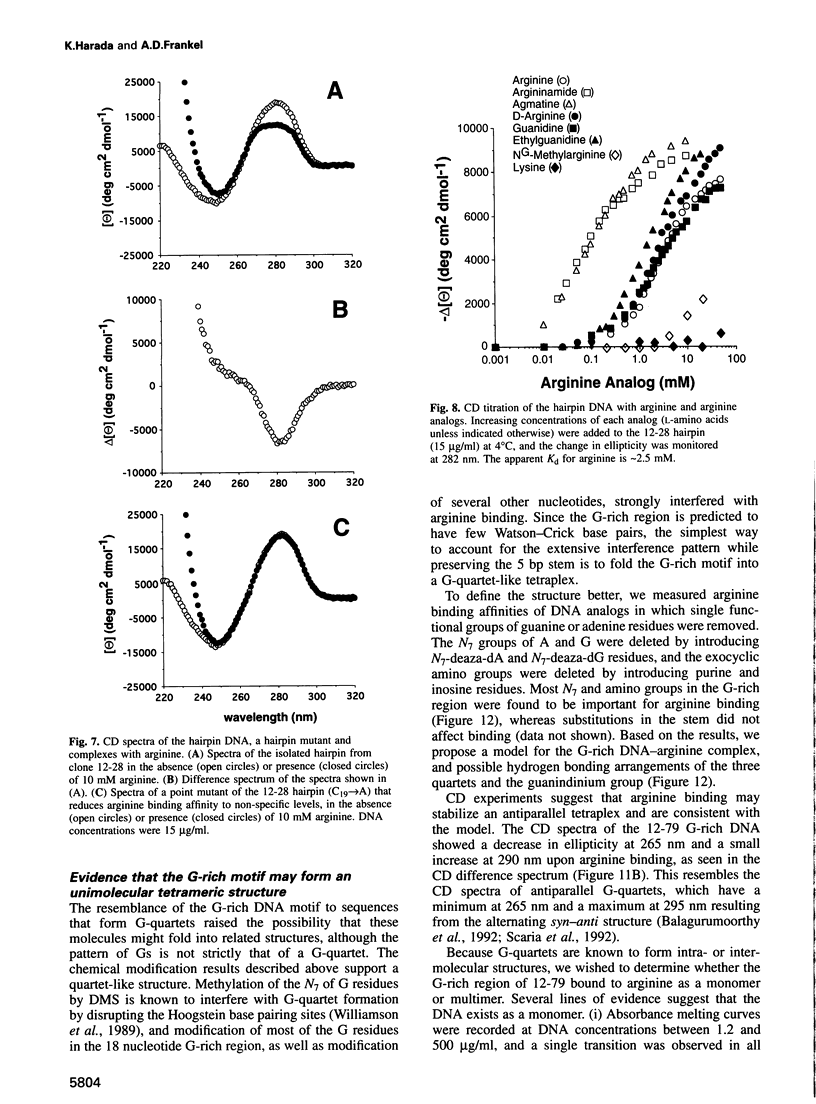
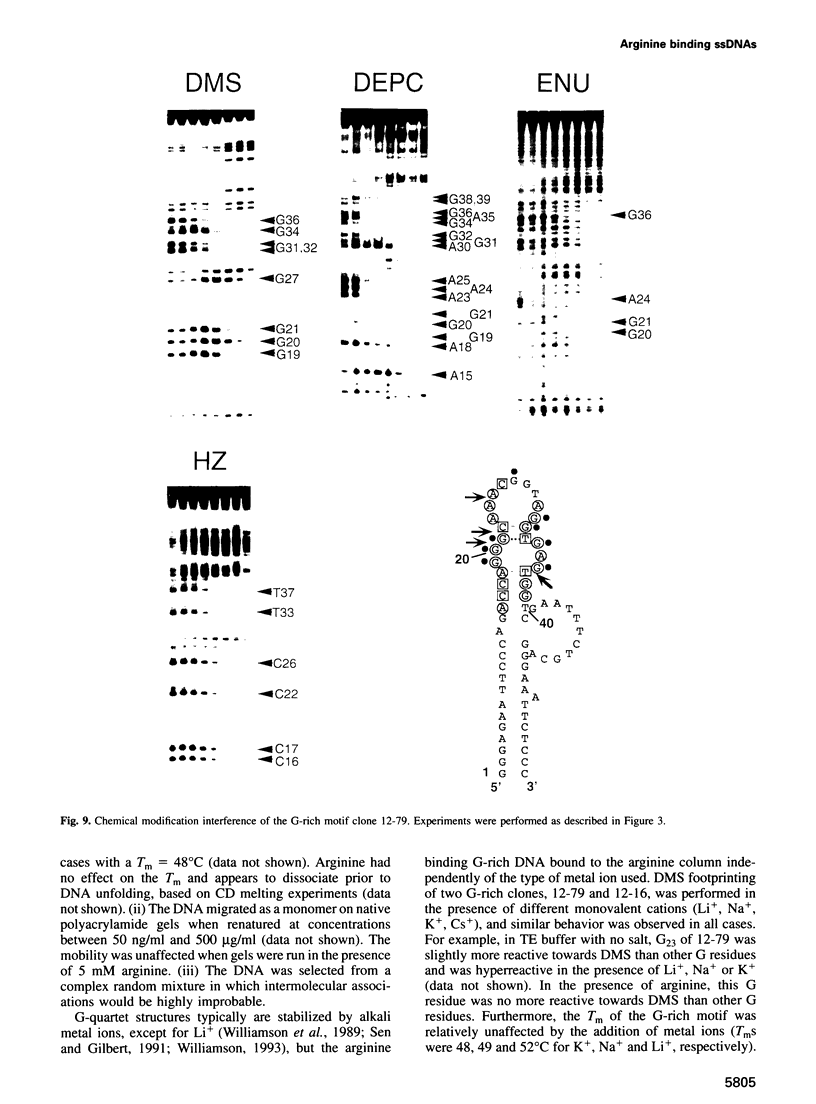
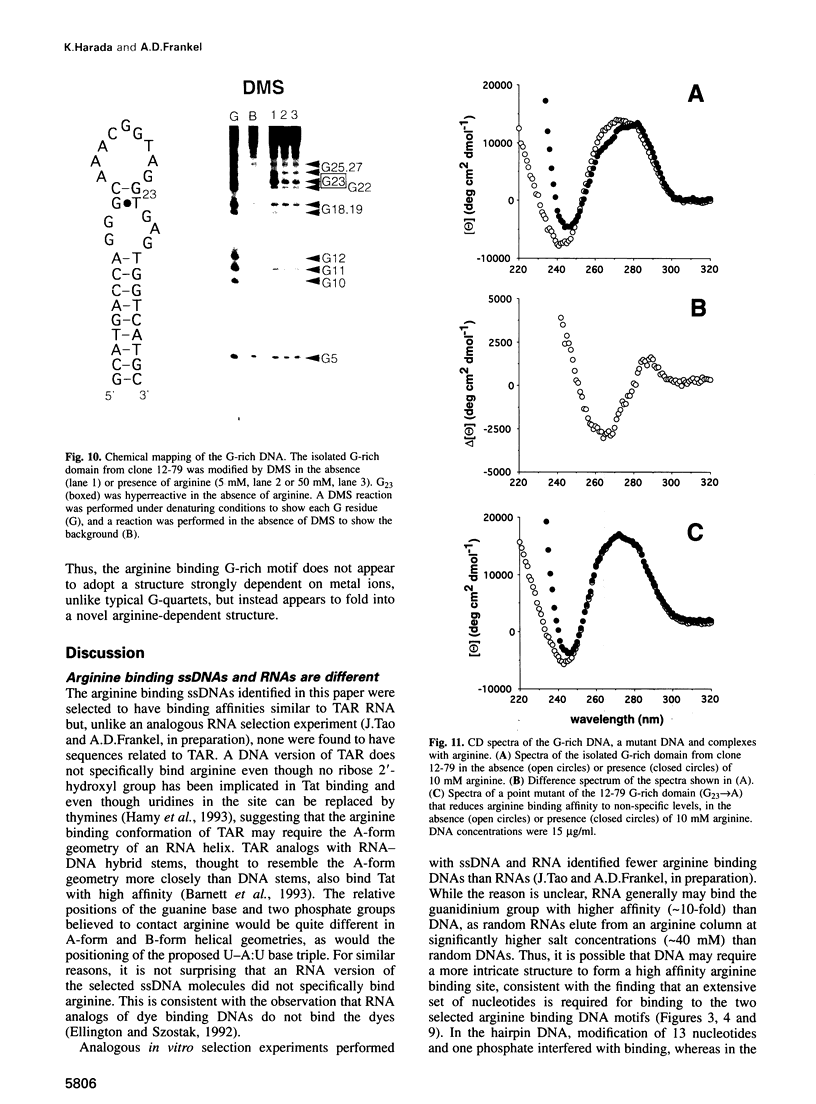
Abstract
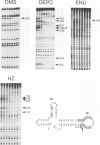
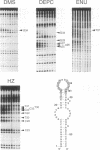
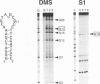
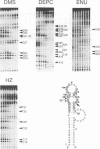
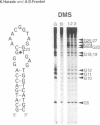
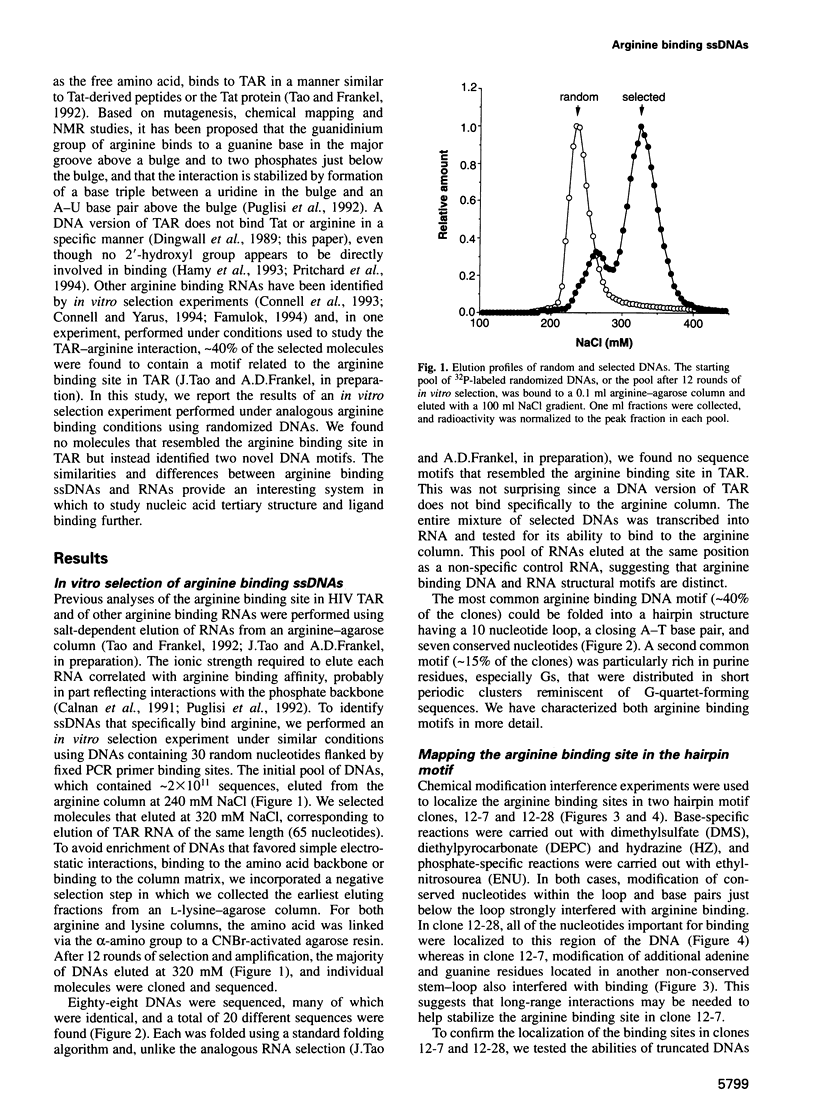
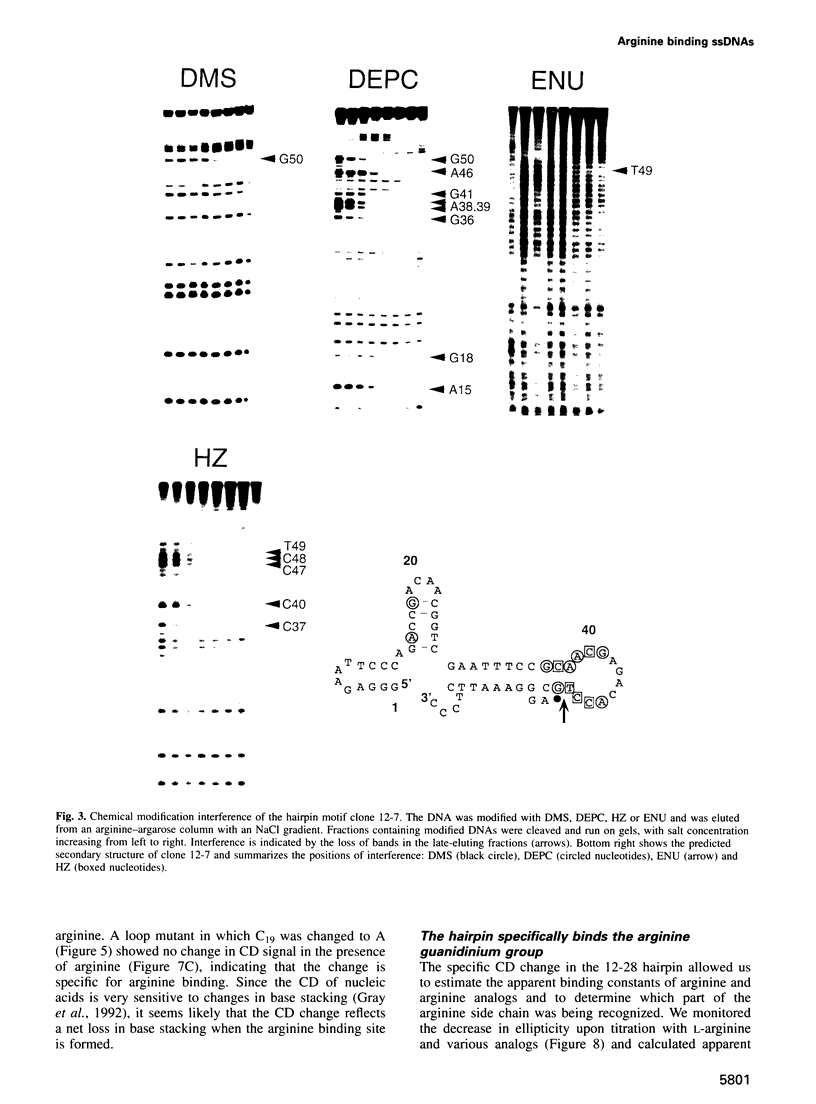
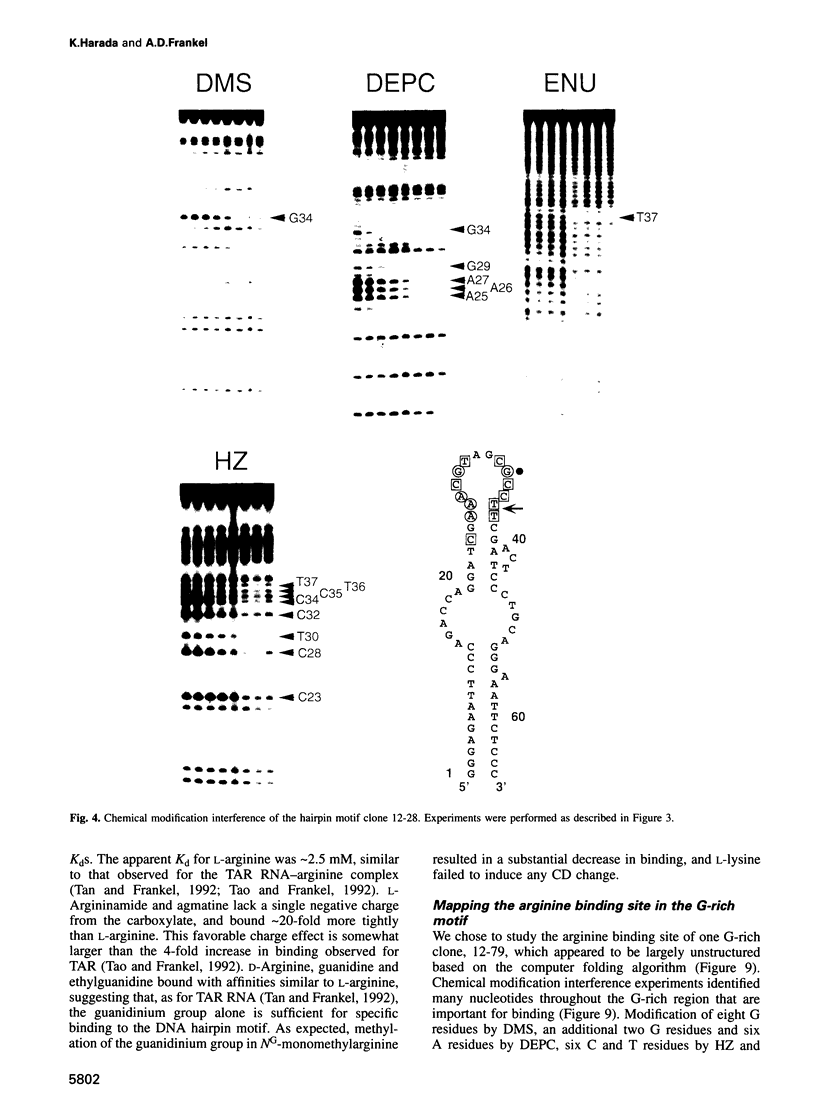
RNA tertiary structure is known to play critical roles in RNA-protein recognition and RNA function. To examine how DNA tertiary structure might relate to RNA structure, we performed in vitro selection experiments to identify single-stranded DNAs that specifically bind arginine, and compared the results with analogous experiments performed with RNA. In the case of RNA, a motif related to the arginine binding site in human immunodeficiency virus TAR RNA was commonly found, whereas in the case of DNA, two novel motifs and no TAR-like structures were found. One DNA motif, found in approximately 40% of the cloned sequences, forms of hairpin structure with a highly conserved 10 nucleotide loop, whereas the second motif is especially rich in G residues. Chemical interference and mutagenesis experiments identified nucleotides in both motifs that form specific arginine binding sites, and dimethylsulfate footprinting experiments identified single guanine residues in both that are protected from methylation in the presence of arginine, suggesting possible sites of arginine contact or conformational changes in the DNAs. Circular dichroism experiments indicated that both DNAs undergo conformational changes upon arginine binding and that the arginine guanidinium group alone is responsible for binding. A model for the G-rich motif is proposed in which mixed guanine and adenine quartets may form a novel DNA structure. Arginine binding DNAs and RNAs should provide useful model systems for studying nucleic acid tertiary structure.