Abstract
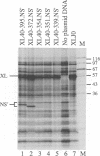
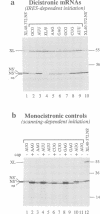
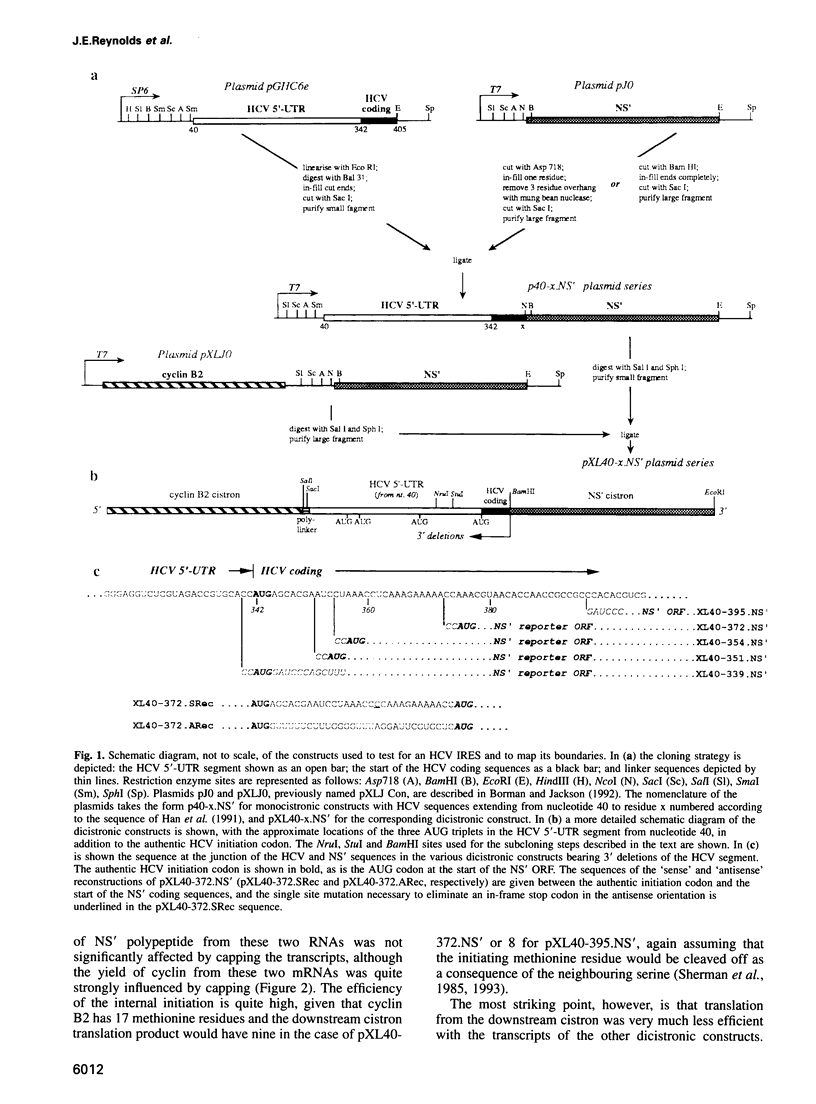
The question of whether hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA is translated by a mechanism of internal ribosome entry has been examined by testing whether insertion of HCV sequences between the two cistrons of a dicistronic mRNA promotes translation of the downstream cistron in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Deletion analysis showed that efficient internal initiation required a segment of the HCV genome extending from about nucleotides 40-370 and that deletions from the 3'-end of this element were highly deleterious. As the authentic initiation codon for HCV polyprotein synthesis is at nucleotide 342, this demonstrates that, besides 5'-UTR sequences, a short length of HCV coding sequences is required for internal initiation. This finding was confirmed in transfection assays of BT7-H cells and was shown to be independent of the nature of the downstream reporter cistron. The strong requirement for coding sequences is in sharp contrast to internal initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. As a probable correlate with this, it was also found that the efficiency of internal initiation was only marginally compromised when the authentic initiation codon was mutated to a non-AUG codon, again in sharp contrast with the picornaviruses. The finding that coding sequences are required for internal initiation has important implications for the design of experiments to test for internal initiation of translation of cellular mRNAs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeck R., Curran J., Matsuoka Y., Compans R., Kolakofsky D. The parainfluenza virus type 1 P/C gene uses a very efficient GUG codon to start its C' protein. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1765–1768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1765-1768.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeck R., Kolakofsky D. Positions +5 and +6 can be major determinants of the efficiency of non-AUG initiation codons for protein synthesis. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3608–3617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borman A., Jackson R. J. Initiation of translation of human rhinovirus RNA: mapping the internal ribosome entry site. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90523-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Zhang H., Ping L. H., Lemon S. M. Secondary structure of the 5' nontranslated regions of hepatitis C virus and pestivirus genomic RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5041–5045. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. Sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. C., Jackson R. J. Efficient initiation of mammalian mRNA translation at a CUG codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6485–6497. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Martínez-Salas E., Sobrino F., de la Torre J. C., Portela A., Ortín J., López-Galindez C., Pérez-Breña P., Villanueva N., Nájera R. The quasispecies (extremely heterogeneous) nature of viral RNA genome populations: biological relevance--a review. Gene. 1985;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi S., Katayama K., Kurihara C., Ishiyama N., Hoshino F. B., Ando T., Oya A. Complete 5' noncoding region is necessary for the efficient internal initiation of hepatitis C virus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):425–432. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünert S., Jackson R. J. The immediate downstream codon strongly influences the efficiency of utilization of eukaryotic translation initiation codons. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3618–3630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Shyamala V., Richman K. H., Brauer M. J., Irvine B., Urdea M. S., Tekamp-Olson P., Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Houghton M. Characterization of the terminal regions of hepatitis C viral RNA: identification of conserved sequences in the 5' untranslated region and poly(A) tails at the 3' end. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. L., Kaminski A., Jackson R. J. The influence of viral coding sequences on the efficiency of internal initiation of translation of cardiovirus RNAs. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):801–807. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J. A detailed kinetic analysis of the in vitro synthesis and processing of encephalomyocarditis virus products. Virology. 