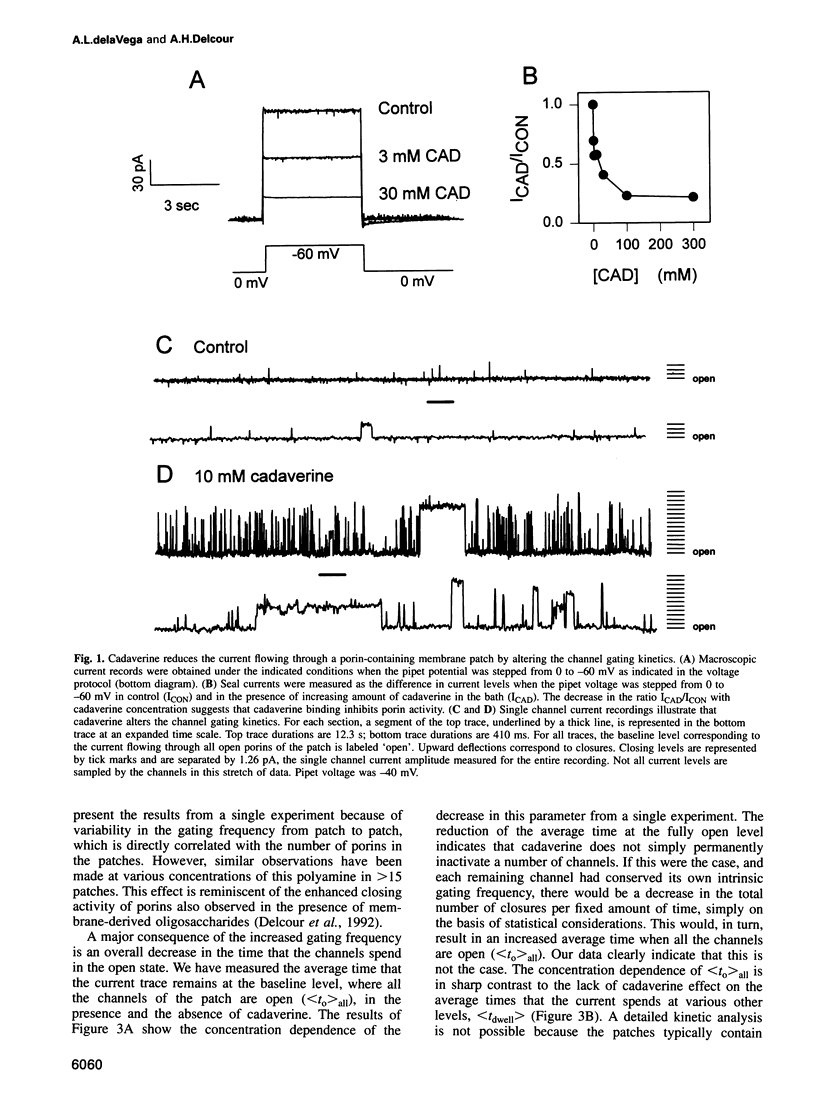
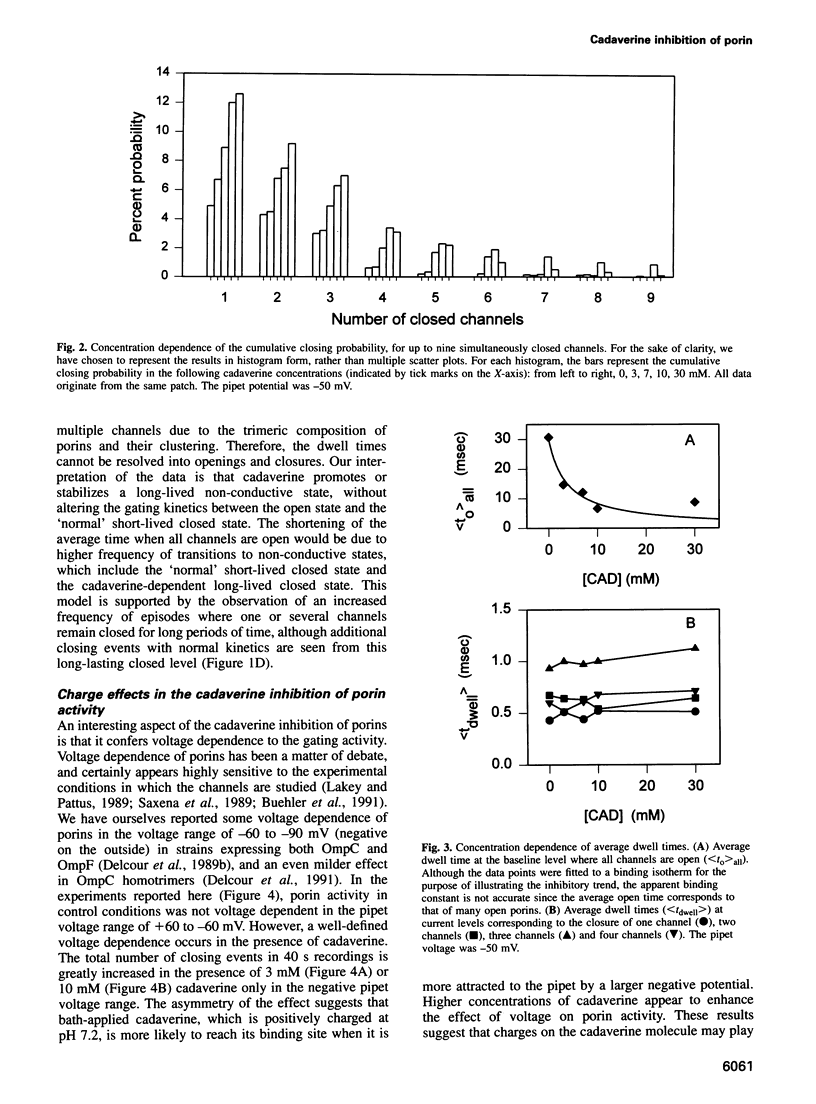
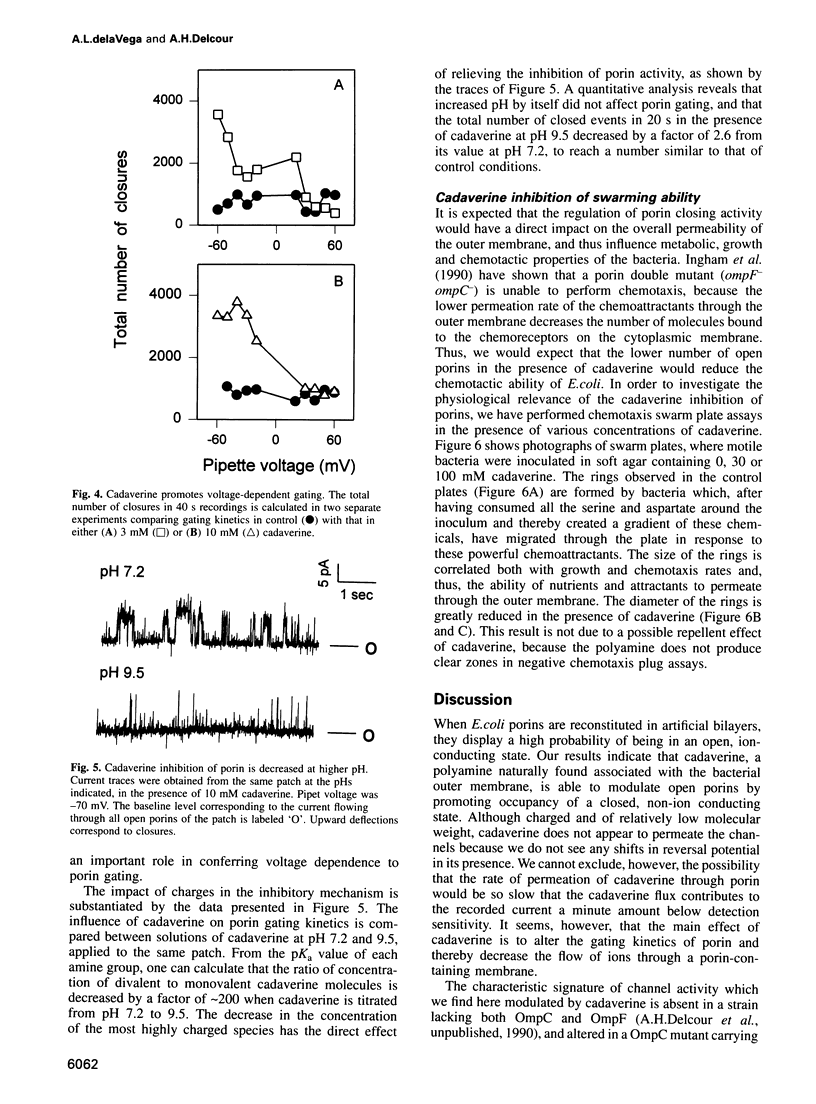
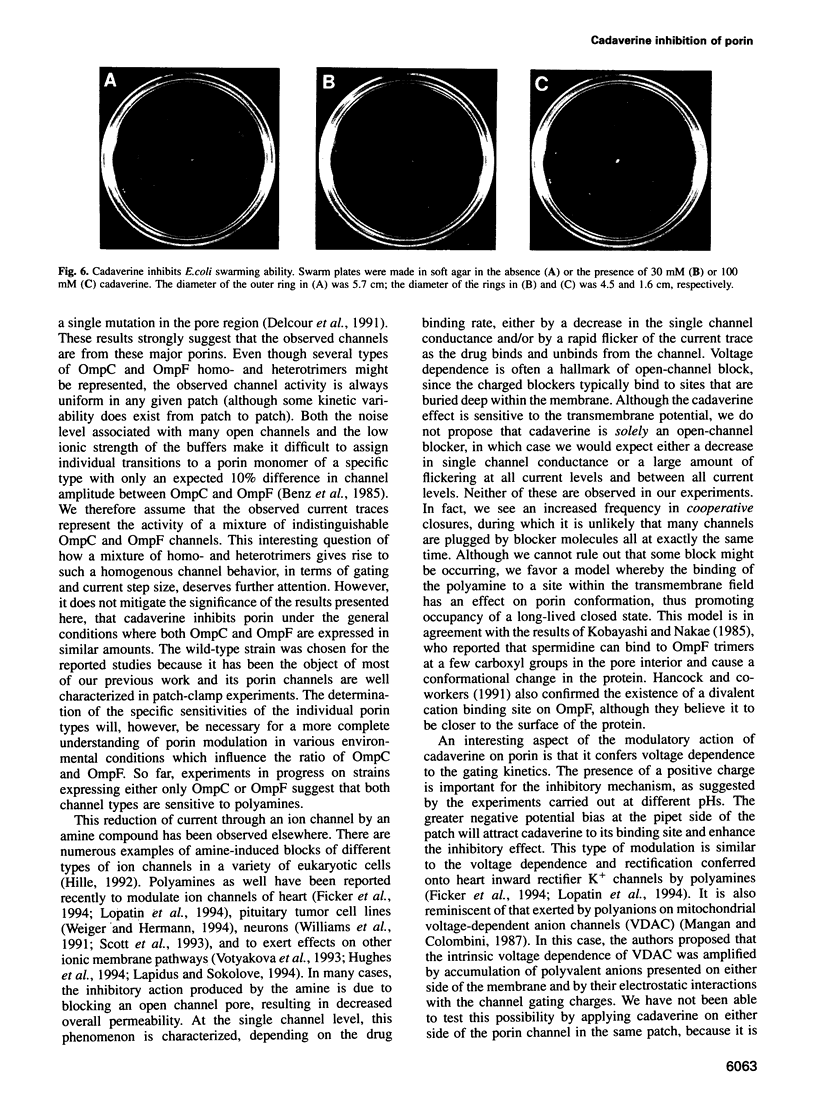
Abstract
We have used the electrophysiological technique of patch-clamp to study the modulation of Escherichia coli porins by cadaverine. Porin channels typically have a very high probability to be open, and were not known to be inhibited by specific compounds until the present study. Experiments performed on patches of outer membrane reconstituted in liposomes reveal that cadaverine applied to the periplasmic side increases the frequency of channel closures in a concentration-dependent fashion, and thereby decreases the total amount of ion flux through a porin-containing membrane. The positive charge on cadaverine is important for inhibition, because the effect is relieved at higher pH where fewer polyamine molecules are charged. Modulation is observed only at negative pipet voltages, and therefore confers voltage dependence to porin activity. Cadaverine increases the number and duration of cooperative closures of more than one channel, suggesting that it does not merely block the pore but exerts its kinetic effect allosterically. As a biological assay of porin inhibition, E. coli behavior in chemotaxis swarm plates was tested and found to be impaired in the presence of cadaverine. Polyamines are naturally found associated with the outer membrane of E.coli, but are lost upon fractionation. We postulate that cadaverine might be a natural regulator of porin activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Schmid A., Hancock R. E. Ion selectivity of gram-negative bacterial porins. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.722-727.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R. Structure and function of porins from gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:359–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buch J. K., Boyle S. M. Biosynthetic arginine decarboxylase in Escherichia coli is synthesized as a precursor and located in the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):522–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.522-527.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechner M., Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Ion channel activities in the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buehler L. K., Kusumoto S., Zhang H., Rosenbusch J. P. Plasticity of Escherichia coli porin channels. Dependence of their conductance on strain and lipid environment. