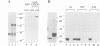Abstract
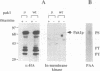
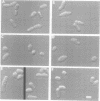
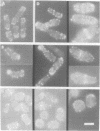
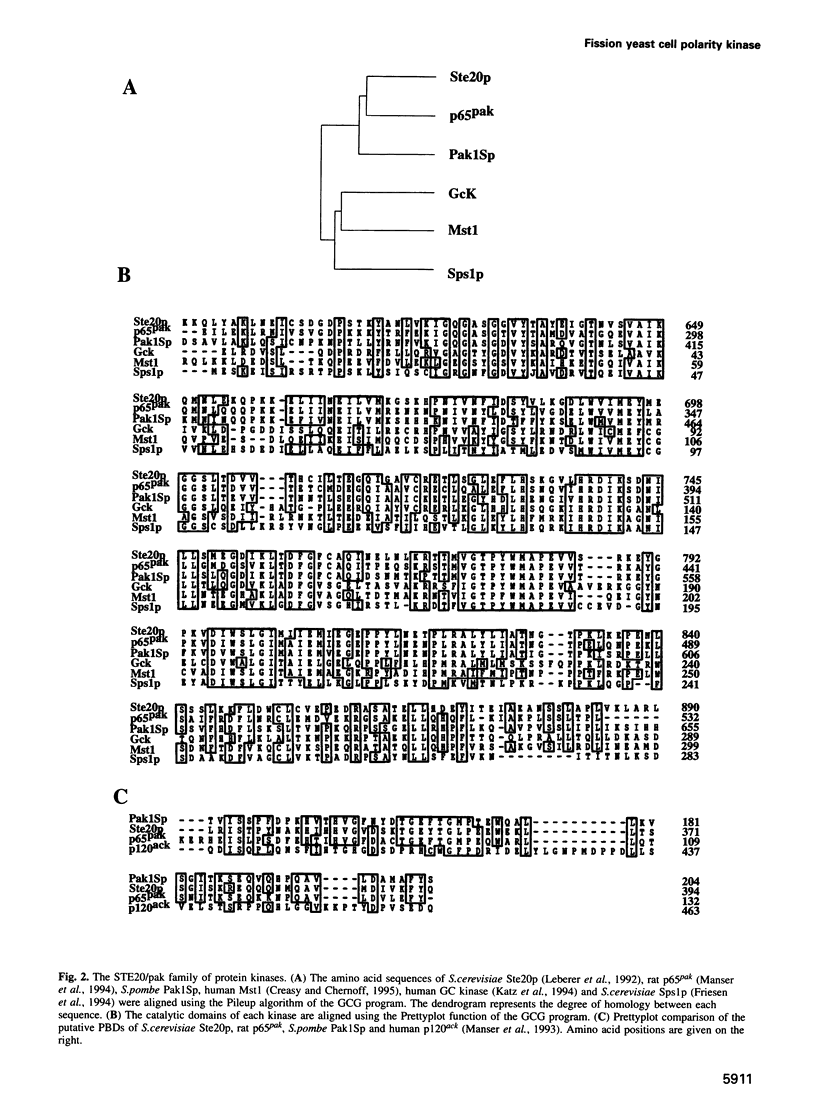
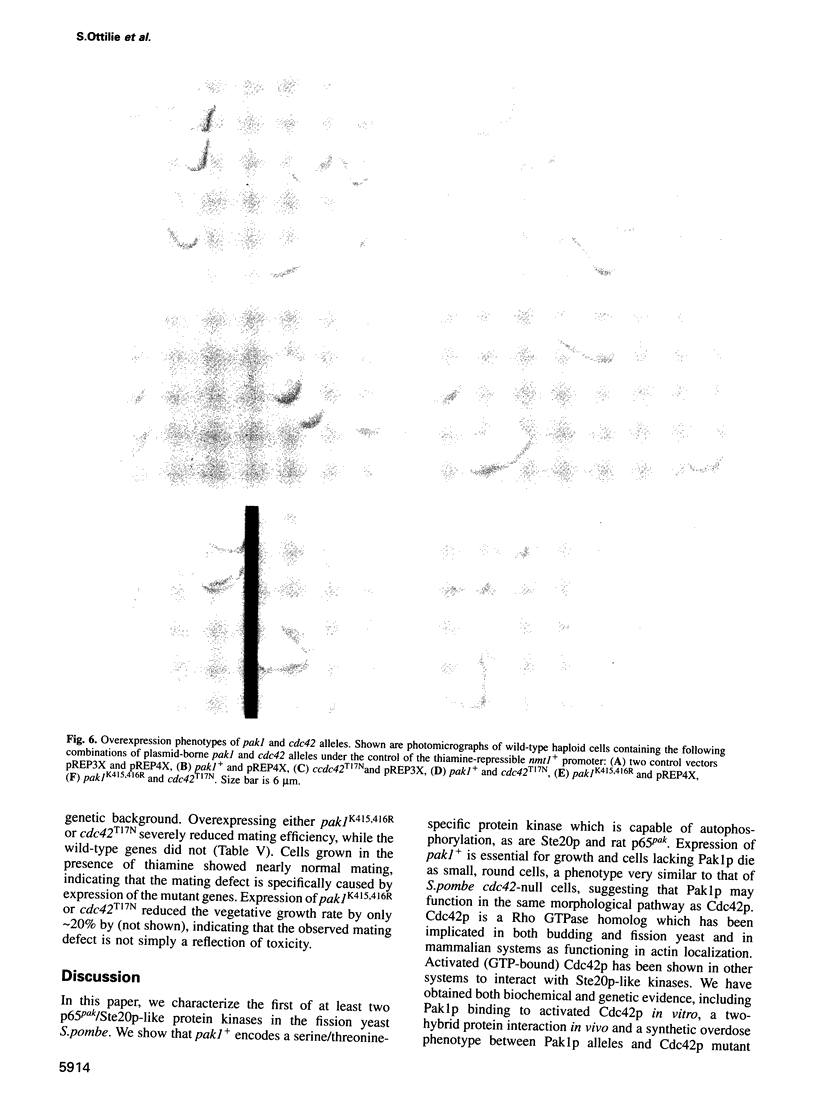
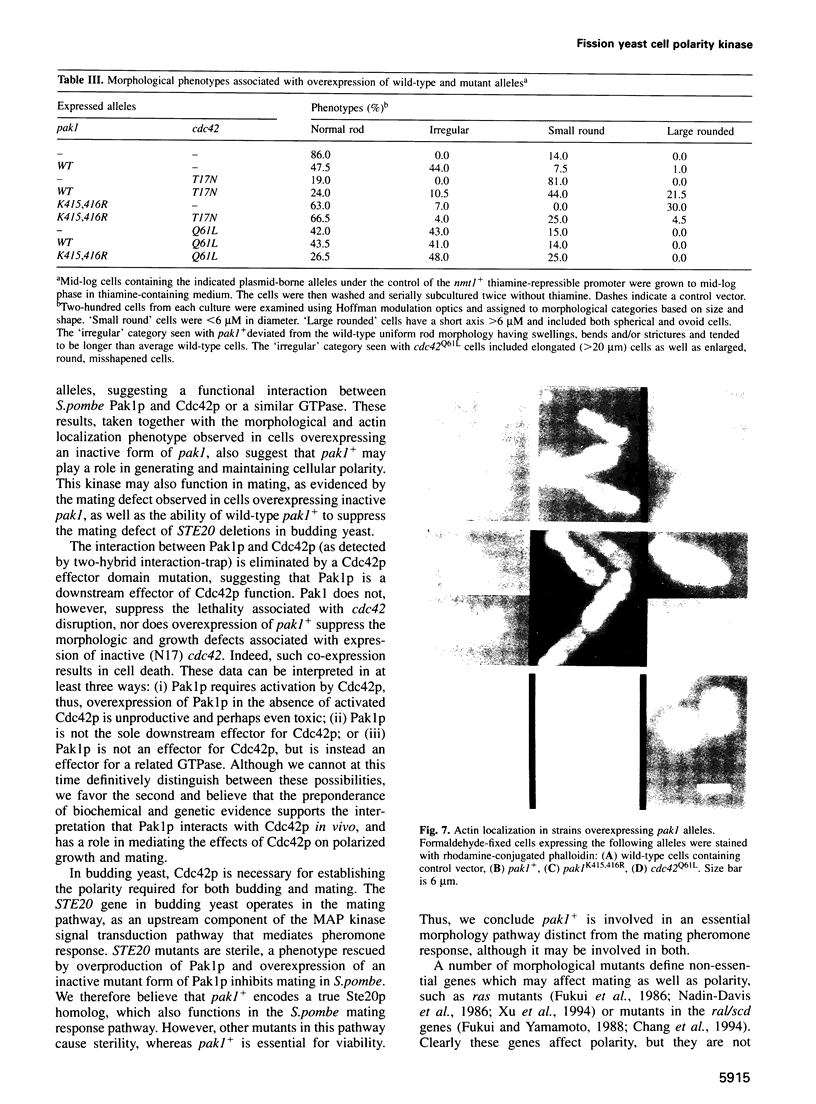
A STE20/p65pak homolog was isolated from fission yeast by PCR. The pak1+ gene encodes a 72 kDa protein containing a putative p21-binding domain near its amino-terminus and a serine/threonine kinase domain near its carboxyl-terminus. The Pak1 protein autophosphorylates on serine residues and preferentially binds to activated Cdc42p both in vitro and in vivo. This binding is mediated through the p21 binding domain on Pak1p and the effector domain on Cdc42p. Overexpression of an inactive mutant form of pak1 gives rise to cells with markedly abnormal shape with mislocalized actin staining. Pak1 overexpression does not, however, suppress lethality associated with cdc42-null cells or the morphologic defeat caused by overexpression of mutant cdc42 alleles. Gene disruption of pak1+ establishes that, like cdc42+, pak1+ function is required for cell viability. In budding yeast, pak1+ expression restores mating function to STE20-null cells and, in fission yeast, overexpression of an inactive form of Pak inhibits mating. These results indicate that the Pak1 protein is likely to be an effector for Cdc42p or a related GTPase, and suggest that Pak1p is involved in the maintenance of cell polarity and in mating.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Johnson D. I., Longnecker R. M., Sloat B. F., Pringle J. R. CDC42 and CDC43, two additional genes involved in budding and the establishment of cell polarity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):131–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. C., Barr M., Wang Y., Jung V., Xu H. P., Wigler M. H. Cooperative interaction of S. pombe proteins required for mating and morphogenesis. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chant J. Cell polarity in yeast. Trends Genet. 1994 Sep;10(9):328–333. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenevert J. Cell polarization directed by extracellular cues in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Nov;5(11):1169–1175. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.11.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasy C. L., Chernoff J. Cloning and characterization of a human protein kinase with homology to Ste20. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21695–21700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz M., Sanchez Y., Bennett T., Sun C. R., Godoy C., Tamanoi F., Duran A., Perez P. