Abstract
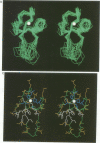
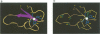
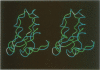
Xenopus nuclear factor XNF7, a maternally expressed protein, functions in patterning of the embryo. XNF7 contains a number of defined protein domains implicated in the regulation of some developmental processes. Among these is a tripartite motif comprising a zinc-binding RING finger and B-box domain next to a predicted alpha-helical coiled-coil domain. Interestingly, this motif is found in a variety of protein including several proto-oncoproteins. Here we describe the solution structure of the XNF7 B-box zinc-binding domain determined at physiological pH by 1H NMR methods. The B-box structure represents the first three-dimensional structure of this new motif and comprises a monomer have two beta-strands, two helical turns and three extended loop regions packed in a novel topology. The r.m.s. deviation for the best 18 structures is 1.15 A for backbone atoms and 1.94 A for all atoms. Structure calculations and biochemical data shows one zinc atom ligated in a Cys2-His2 tetrahedral arrangement. We have used mutant peptides to determine the metal ligation scheme which surprisingly shows that not all of the seven conserved cysteines/histidines in the B-box motif are involved in metal ligation. The B-box structure is not similar in tertiary fold to any other known zinc-binding motif.
Full text
PDF
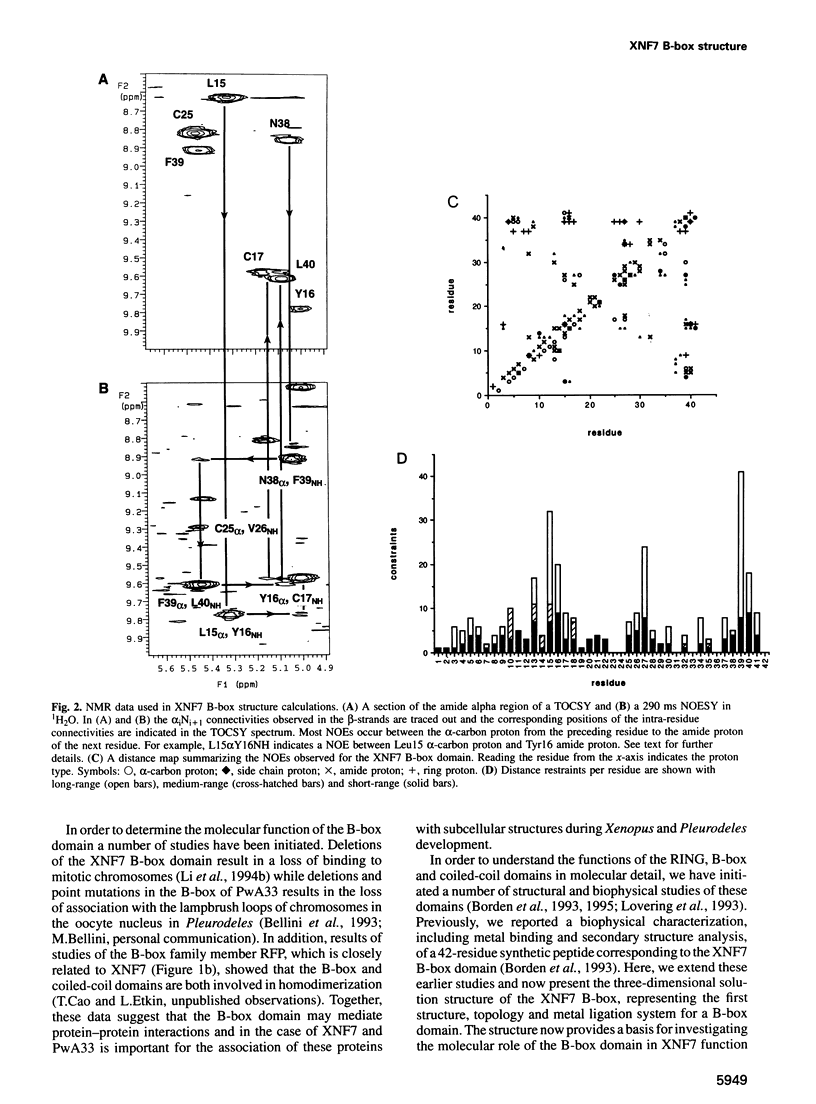
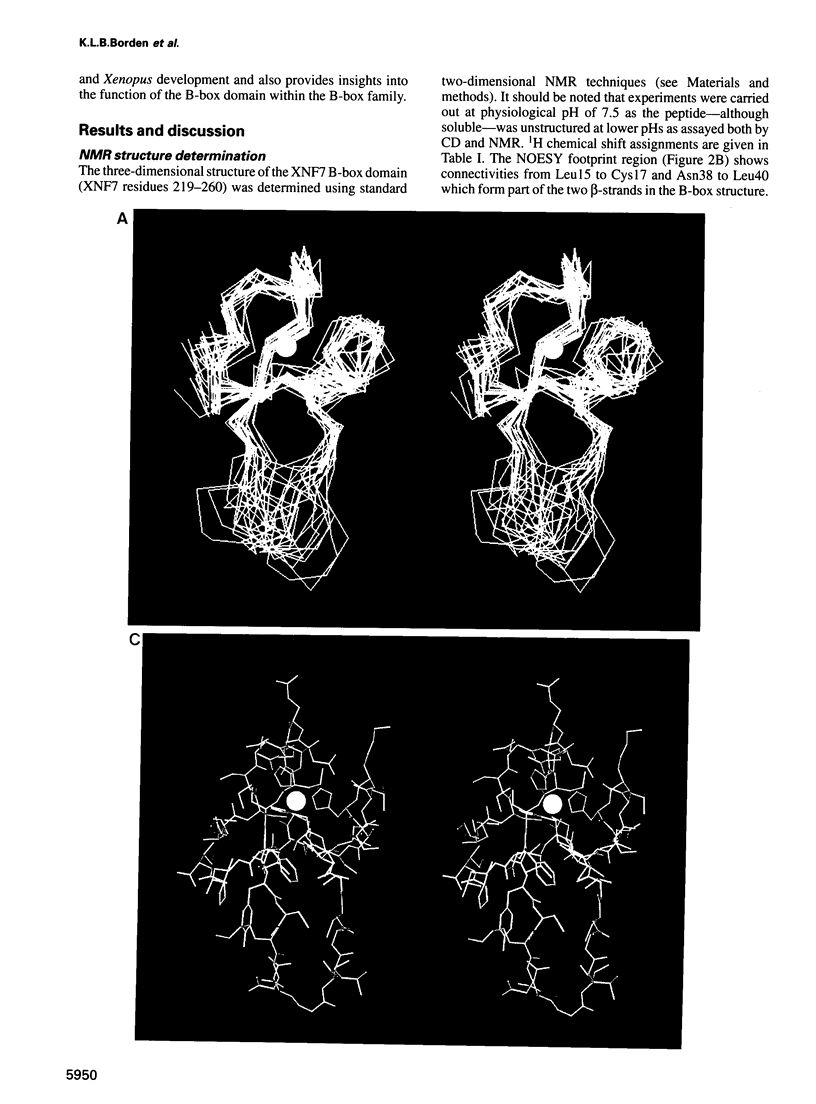
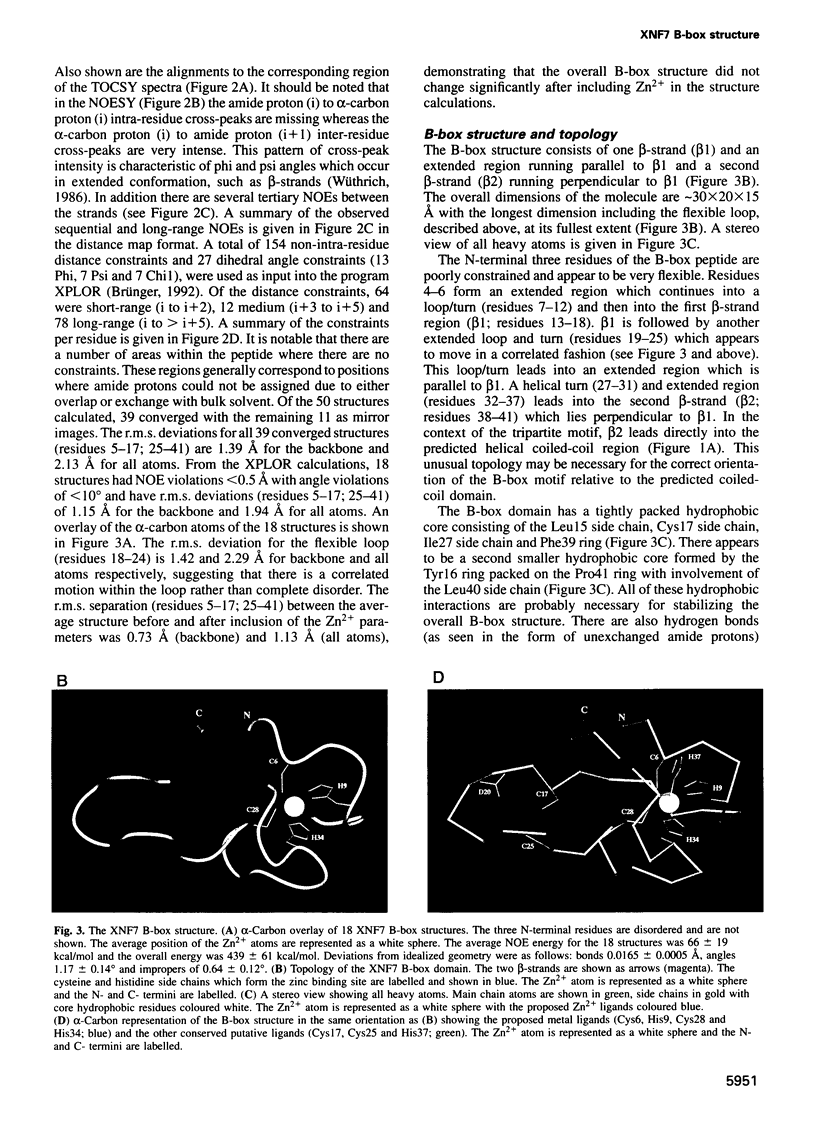
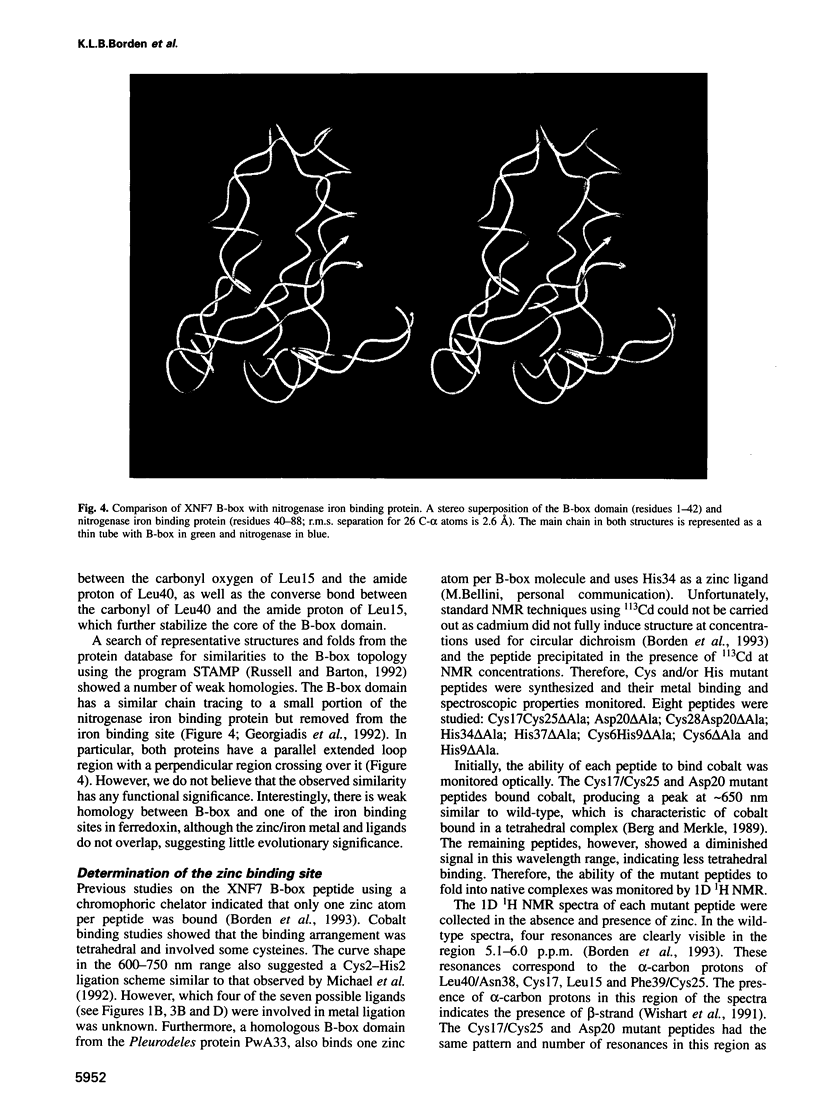




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellini M., Lacroix J. C., Gall J. G. A putative zinc-binding protein on lampbrush chromosome loops. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden K. L., Boddy M. N., Lally J., O'Reilly N. J., Martin S., Howe K., Solomon E., Freemont P. S. The solution structure of the RING finger domain from the acute promyelocytic leukaemia proto-oncoprotein PML. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1532–1541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
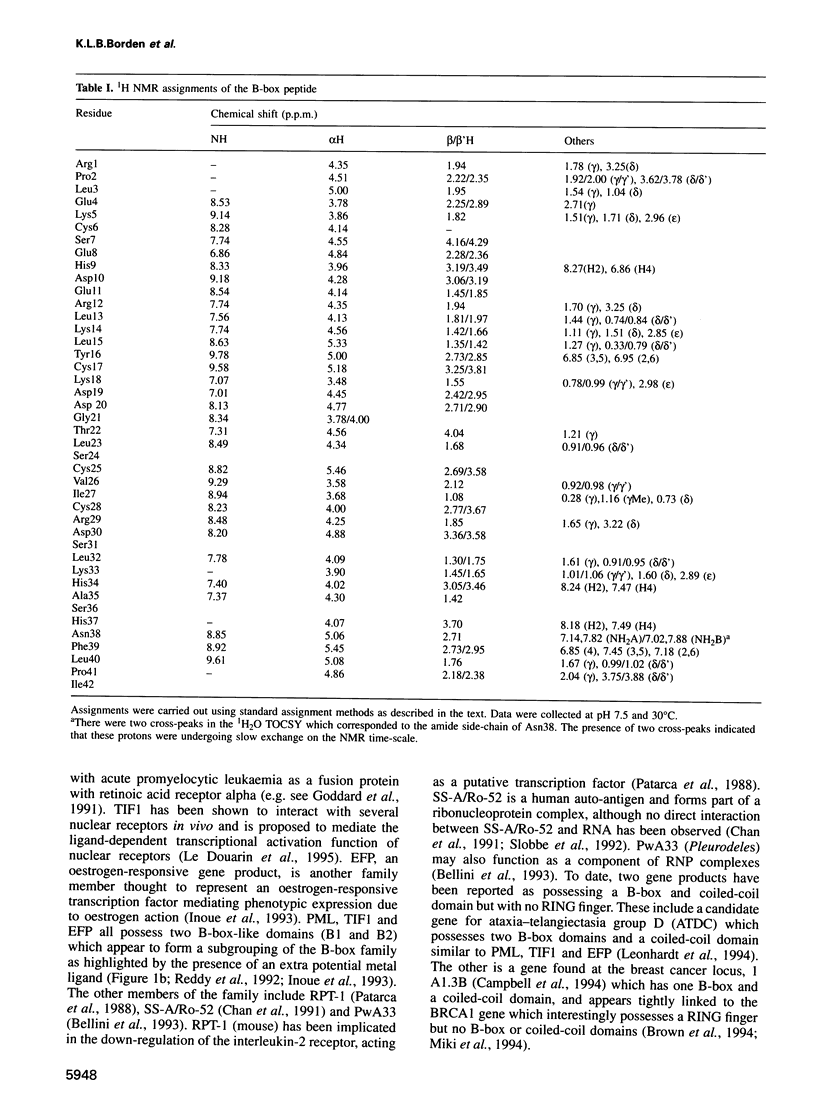