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antao V. P., Tinoco I., Jr Thermodynamic parameters for loop formation in RNA and DNA hairpin tetraloops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):819–824. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awang G., Sen D. Mode of dimerization of HIV-1 genomic RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11453–11457. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagurumoorthy P., Brahmachari S. K., Mohanty D., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Hairpin and parallel quartet structures for telomeric sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4061–4067. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett R. W., Delling U., Kuperman R., Sonenberg N., Sumner-Smith M. Rotational symmetry in ribonucleotide strand requirements for binding of HIV-1 Tat protein to TAR RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):151–154. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battiste J. L., Tan R., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Binding of an HIV Rev peptide to Rev responsive element RNA induces formation of purine-purine base pairs. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 15;33(10):2741–2747. doi: 10.1021/bi00176a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Yaremchuk A., Tukalo M., Cusack S. The 2.9 A crystal structure of T. thermophilus seryl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Ser). Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1404–1410. doi: 10.1126/science.8128220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock L. C., Griffin L. C., Latham J. A., Vermaas E. H., Toole J. J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):564–566. doi: 10.1038/355564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breaker R. R., Joyce G. F. A DNA enzyme that cleaves RNA. Chem Biol. 1994 Dec;1(4):223–229. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(94)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Tidor B., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Arginine-mediated RNA recognition: the arginine fork. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1167–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Moore P. B. Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA tetraplex containing G- and U-quartet structures. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8406–8414. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell G. J., Illangesekare M., Yarus M. Three small ribooligonucleotides with specific arginine sites. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5497–5502. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell G. J., Yarus M. RNAs with dual specificity and dual RNAs with similar specificity. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1137–1141. doi: 10.1126/science.7513905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckett D. R., Murchie A. I., Diekmann S., von Kitzing E., Kemper B., Lilley D. M. The structure of the Holliday junction, and its resolution. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):850–852. doi: 10.1038/355850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Strauss F. Association of poly(CA).poly(TG) DNA fragments into four-stranded complexes bound by HMG1 and 2. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):433–436. doi: 10.1126/science.8153633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glucksmann M. A., Markiewicz P., Malone C., Rothman-Denes L. B. Specific sequences and a hairpin structure in the template strand are required for N4 virion RNA polymerase promoter recognition. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90173-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. M., Ratliff R. L., Vaughan M. R. Circular dichroism spectroscopy of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1992;211:389–406. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)11021-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamy F., Asseline U., Grasby J., Iwai S., Pritchard C., Slim G., Butler P. J., Karn J., Gait M. J. Hydrogen-bonding contacts in the major groove are required for human immunodeficiency virus type-1 tat protein recognition of TAR RNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):111–123. