Abstract
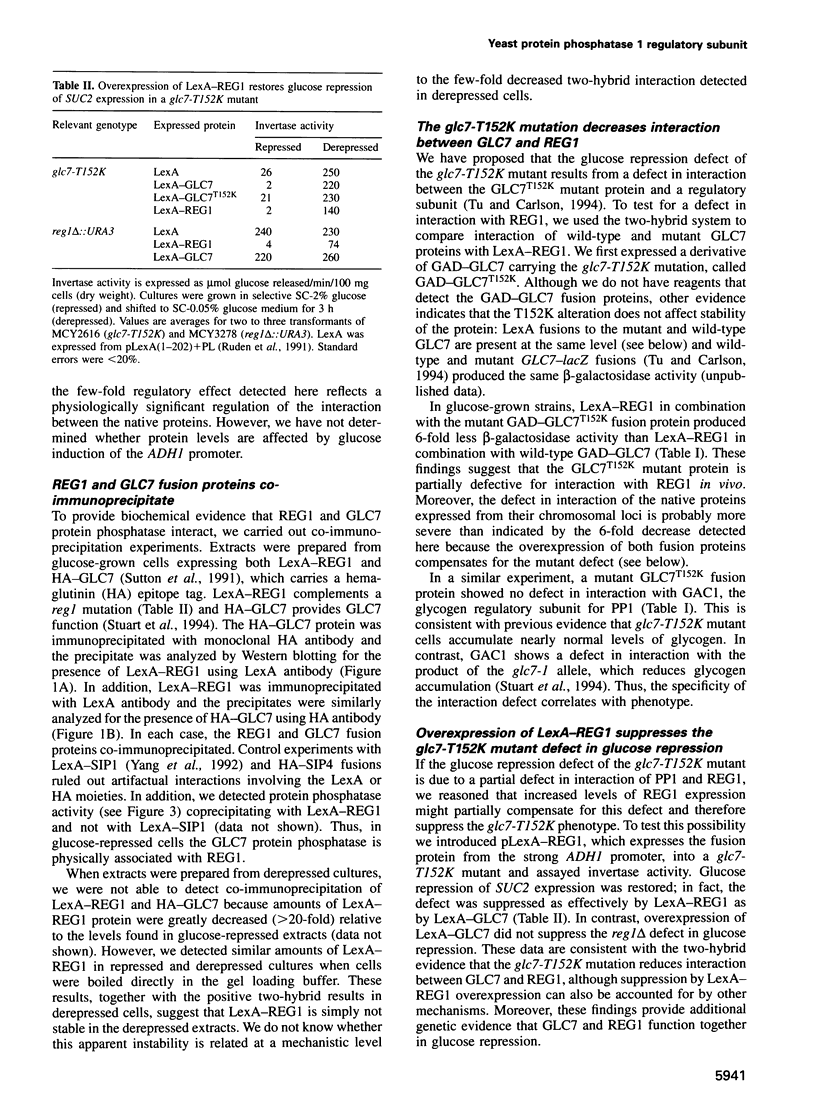
Protein phosphatase type 1 (PP1) is encoded by GLC7, an essential gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The GLC7 phosphatase is required for glucose repression and appears to function antagonistically to the SNF1 protein kinase. Previously, we characterized a mutation, glc7-T152K, that relieves glucose repression but does not interfere with the function of GLC7 in glycogen metabolism. We proposed that the mutant GLC7T152K phosphatase is defective in its interaction with a regulatory subunit that directs participation of PP1 in the glucose repression mechanism. Here, we present evidence that REG1, a protein required for glucose repression, is one such regulatory subunit. We show that REG1 is physically associated with GLC7. REG1 interacts with GLC7 strongly and specifically in the two-hybrid system, and REG1 and GLC7 fusion proteins co-immunoprecipitate from cell extracts. Moreover, overexpression of a REG1 fusion protein suppresses the glc7-T152K mutant defect in glucose repression. This and other genetic evidence indicate that the two proteins function together in regulating glucose repression. These results suggest that REG1 is a regulatory subunit of PP1 that targets its activity to proteins in the glucose repression regulatory pathway.