- Borden K. L., Martin S. R., O'Reilly N. J., Lally J. M., Reddy B. A., Etkin L. D., Freemont P. S. Characterisation of a novel cysteine/histidine-rich metal binding domain from Xenopus nuclear factor XNF7. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 6;335(2):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80741-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. A., Nicolai H., Xu C. F., Griffiths B. L., Jones K. A., Solomon E., Hosking L., Trowsdale J., Black D. M., McFarlane R. Regulation of BRCA1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):733–733. doi: 10.1038/372733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. G., Nicolai H. M., Foulkes W. D., Senger G., Stamp G. W., Allan G., Boyer C., Jones K., Bast R. C., Jr, Solomon E. A novel gene encoding a B-box protein within the BRCA1 region at 17q21.1. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):589–594. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Hamel J. C., Buyon J. P., Tan E. M. Molecular definition and sequence motifs of the 52-kD component of human SS-A/Ro autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):68–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI115003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S. The RING finger. A novel protein sequence motif related to the zinc finger. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:174–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiadis M. M., Komiya H., Chakrabarti P., Woo D., Kornuc J. J., Rees D. C. Crystallographic structure of the nitrogenase iron protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1653–1659. doi: 10.1126/science.1529353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard A. D., Borrow J., Freemont P. S., Solomon E. Characterization of a zinc finger gene disrupted by the t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1720570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. B., Zhang T., Kim P. S., Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1401–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.8248779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Orimo A., Hosoi T., Kondo S., Toyoshima H., Kondo T., Ikegami A., Ouchi Y., Orimo H., Muramatsu M. Genomic binding-site cloning reveals an estrogen-responsive gene that encodes a RING finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11117–11121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakizuka A., Miller W. H., Jr, Umesono K., Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Murty V. V., Dmitrovsky E., Evans R. M. Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90112-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karas M., Hillenkamp F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal Chem. 1988 Oct 15;60(20):2299–2301. doi: 10.1021/ac00171a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Perez A., Lutz Y., Rochette-Egly C., Gaub M. P., Durand B., Lanotte M., Berger R., Chambon P. Structure, localization and transcriptional properties of two classes of retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion proteins in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): structural similarities with a new family of oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):629–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin B., Zechel C., Garnier J. M., Lutz Y., Tora L., Pierrat P., Heery D., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P., Losson R. The N-terminal part of TIF1, a putative mediator of the ligand-dependent activation function (AF-2) of nuclear receptors, is fused to B-raf in the oncogenic protein T18. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2020–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt E. A., Kapp L. N., Young B. R., Murnane J. P. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a candidate gene for ataxia-telangiectasia group D (ATDC). Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):130–136. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Shou W., Kloc M., Reddy B. A., Etkin L. D. Cytoplasmic retention of Xenopus nuclear factor 7 before the mid blastula transition uses a unique anchoring mechanism involving a retention domain and several phosphorylation sites. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):7–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Hanson I. M., Borden K. L., Martin S., O'Reilly N. J., Evan G. I., Rahman D., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J., Freemont P. S. Identification and preliminary characterization of a protein motif related to the zinc finger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael S. F., Kilfoil V. J., Schmidt M. H., Amann B. T., Berg J. M. Metal binding and folding properties of a minimalist Cys2His2 zinc finger peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4796–4800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Crescenzi M., Molloy C. J., Blam S. B., Reynolds S. H., Aaronson S. A. Development of a highly efficient expression cDNA cloning system: application to oncogene isolation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5167–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Swensen J., Shattuck-Eidens D., Futreal P. A., Harshman K., Tavtigian S., Liu Q., Cochran C., Bennett L. M., Ding W. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):66–71. doi: 10.1126/science.7545954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Kloc M., Reddy B., Eastman E., Dreyer C., Etkin L. xlgv7: a maternal gene product localized in nuclei of the central nervous system in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):572–583. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M., Reddy B. A., Kloc M., Li X. X., Dreyer C., Etkin L. D. The nuclear-cytoplasmic distribution of the Xenopus nuclear factor, xnf7, coincides with its state of phosphorylation during early development. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):569–575. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus D., Nakaseko Y., Schwabe J. W., Klug A. Solution structures of two zinc-finger domains from SWI5 obtained using two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. A zinc-finger structure with a third strand of beta-sheet. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):637–651. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90846-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins from interproton distance data by hybrid distance geometry-dynamical simulated annealing calculations. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. A., Etkin L. D. A unique bipartite cysteine-histidine motif defines a subfamily of potential zinc-finger proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6330–6330. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. A., Etkin L. D., Freemont P. S. A novel zinc finger coiled-coil domain in a family of nuclear proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Sep;17(9):344–345. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90308-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. A., Kloc M., Etkin L. The cloning and characterization of a maternally expressed novel zinc finger nuclear phosphoprotein (xnf7) in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1991 Nov;148(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90321-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. B., Barton G. J. Multiple protein sequence alignment from tertiary structure comparison: assignment of global and residue confidence levels. Proteins. 1992 Oct;14(2):309–323. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobbe R. L., Pluk W., van Venrooij W. J., Pruijn G. J. Ro ribonucleoprotein assembly in vitro. Identification of RNA-protein and protein-protein interactions. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90890-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Inaguma Y., Hiai H., Hirose F. Developmentally regulated expression of a human "finger"-containing gene encoded by the 5' half of the ret transforming gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1853–1856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Braun W., Havel T. F., Schaumann T., Go N., Wüthrich K. Protein structures in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. The polypeptide fold of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor determined using two different algorithms, DISGEO and DISMAN. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):611–639. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart D. S., Sykes B. D., Richards F. M. Relationship between nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift and protein secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):311–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90214-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Lavau C., Marchio A., Chomienne C., Degos L., Dejean A. The PML-RAR alpha fusion mRNA generated by the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90113-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]