Abstract
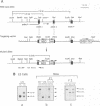
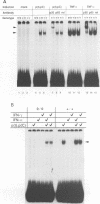
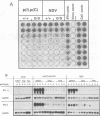
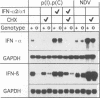
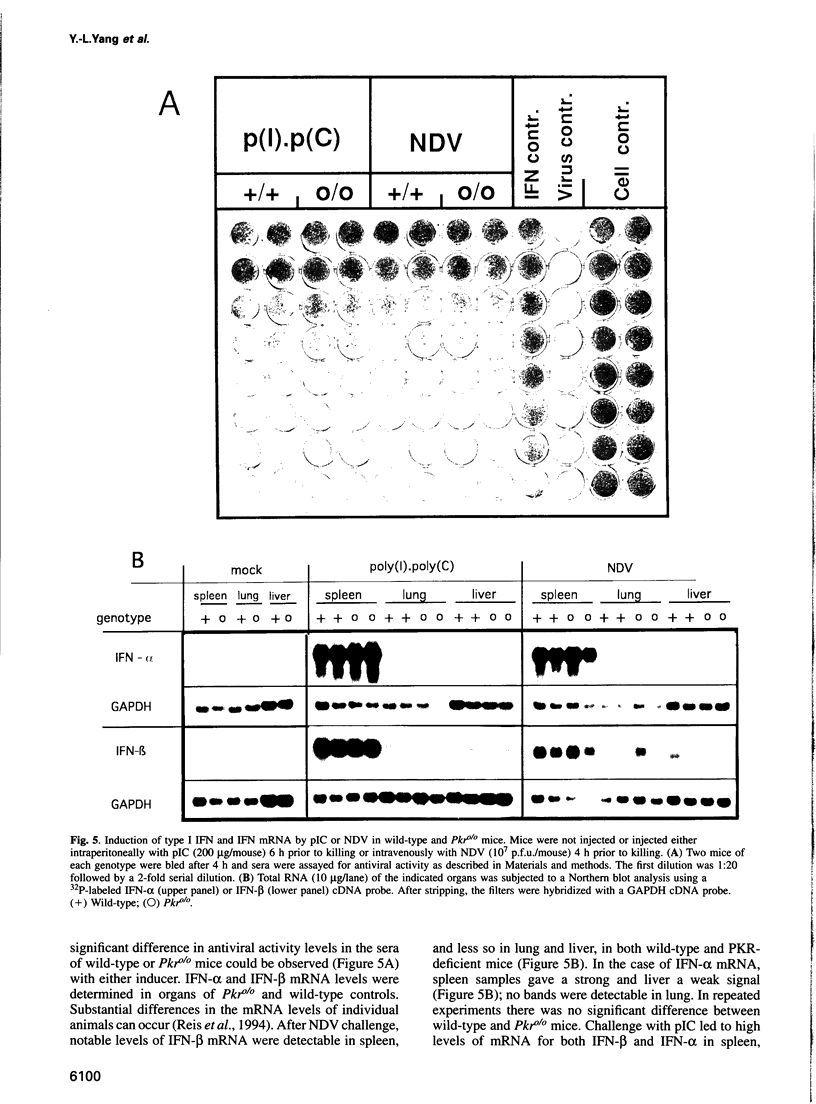
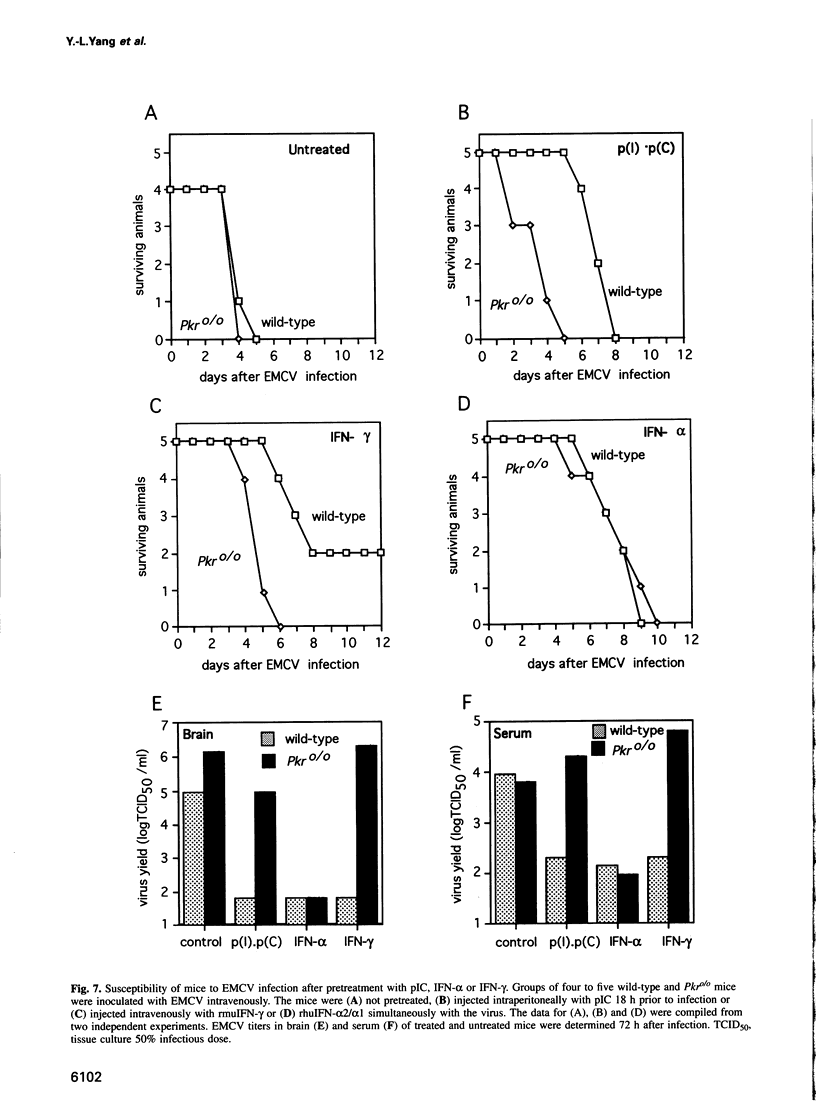
Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) has been implicated in interferon (IFN) induction, antiviral response and tumor suppression. We have generated mice devoid of functional PKR (Pkr%). Although the mice are physically normal and the induction of type I IFN genes by poly(I).poly(C) (pIC) and virus is unimpaired, the antiviral response induced by IFN-gamma and pIC was diminished. However, in embryo fibroblasts from Pkr knockout mice, the induction of type I IFN as well as the activation of NF-kappa B by pIC, were strongly impaired but restored by priming with IFN. Thus, PKR is not directly essential for responses to pIC, and a pIC-responsive system independent of PKR is induced by IFN. No evidence of the tumor suppressor activity of PKR was demonstrated.