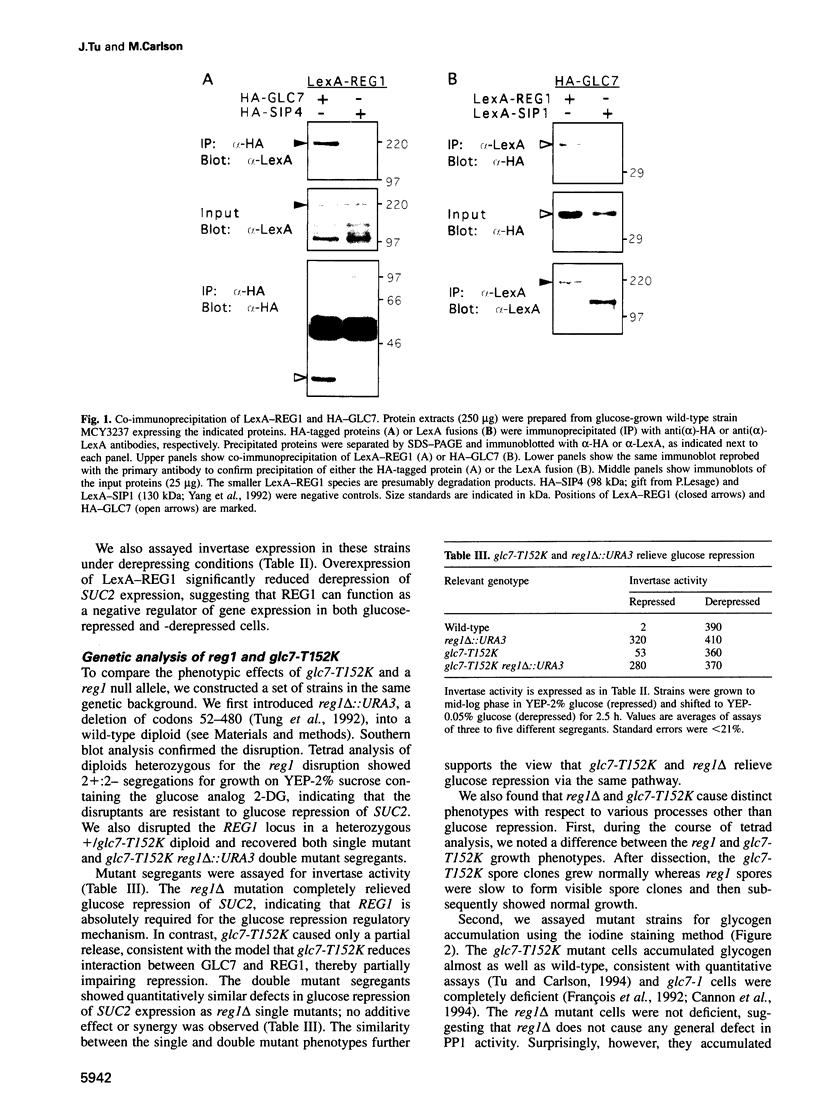
Full text
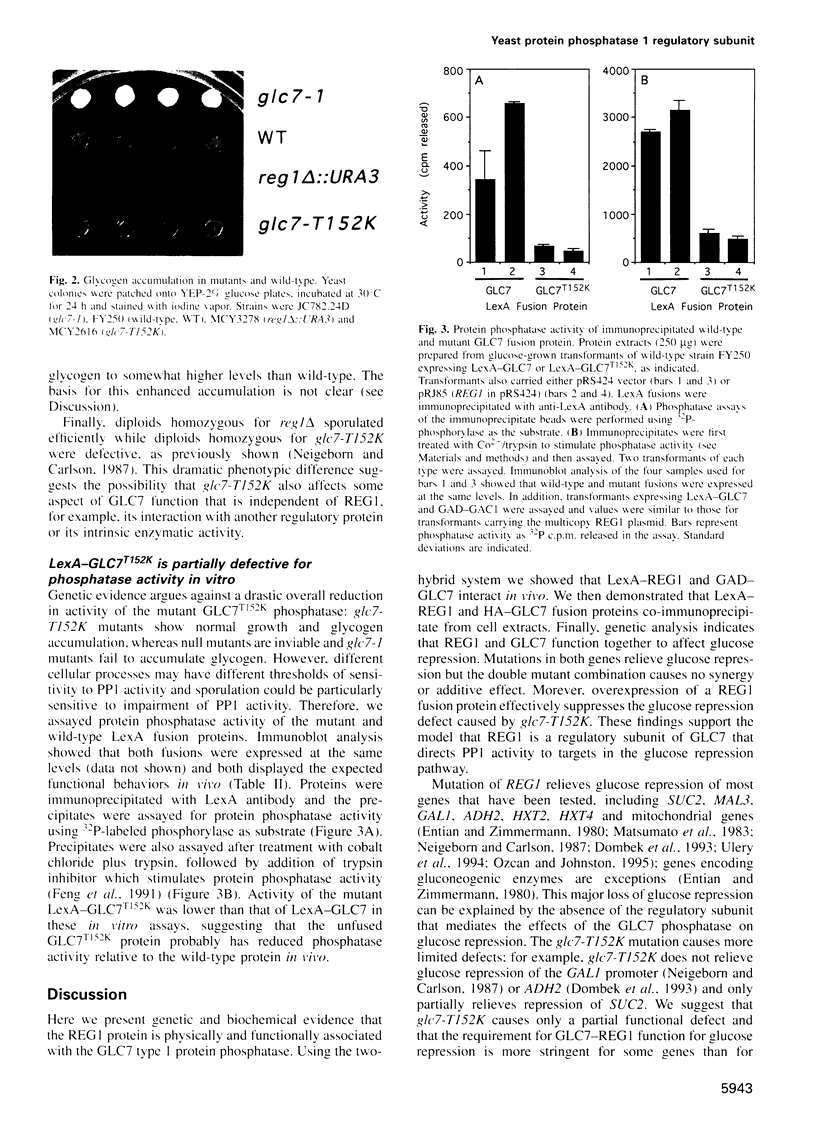
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axton J. M., Dombrádi V., Cohen P. T., Glover D. M. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90286-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Krebber H., Kempf T., Hermes I., Ponstingl H. Human RanGTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 is a homologue of yeast Rna1p involved in mRNA processing and transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1749–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of a type 1 protein phosphatase encoded by bws1+ in fission yeast mitotic control. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. F., Pringle J. R., Fiechter A., Khalil M. Characterization of glycogen-deficient glc mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1994 Feb;136(2):485–503. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester V. E. Heritable glycogen-storage deficiency in yeast and its induction by ultra-violet light. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Apr;51(1):49–56. doi: 10.1099/00221287-51-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Signal integration at the level of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and their substrates. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohadwala M., da Cruz e Silva E. F., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Carbonaro-Hall D. A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Berndt N. Phosphorylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 by cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombek K. M., Camier S., Young E. T. ADH2 expression is repressed by REG1 independently of mutations that alter the phosphorylation of the yeast transcription factor ADR1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4391–4399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D., Zimmermann F. K. Glycolytic enzymes and intermediates in carbon catabolite repression mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):345–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00267449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. R., Johnston M. Genetic and molecular characterization of GAL83: its interaction and similarities with other genes involved in glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 Nov;135(3):655–664. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Z. H., Wilson S. E., Peng Z. Y., Schlender K. K., Reimann E. M., Trumbly R. J. The yeast GLC7 gene required for glycogen accumulation encodes a type 1 protein phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23796–23801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francisco L., Wang W., Chan C. S. Type 1 protein phosphatase acts in opposition to IpL1 protein kinase in regulating yeast chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4731–4740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. M., Thompson-Jaeger S., Skroch J., Zellenka U., Spevak W., Tatchell K. GAC1 may encode a regulatory subunit for protein phosphatase type 1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):87–96. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisamoto N., Frederick D. L., Sugimoto K., Tatchell K., Matsumoto K. The EGP1 gene may be a positive regulator of protein phosphatase type 1 in the growth control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3767–3776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisamoto N., Sugimoto K., Matsumoto K. The Glc7 type 1 protein phosphatase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for cell cycle progression in G2/M. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3158–3165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Cohen P. On target with a new mechanism for the regulation of protein phosphorylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90109-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Redd M. J., Schultz J., Carlson M., Johnson A. D. Ssn6-Tup1 is a general repressor of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita N., Ohkura H., Yanagida M. Distinct, essential roles of type 1 and 2A protein phosphatases in the control of the fission yeast cell division cycle. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90173-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Bossolt K. L., Franke E. K., Kalpana G. V., Goff S. P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein binds to cyclophilins A and B. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1067–1078. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90637-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKelvie S. H., Andrews P. D., Stark M. J. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene SDS22 encodes a potential regulator of the mitotic function of yeast type 1 protein phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3777–3785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yoshimatsu T., Oshima Y. Recessive mutations conferring resistance to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1405–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1405-1414.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermoud J. E., Cohen P. T., Lamond A. I. Regulation of mammalian spliceosome assembly by a protein phosphorylation mechanism. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5679–5688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06906.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Ronne H. Yeast MIG1 repressor is related to the mammalian early growth response and Wilms' tumour finger proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2891–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Mutations causing constitutive invertase synthesis in yeast: genetic interactions with snf mutations. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):247–253. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederacher D., Entian K. D. Characterization of Hex2 protein, a negative regulatory element necessary for glucose repression in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Yanagida M. S. pombe gene sds22+ essential for a midmitotic transition encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein that positively modulates protein phosphatase-1. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90216-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozcan S., Johnston M. Three different regulatory mechanisms enable yeast hexose transporter (HXT) genes to be induced by different levels of glucose. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruden D. M., Ma J., Li Y., Wood K., Ptashne M. Generating yeast transcriptional activators containing no yeast protein sequences. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):250–252. doi: 10.1038/350250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. M., Yamano H., Kinoshita N., Yanagida M. Mitotic regulation of protein phosphatases by the fission yeast sds22 protein. Curr Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):13–26. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90140-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. S., Frederick D. L., Varner C. M., Tatchell K. The mutant type 1 protein phosphatase encoded by glc7-1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae fails to interact productively with the GAC1-encoded regulatory subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):896–905. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Lin F., Arndt K. T. The SIT4 protein phosphatase is required in late G1 for progression into S phase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:75–81. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treitel M. A., Carlson M. Repression by SSN6-TUP1 is directed by MIG1, a repressor/activator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3132–3136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu J., Carlson M. The GLC7 type 1 protein phosphatase is required for glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6789–6796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu J., Vallier L. G., Carlson M. Molecular and genetic analysis of the SNF7 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1993 Sep;135(1):17–23. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., Norbeck L. L., Nolan S. L., Atkinson N. S., Hopper A. K. SRN1, a yeast gene involved in RNA processing, is identical to HEX2/REG1, a negative regulator in glucose repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2673–2680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulery T. L., Jang S. H., Jaehning J. A. Glucose repression of yeast mitochondrial transcription: kinetics of derepression and role of nuclear genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1160–1170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Cannon J. F., Dever T. E., Hinnebusch A. G. Truncated protein phosphatase GLC7 restores translational activation of GCN4 expression in yeast mutants defective for the eIF-2 alpha kinase GCN2. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5700–5710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., Hubbard E. J., Carlson M. A protein kinase substrate identified by the two-hybrid system. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):680–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1496382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., Jiang R., Carlson M. A family of proteins containing a conserved domain that mediates interaction with the yeast SNF1 protein kinase complex. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5878–5886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Guha S., Volkert F. C. The Saccharomyces SHP1 gene, which encodes a regulator of phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 with differential effects on glycogen metabolism, meiotic differentiation, and mitotic cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2037–2050. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




