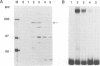
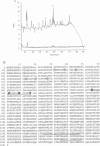
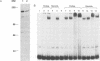
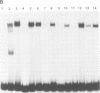
Abstract
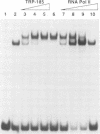
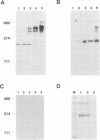
Activation of HIV-1 gene expression by the transactivator Tat is dependent on an RNA regulatory element located downstream of the transcription initiation site known as TAR. To characterize cellular factors that bind to TAR RNA and are involved in the regulation of HIV-1 transcription, HeLa nuclear extract was fractionated and RNA gel-retardation analysis was performed. This analysis indicated that only two cellular factors, RNA polymerase II and the previously characterized TAR RNA loop binding protein TRP-185, were capable of binding specifically to TAR RNA. To elucidate the function of TRP-185, it was purified from HeLa nuclear extract, amino acid microsequence analysis was performed and a cDNA encoding TRP-185 was isolated. TRP-185 is a novel protein of 1621 amino acids which contains a leucine zipper and potentially a novel RNA binding motif. In gel-retardation assays, the binding of both recombinant TRP-185 and RNA polymerase II was dependent on the presence of an additional group of proteins designated cellular cofactors. Both the TAR RNA loop and bulge sequences were critical for RNA polymerase II binding, while TRP-185 binding was dependent only on TAR RNA loop sequences. Since binding of TRP-185 and RNA polymerase II to TAR RNA was found to be mutually exclusive, our results suggest that TRP-185 may function either alone or in conjunction with Tat to disengage RNA polymerase II which is stalled upon binding to nascently synthesized TAR RNA during transcriptional elongation.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Aloni Y. Transcriptional elongation by purified RNA polymerase II is blocked at the trans-activation-responsive region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4910–4918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4910-4918.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is sequence specific for both the single-stranded bulge and loop of the trans-acting-responsive hairpin: a quantitative analysis. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5501–5504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5501-5504.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
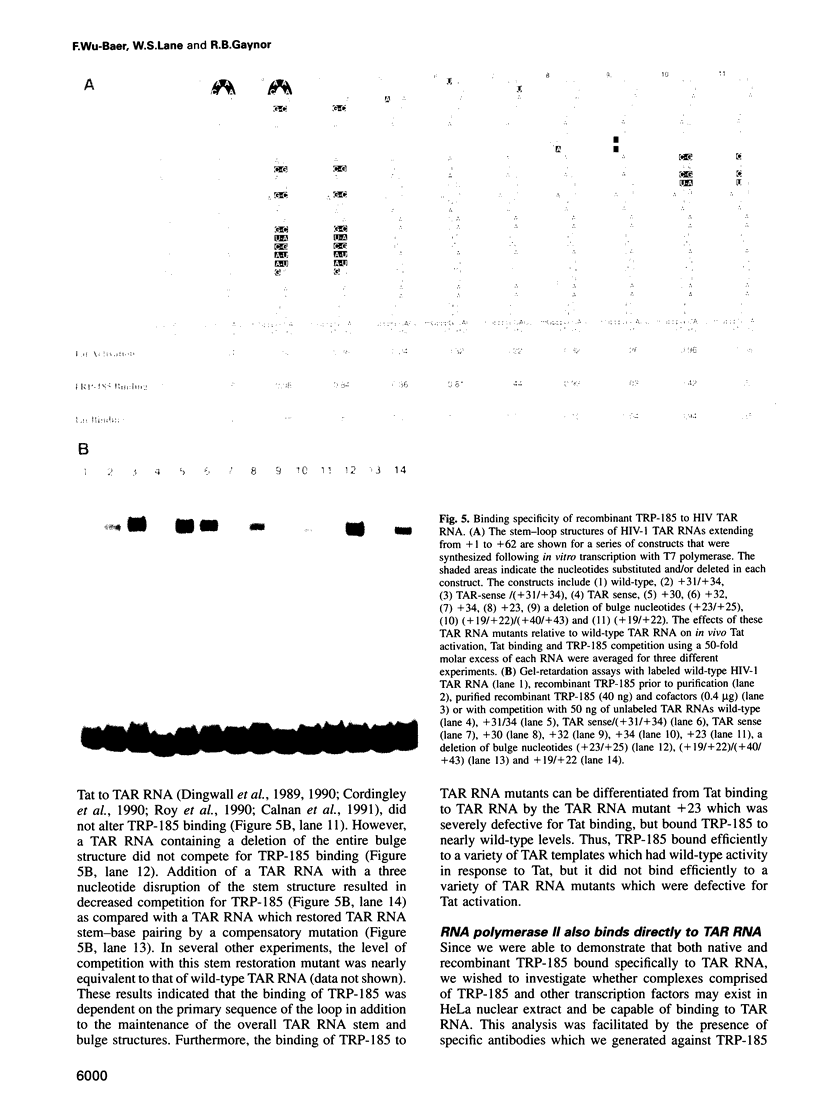
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. New models for the mechanism of transcription elongation and its regulation. Harvey Lect. 1992 1993;88:1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher M. J., Lowe A. D., Gait M. J., Karn J. The RNA element encoded by the trans-activation-responsive region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is functional when displaced downstream of the start of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2408–2412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase by the murine homologue of the cell-cycle control protein cdc2. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):679–684. doi: 10.1038/339679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., LaFemina R. L., Callahan P. L., Condra J. H., Sardana V. V., Graham D. J., Nguyen T. M., LeGrow K., Gotlib L., Schlabach A. J. Sequence-specific interaction of Tat protein and Tat peptides with the transactivation-responsive sequence element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8985–8989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Control of transcription termination by RNA-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:893–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.004333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elroy-Stein O., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Cap-independent translation of mRNA conferred by encephalomyocarditis virus 5' sequence improves the performance of the vaccinia virus/bacteriophage T7 hybrid expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6126–6130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Soultanakis E., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 LTR TATA and TAR region sequences required for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):765–778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Wu F. K., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Interactions of cellular proteins involved in the transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3761–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. Cellular transcription factors involved in the regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):347–363. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Transcription factors IIE and IIH and ATP hydrolysis direct promoter clearance by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeble M. A., Churcher M. J., Lowe A. D., Gait M. J., Karn J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivator protein, tat, stimulates transcriptional read-through of distal terminator sequences in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6184–6188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gonazalez J., Gaynor R. Role of SP1-binding domains in in vivo transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2585-2591.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Hsu C., Race E., Gaynor R. B. Differential growth kinetics are exhibited by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR mutants. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5899–5910. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5899-5910.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. E., Galphin J. C., Westhafer M. A., Schochetman G. TAR loop-dependent human immunodeficiency virus trans activation requires factors encoded on human chromosome 12. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):5020–5024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.5020-5024.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The RNA polymerase II ternary complex cleaves the nascent transcript in a 3'----5' direction in the presence of elongation factor SII. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1342–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
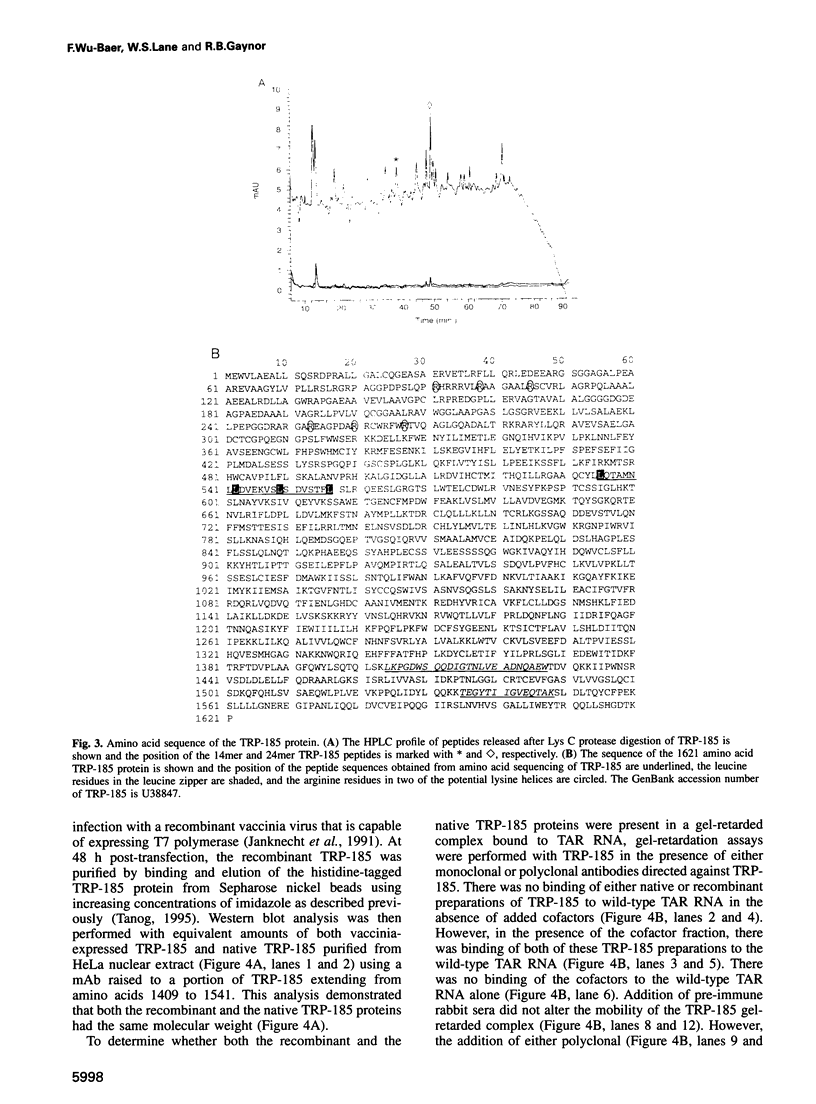