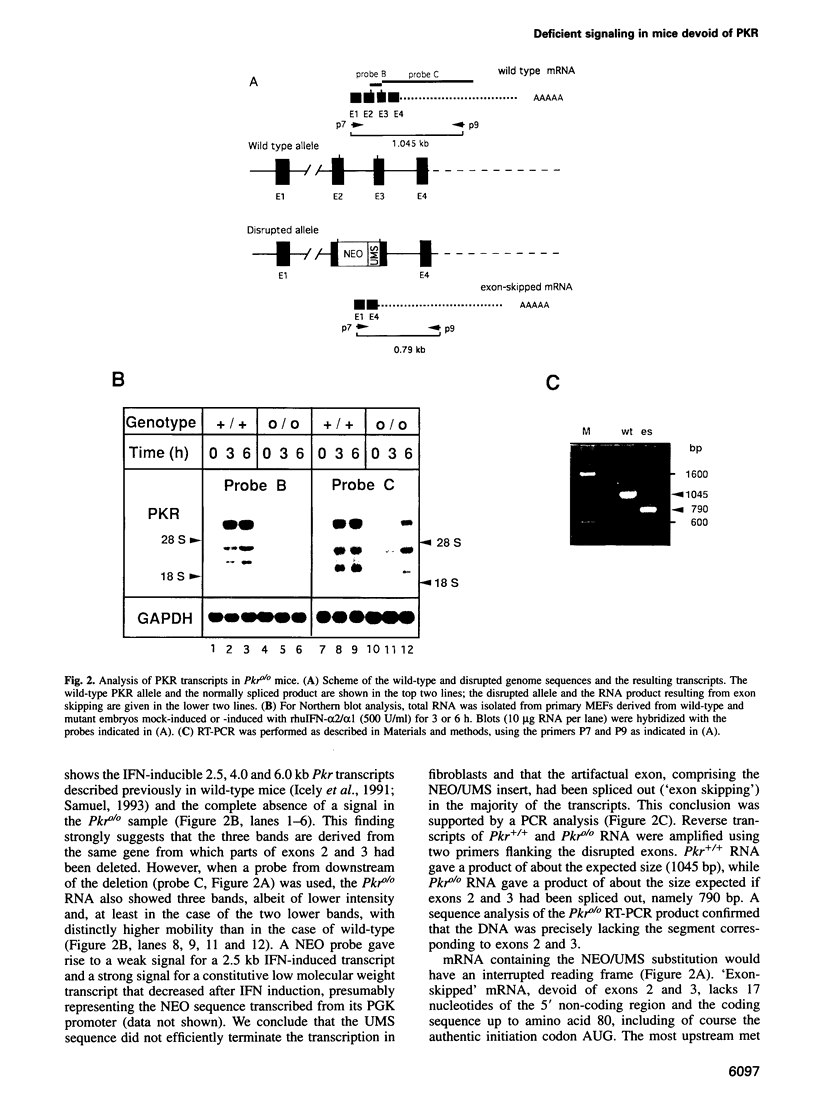
Full text
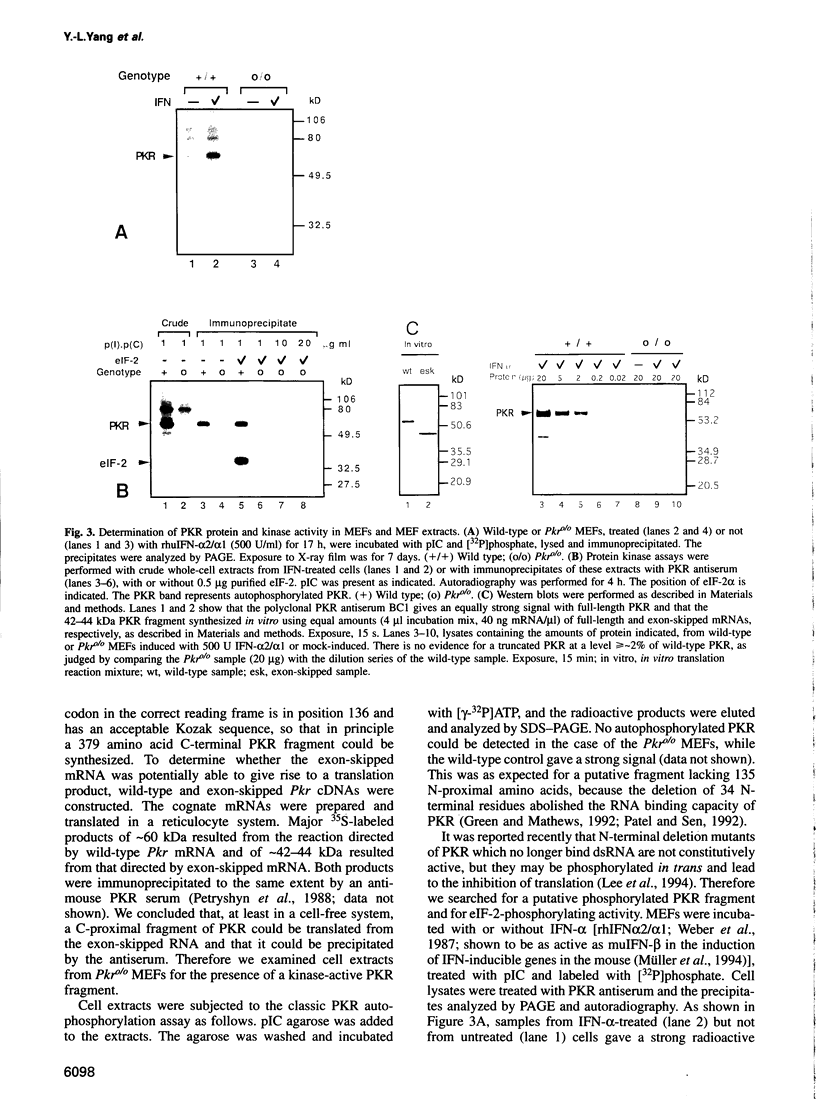
PDF
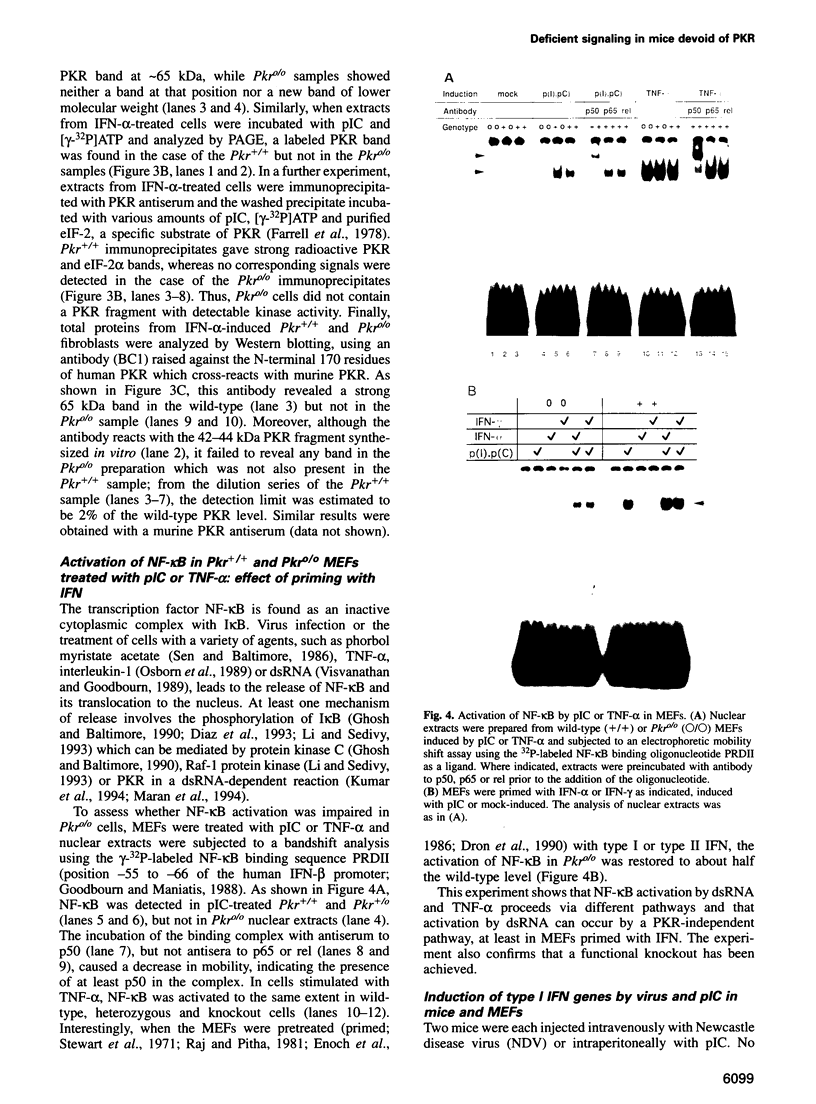





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belardelli F., Vignaux F., Proietti E., Gresser I. Injection of mice with antibody to interferon renders peritoneal macrophages permissive for vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):602–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. L., Feng L., Schappert K., Meurs E., Donahue T. F., Friesen J. D., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1553–1562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der S. D., Lau A. S. Involvement of the double-stranded-RNA-dependent kinase PKR in interferon expression and interferon-mediated antiviral activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8841–8845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Chen J. J., Barber G. N., Cigan A. M., Feng L., Donahue T. F., London I. M., Katze M. G., Hinnebusch A. G. Mammalian eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinases functionally substitute for GCN2 protein kinase in the GCN4 translational control mechanism of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4616–4620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Lacasa M., Tovey M. G. Priming affects the activity of a specific region of the promoter of the human beta interferon gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):854–858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Dubois M. F., Ratner L., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two distinct pathways for inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Chong K., Kumar A., Williams B. R. Identification of double-stranded RNA-binding domains in the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated p68 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5447–5451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flenniken A. M., Galabru J., Rutherford M. N., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Expression of interferon-induced genes in different tissues of mice. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3077–3083. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3077-3083.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Hammer J., Taniguchi T. Involvement of a cis-element that binds an H2TF-1/NF kappa B like factor(s) in the virus-induced interferon-beta gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3335–3346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Robert N., Buffet-Janvresse C., Rivière Y., Hovanessian A. G. Continuous production of interferon in normal mice: effect of anti-interferon globulin, sex, age, strain and environment on the levels of 2-5A synthetase and p67K kinase. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):711–718. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Maniatis T. Overlapping positive and negative regulatory domains of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1447–1451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Two RNA-binding motifs in the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, DAI. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2478–2490. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Galabru J. The double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is also activated by heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Hendriks W., Althage A., Hemmi S., Bluethmann H., Kamijo R., Vilcek J., Zinkernagel R. M., Aguet M. Immune response in mice that lack the interferon-gamma receptor. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1742–1745. doi: 10.1126/science.8456301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icely P. L., Gros P., Bergeron J. J., Devault A., Afar D. E., Bell J. C. TIK, a novel serine/threonine kinase, is recognized by antibodies directed against phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16073–16077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iten E., Ziemiecki A., Schäfer R. The transformation-suppressive function is lost in tumorigenic cells and is restored upon transfer of a suppressor gene. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1989;113:78–89. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-83638-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G. The war against the interferon-induced dsRNA-activated protein kinase: can viruses win? J Interferon Res. 1992 Aug;12(4):241–248. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Tomita J., Black T., Krug R. M., Safer B., Hovanessian A. Influenza virus regulates protein synthesis during infection by repressing autophosphorylation and activity of the cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3710–3717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3710-3717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koi M., Barrett J. C. Loss of tumor-suppressive function during chemically induced neoplastic progression of Syrian hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5992–5996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Haque J., Lacoste J., Hiscott J., Williams B. R. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activates transcription factor NF-kappa B by phosphorylating I kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6288–6292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. B., Esteban M. The interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated human p68 protein kinase inhibits the replication of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):1037–1041. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. B., Green S. R., Mathews M. B., Esteban M. Activation of the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-activated human protein kinase in vivo in the absence of its dsRNA binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10551–10555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Tumor-suppressor genes: news about the interferon connection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5893–5895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Sedivy J. M. Raf-1 protein kinase activates the NF-kappa B transcription factor by dissociating the cytoplasmic NF-kappa B-I kappa B complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald N. J., Kuhl D., Maguire D., Näf D., Gallant P., Goswamy A., Hug H., Büeler H., Chaturvedi M., de la Fuente J. Different pathways mediate virus inducibility of the human IFN-alpha 1 and IFN-beta genes. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90091-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Maitra R. K., Kumar A., Dong B., Xiao W., Li G., Williams B. R., Torrence P. F., Silverman R. H. Blockage of NF-kappa B signaling by selective ablation of an mRNA target by 2-5A antisense chimeras. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):789–792. doi: 10.1126/science.7914032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Interferon induction by viruses. XVI. 2-Aminopurine blocks selectively and reversibly an early stage in interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1637–1645. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kimura T., Kitagawa M., Pfeffer K., Kawakami T., Watanabe N., Kündig T. M., Amakawa R., Kishihara K., Wakeham A. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):83–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Galabru J., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Hovanessian A. G. Tumor suppressor function of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Watanabe Y., Kadereit S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Constitutive expression of human double-stranded RNA-activated p68 kinase in murine cells mediates phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and partial resistance to encephalomyocarditis virus growth. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5805–5814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5805-5814.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Steinhoff U., Reis L. F., Hemmi S., Pavlovic J., Zinkernagel R. M., Aguet M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1918–1921. doi: 10.1126/science.8009221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. C., Sen G. C. Identification of the double-stranded RNA-binding domain of the human interferon-inducible protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7671–7676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovic J., Zürcher T., Haller O., Staeheli P. Resistance to influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus conferred by expression of human MxA protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3370–3375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3370-3375.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Detection of activated double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3-F442A cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Growth-related expression of a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14736–14742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Ruffner H., Stark G., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Mice devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) show normal expression of type I interferon genes. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4798–4806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Agy M., Hovanessian A. G., Sonenberg N., Katze M. G. The integrity of the stem structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat-responsive sequence of RNA is required for interaction with the interferon-induced 68,000-Mr protein kinase. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):632–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.632-640.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner H., Reis L. F., Näf D., Weissmann C. Induction of type I interferon genes and interferon-inducible genes in embryonal stem cells devoid of interferon regulatory factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11503–11507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Kumar A., Nissim A., Chebath J., Williams B. R. The murine 2-5A synthetase locus: three distinct transcripts from two linked genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1917–1924. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. The eIF-2 alpha protein kinases, regulators of translation in eukaryotes from yeasts to humans. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7603–7606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer R., Hoffmann H., Willecke K. Suppression of tumorigenicity in hybrids of tumorigenic Chinese hamster cells and diploid mouse fibroblasts: dependence on the presence of at least three different mouse chromosomes and independence of hamster genome dosage. Cancer Res. 1983 May;43(5):2240–2246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Zhou A. M., Silverman R. H. Direct evidence for translational regulation by leader RNA and Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7492–7496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha W. C., Liou H. C., Tuomanen E. I., Baltimore D. Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Gosser L. B., Lockart R. Z., Jr Priming: a nonantiviral function of interferon. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):792–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.792-801.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: structure of the mouse PKR gene encoding the interferon-inducible RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):7995–7999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.7995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Ishihara M., Kitagawa M., Harada H., Kimura T., Matsuyama T., Lamphier M. S., Aizawa S., Mak T. W., Taniguchi T. Cellular commitment to oncogene-induced transformation or apoptosis is dependent on the transcription factor IRF-1. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H., Valenzuela D., Lujber G., Gubler M., Weissmann C. Single amino acid changes that render human IFN-alpha 2 biologically active on mouse cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):591–598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Cohen L., Hiscott J. Multiple protein-DNA interactions within the human interferon-beta regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1139–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]