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirao I., Kawai G., Yoshizawa S., Nishimura Y., Ishido Y., Watanabe K., Miura K. Most compact hairpin-turn structure exerted by a short DNA fragment, d(GCGAAGC) in solution: an extraordinarily stable structure resistant to nucleases and heat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 25;22(4):576–582. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.4.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huertas D., Bellsolell L., Casasnovas J. M., Coll M., Azorín F. Alternating d(GA)n DNA sequences form antiparallel stranded homoduplexes stabilized by the formation of G.A base pairs. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):4029–4038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizenga D. E., Szostak J. W. A DNA aptamer that binds adenosine and ATP. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 17;34(2):656–665. doi: 10.1021/bi00002a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. K., Tinoco I., Jr The solution structure of a d[C(TTCG)G] DNA hairpin and comparison to the unusually stable RNA analogue. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3287–3293. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena S. D., Johnston B. H. Intramolecular triple-helix formation at (PunPyn).(PunPyn) tracts: recognition of alternate strands via Pu.PuPy and Py.PuPy base triplets. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):320–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Roe B. A. Aminoacylation of synthetic DNAs corresponding to Escherichia coli phenylalanine and lysine tRNAs. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):74–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2455342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S. The stability of polypurine tetraplexes in the presence of mono- and divalent cations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6057–6060. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard G. A., Zhang S., Peterson M. R., Harrop S. J., Helliwell J. R., Cruse W. B., d'Estaintot B. L., Kennard O., Brown T., Hunter W. N. Self-association of a DNA loop creates a quadruplex: crystal structure of d(GCATGCT) at 1.8 A resolution. Structure. 1995 Apr 15;3(4):335–340. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim A. C., Barton J. K. Chemical probing of tDNAPhe with transition metal complexes: a structural comparison of RNA and DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):11029–11034. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya R. F., Schultze P., Smith F. W., Roe J. A., Feigon J. Thrombin-binding DNA aptamer forms a unimolecular quadruplex structure in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3745–3749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masai H., Nomura N., Arai K. The ABC-primosome. A novel priming system employing dnaA, dnaB, dnaC, and primase on a hairpin containing a dnaA box sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15134–15144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao D. M., Honda Y., Tanaka K., Higashi A., Nakamura T., Taguchi Y., Sakai H., Komano T., Bagdasarian M. A base-paired hairpin structure essential for the functional priming signal for DNA replication of the broad host range plasmid RSF1010. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 25;21(21):4900–4903. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.21.4900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. Tetraplex folding of telomere sequences and the inclusion of adenine bases. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):993–1001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06344.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan K., Padmanabhan K. P., Ferrara J. D., Sadler J. E., Tulinsky A. The structure of alpha-thrombin inhibited by a 15-mer single-stranded DNA aptamer. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17651–17654. doi: 10.2210/pdb1hut/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette J., Nicoghosian K., Qi G. R., Beauchemin N., Cedergren R. The conformation of single-stranded nucleic acids tDNA versus tRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Pon R. T., Jiang M. Y., Usman N., Pika J., Ogilvie K. K., Cedergren R. The synthesis and functional evaluation of RNA and DNA polymers having the sequence of Escherichia coli tRNA(fMet). Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pley H. W., Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of a hammerhead ribozyme. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):68–74. doi: 10.1038/372068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. E., Grasby J. A., Hamy F., Zacharek A. M., Singh M., Karn J., Gait M. J. Methylphosphonate mapping of phosphate contacts critical for RNA recognition by the human immunodeficiency virus tat and rev proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 11;22(13):2592–2600. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.13.2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tan R., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Conformation of the TAR RNA-arginine complex by NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1621097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., Cech T. R. Ribozyme recognition of RNA by tertiary interactions with specific ribose 2'-OH groups. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):628–631. doi: 10.1038/350628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A. DNA comes in many forms. Gene. 1993 Dec 15;135(1-2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M., Krishnaswamy S., Boeglin M., Poterszman A., Mitschler A., Podjarny A., Rees B., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Class II aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases: crystal structure of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Asp). Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1682–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2047877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaria P. V., Shire S. J., Shafer R. H. Quadruplex structure of d(G3T4G3) stabilized by K+ or Na+ is an asymmetric hairpin dimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10336–10340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Heaphy S. Evidence for interstrand quadruplex formation in the dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 genomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan R., Frankel A. D. Circular dichroism studies suggest that TAR RNA changes conformation upon specific binding of arginine or guanidine. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 27;31(42):10288–10294. doi: 10.1021/bi00157a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao J., Frankel A. D. Specific binding of arginine to TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2723–2726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. Y., McCurdy S., Shea R. G., Swaminathan S., Bolton P. H. A DNA aptamer which binds to and inhibits thrombin exhibits a new structural motif for DNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):1899–1904. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Celander D. W. Rapid procedure for chemical sequencing of small oligonucleotides without ethanol precipitation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):379–379. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann A., Hillen W. DNA contacts probed by modification protection and interference studies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:365–379. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08020-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. H., Usman N., Chartrand P., Cedergren R. Minimum ribonucleotide requirement for catalysis by the RNA hammerhead domain. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5005–5009. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]