1986 Feb;149(1):114–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt S. L., Gibbs C. L., Kaminski A. Internal initiation of translation of picornavirus RNAs. Mol Biol Rep. 1994 May;19(3):147–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00986957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Belsham G. J., Jackson R. J. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: parameters influencing the selection of the internal initiation site. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1673–1681. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Hunt S. L., Gibbs C. L., Jackson R. J. Internal initiation of mRNA translation in eukaryotes. Genet Eng (N Y) 1994;16:115–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Nicholson R., Sonenberg N. In vitro mutational analysis of cis-acting RNA translational elements within the poliovirus type 2 5' untranslated region. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5895–5901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5895-5901.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Ono E., Gupta K. C. Initiation of translation at CUG, GUG, and ACG codons in mammalian cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S. Translation initiation at non-AUG triplets in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5031–5035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Flynn M. E., Kaplan G., Racaniello V., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of upstream AUG codons of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4486–4492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4486-4492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Gmyl A. P., Maslova S. V., Svitkin Y. V., Sinyakov A. N., Agol V. I. Prokaryotic-like cis elements in the cap-independent internal initiation of translation on picornavirus RNA. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90211-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Hesse R., Pallansch M. A., Nottay B. K., Kew O. M. Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus type 1 genotypes. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnbrand R., Bredenbeek P., van der Straaten T., Whetter L., Inchauspé G., Lemon S., Spaan W. Almost the entire 5' non-translated region of hepatitis C virus is required for cap-independent translation. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 29;365(2-3):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00458-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Miyamura T., Ohbayashi A., Harada H., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Watanabe Y., Koi S., Onji M., Ohta Y. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6547–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W., Tsunasawa S. Methionine or not methionine at the beginning of a protein. Bioessays. 1985 Jul;3(1):27–31. doi: 10.1002/bies.950030108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., McOmish F., Yap P. L., Chan S. W., Lin C. K., Dusheiko G., Saeed A. A., Holmes E. C. Sequence variability in the 5' non-coding region of hepatitis C virus: identification of a new virus type and restrictions on sequence diversity. J Gen Virol. 1993 Apr;74(Pt 4):661–668. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-4-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa A., Mori C., Fuke I., Manabe S., Murakami S., Fujita J., Onishi E., Andoh T., Yoshida I., Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1105-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama-Kohara K., Iizuka N., Kohara M., Nomoto A. Internal ribosome entry site within hepatitis C virus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1476–1483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1476-1483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Sarnow P., Siddiqui A. Translation of human hepatitis C virus RNA in cultured cells is mediated by an internal ribosome-binding mechanism. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3338-3344.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetter L. E., Day S. P., Elroy-Stein O., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Low efficiency of the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA in directing cap-independent translation in permissive monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5253–5263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5253-5263.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo B. J., Spaete R. R., Geballe A. P., Selby M., Houghton M., Han J. H. 5' end-dependent translation initiation of hepatitis C viral RNA and the presence of putative positive and negative translational control elements within the 5' untranslated region. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):889–899. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90264-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]