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24446–24450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan S. W., Schirmer T., Rummel G., Steiert M., Ghosh R., Pauptit R. A., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):727–733. doi: 10.1038/358727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dargent B., Hofmann W., Pattus F., Rosenbusch J. P. The selectivity filter of voltage-dependent channels formed by phosphoporin (PhoE protein) from E. coli. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):773–778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Adler J., Kung C. A single amino acid substitution alters conductance and gating of OmpC porin of Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1991 Feb;119(3):267–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01868731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Adler J., Kung C., Martinac B. Membrane-derived oligosaccharides (MDO's) promote closing of an E. coli porin channel. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80622-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Modified reconstitution method used in patch-clamp studies of Escherichia coli ion channels. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):631–636. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82710-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Voltage-sensitive ion channel of Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1989 Dec;112(3):267–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01870957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficker E., Taglialatela M., Wible B. A., Henley C. M., Brown A. M. Spermine and spermidine as gating molecules for inward rectifier K+ channels. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1068–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7973666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Farmer S. W., Li Z. S., Poole K. Interaction of aminoglycosides with the outer membranes and purified lipopolysaccharide and OmpF porin of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1309–1314. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G., Starling A. P., East J. M., Lee A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of the Ca(2+)-ATPase by spermine and other polycationic compounds. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 26;33(16):4745–4754. doi: 10.1021/bi00182a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham C., Buechner M., Adler J. Effect of outer membrane permeability on chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3577–3583. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3577-3583.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii J., Nakae T. Lipopolysaccharide promoted opening of the porin channel. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 12;320(3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80597-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Nakae T. The mechanism of ion selectivity of OmpF-porin pores of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski P., Vaara M. Polyamines as constituents of the outer membranes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3695–3699. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3695-3699.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Pattus F. The voltage-dependent activity of Escherichia coli porins in different planar bilayer reconstitutions. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):303–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus R. G., Sokolove P. M. The mitochondrial permeability transition. Interactions of spermine, ADP, and inorganic phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18931–18936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopatin A. N., Makhina E. N., Nichols C. G. Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):366–369. doi: 10.1038/372366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangan P. S., Colombini M. Ultrasteep voltage dependence in a membrane channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4896–4900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A comparative study on the genes for three porins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. DNA sequence of the osmoregulated ompC gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6932–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Signal transduction and gene regulation through the phosphorylation of two regulatory components: the molecular basis for the osmotic regulation of the porin genes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1077–1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan H., Lonsdale J. T., Alder G. Polarity-dependent voltage-gated porin channels from Escherichia coli in lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 29;1021(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90031-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro G. F., Hercules K., Morgan J., Sauerbier W. Dependence of the putrescine content of Escherichia coli on the osmotic strength of the medium. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1272–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Identification of the outer membrane protein of E. coli that produces transmembrane channels in reconstituted vesicle membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):877–884. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90913-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Porins and specific diffusion channels in bacterial outer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):3905–3908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with liposomes reconstituted from purified proteins. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.241-252.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Transport across the bacterial outer membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1993 Dec;25(6):581–589. doi: 10.1007/BF00770245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramani N., Hedeshian M., Freundlich M. micF antisense RNA has a major role in osmoregulation of OmpF in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(16):5005–5010. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.16.5005-5010.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes forms voltage-controlled channels in lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein in planar membranes: clusters of channels in a native environment and their functional reassembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Sutton K. G., Dolphin A. C. Interactions of polyamines with neuronal ion channels. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Apr;16(4):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen K., Hellman J., Nikaido H. Porin channels in intact cells of Escherichia coli are not affected by Donnan potentials across the outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1182–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todt J. C., Rocque W. J., McGroarty E. J. Effects of pH on bacterial porin function. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10471–10478. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Tokunaga H., Nakae T. The outer membrane permeability of Gram-negative bacteria: determination of permeability rate in reconstituted vesicle membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80700-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Votyakova T. V., Bazhenova E. N., Zvjagilskaya R. A. Yeast mitochondrial calcium uptake: regulation by polyamines and magnesium ions. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1993 Oct;25(5):569–574. doi: 10.1007/BF01108413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiger T., Hermann A. Polyamines block Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in pituitary tumor cells (GH3). J Membr Biol. 1994 Jun;140(2):133–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00232901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K., Romano C., Dichter M. A., Molinoff P. B. Modulation of the NMDA receptor by polyamines. Life Sci. 1991;48(6):469–498. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90463-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. Z., Shi B., McGroarty E. J., Tien H. T. Channel-closing activity of porins from Escherichia coli in bilayer lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 6;862(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