- Janknecht R., de Martynoff G., Lou J., Hipskind R. A., Nordheim A., Stunnenberg H. G. Rapid and efficient purification of native histidine-tagged protein expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8972–8976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. L., Chamberlin M. J. Complexes of yeast RNA polymerase II and RNA are substrates for TFIIS-induced RNA cleavage. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. RNA polymerase: regulation of transcript elongation and termination. FASEB J. 1991 Oct;5(13):2833–2842. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.13.1916107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaver B., Berkhout B. Evolution of a disrupted TAR RNA hairpin structure in the HIV-1 virus. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2650–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
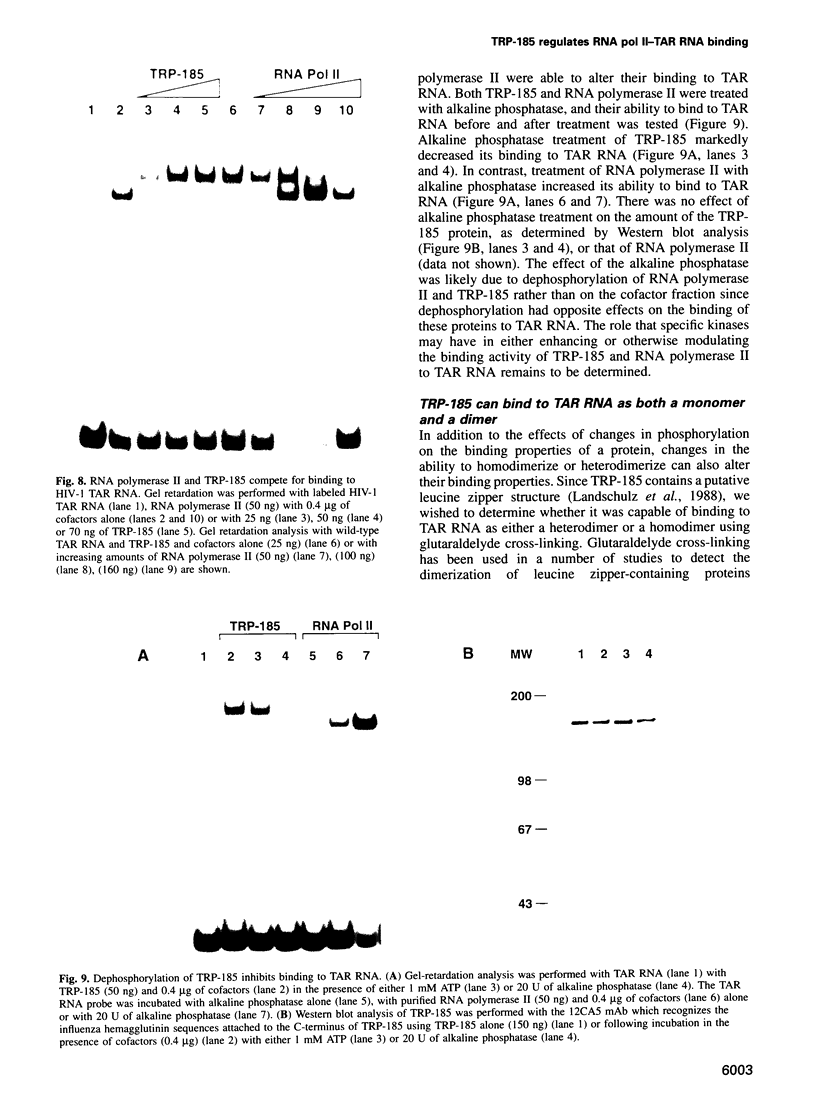
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane W. S., Galat A., Harding M. W., Schreiber S. L. Complete amino acid sequence of the FK506 and rapamycin binding protein, FKBP, isolated from calf thymus. J Protein Chem. 1991 Apr;10(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01024778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. HIV-1 Tat protein increases transcriptional initiation and stabilizes elongation. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laspia M. F., Rice A. P., Mathews M. B. Synergy between HIV-1 Tat and adenovirus E1A is principally due to stabilization of transcriptional elongation. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2397–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Kraus K. W., Wolfner M. F., Lis J. T. DNA sequence requirements for generating paused polymerase at the start of hsp70. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):284–295. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Welsh T. M., Peterlin B. M. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat specifies two different transcription complexes, only one of which is regulated by Tat. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1752–1760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1752-1760.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein trans-activates transcription in vitro. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):791–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxon M. E., Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Transcription factor IIE binds preferentially to RNA polymerase IIa and recruits TFIIH: a model for promoter clearance. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 1;8(5):515–524. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Rogge L., Foeckler R., Karaghiosoff M., Winnacker E. L. Structural and functional organization of a porcine gene coding for nuclear factor I. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8191–8200. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Amons R. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudler E., Goldfarb A., Kashlev M. Discontinuous mechanism of transcription elongation. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):793–796. doi: 10.1126/science.8047884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudler E., Kashlev M., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Coupling between transcription termination and RNA polymerase inchworming. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T., Hardin S., Greenleaf A., Lis J. T. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain and transcriptional elongation. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):75–77. doi: 10.1038/370075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Rosen C. A. Contribution of the TATA motif to Tat-mediated transcriptional activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5594–5597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5594-5597.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou S. H., Garcia-Martínez L. F., Paulssen E. J., Gaynor R. B. Role of flanking E box motifs in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TATA element function. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7188–7199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7188-7199.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Walker M. D. Elevated levels of mRNA can account for the trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9734–9738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasabapathy R., Sheldon M., Johal L., Hernandez N. The HIV-1 long terminal repeat contains an unusual element that induces the synthesis of short RNAs from various mRNA and snRNA promoters. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2061–2074. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon M., Ratnasabapathy R., Hernandez N. Characterization of the inducer of short transcripts, a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcriptional element that activates the synthesis of short RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1251–1263. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline C. T., Milocco L. H., Jones K. A. Two distinct nuclear transcription factors recognize loop and bulge residues of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2508–2520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Ebright R. H. Rapid RNA polymerase genetics: one-day, no-column preparation of reconstituted recombinant Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Meier T. I., Chan C. L., Feng G., Lee D. N., Landick R. Discontinuous movements of DNA and RNA in RNA polymerase accompany formation of a paused transcription complex. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Crothers D. M. RNA recognition by Tat-derived peptides: interaction in the major groove? Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):577–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Garcia J., Sigman D., Gaynor R. tat regulates binding of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activating region RNA loop-binding protein TRP-185. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2128–2140. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Sharp P. A. Novel mechanism and factor for regulation by HIV-1 Tat. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):321–328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]