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe cwg2+ gene codes for the beta subunit of a geranylgeranyltransferase type I required for beta-glucan synthesis. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5245–5254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06220.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Identification of a 42-kilodalton phosphotyrosyl protein as a serine(threonine) protein kinase by renaturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3020–3026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsburg S. L. Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces pombe expression systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2955–2956. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen H., Lunz R., Doyle S., Segall J. Mutation of the SPS1-encoded protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae leads to defects in transcription and morphology during spore formation. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 15;8(18):2162–2175. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.18.2162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kozasa T., Kaziro Y., Takeda T., Yamamoto M. Role of a ras homolog in the life cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Yamamoto M. Isolation and characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe mutants phenotypically similar to ras1-. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):26–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00331298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm C., Kohli J., Murray J., Maundrell K. Genetic engineering of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a system for gene disruption and replacement using the ura4 gene as a selectable marker. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00331307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Whalen G., Kehrl J. H. Differential expression of a novel protein kinase in human B lymphocytes. Preferential localization in the germinal center. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16802–16809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Dignard D., Harcus D., Thomas D. Y., Whiteway M. The protein kinase homologue Ste20p is required to link the yeast pheromone response G-protein beta gamma subunits to downstream signalling components. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4815–4824. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Elements of the yeast pheromone response pathway required for filamentous growth of diploids. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1741–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8259520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Tan L., Lim L. A non-receptor tyrosine kinase that inhibits the GTPase activity of p21cdc42. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):364–367. doi: 10.1038/363364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser E., Leung T., Salihuddin H., Zhao Z. S., Lim L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):40–46. doi: 10.1038/367040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKune K., Richards K. L., Edwards A. M., Young R. A., Woychik N. A. RPB7, one of two dissociable subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II, is essential for cell viability. Yeast. 1993 Mar;9(3):295–299. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. J., Johnson D. I. Cdc42p GTPase is involved in controlling polarized cell growth in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1075–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Klar A., Nurse P. Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:795–823. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94059-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S., Innis M. A., Clark R., McCormick F., Ullrich A., Polakis P. Molecular cloning and expression of a G25K cDNA, the human homolog of the yeast cell cycle gene CDC42. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5977–5982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadin-Davis S. A., Nasim A., Beach D. Involvement of ras in sexual differentiation but not in growth control in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2963–2971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Fission yeast morphogenesis--posing the problems. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Jun;5(6):613–616. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.6.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paravicini G., Cooper M., Friedli L., Smith D. J., Carpentier J. L., Klig L. S., Payton M. A. The osmotic integrity of the yeast cell requires a functional PKC1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4896–4905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R., Yablonski D., Simchen G., Levitzki A. Cloning of the STE5 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a suppressor of the mating defect of cdc25 temperature-sensitive mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5474–5478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramer S. W., Davis R. W. A dominant truncation allele identifies a gene, STE20, that encodes a putative protein kinase necessary for mating in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):452–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N., Connell L., Errede B. STE11 is a protein kinase required for cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1862–1874. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas J. C., Diaz M., Duran A., Perez P. Isolation and characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe mutants defective in cell wall (1-3)beta-D-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3456–3462. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3456-3462.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas J. C., Roncero C., Rico H., Durán A. Characterization of a Schizosaccharomyces pombe morphological mutant altered in the galactomannan content. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Apr 15;63(2-3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90096-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjo K., Koland J. G., Hart M. J., Narasimhan V., Johnson D. I., Evans T., Cerione R. A. Molecular cloning of the gene for the human placental GTP-binding protein Gp (G25K): identification of this GTP-binding protein as the human homolog of the yeast cell-division-cycle protein CDC42. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9853–9857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell V., Nurse P. Genetic analysis of cell morphogenesis in fission yeast--a role for casein kinase II in the establishment of polarized growth. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2066–2074. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Assay of yeast mating reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:77–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94008-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Two novel protein kinase C-related genes of fission yeast are essential for cell viability and implicated in cell shape control. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. P., White M., Marcus S., Wigler M. Concerted action of RAS and G proteins in the sexual response pathways of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Tamaoki T., Choe H. R., Tanaka H., Kataoka T. Adenylate cyclases in yeast: a comparison of the genes from Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziman M., O'Brien J. M., Ouellette L. A., Church W. R., Johnson D. I. Mutational analysis of CDC42Sc, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene that encodes a putative GTP-binding protein involved in the control of cell polarity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3537–3544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziman M., Preuss D., Mulholland J., O'Brien J. M., Botstein D., Johnson D. I. Subcellular localization of Cdc42p, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae GTP-binding protein involved in the control of cell polarity. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1307–1316. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]