Abstract
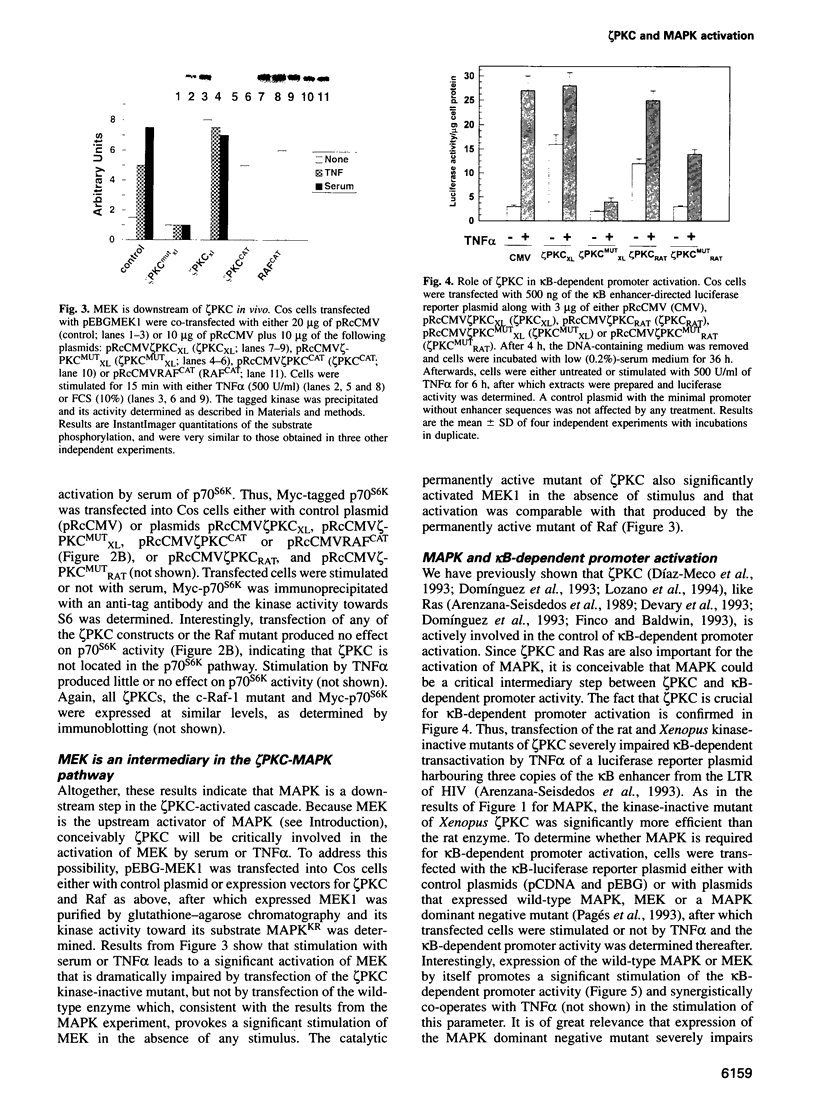
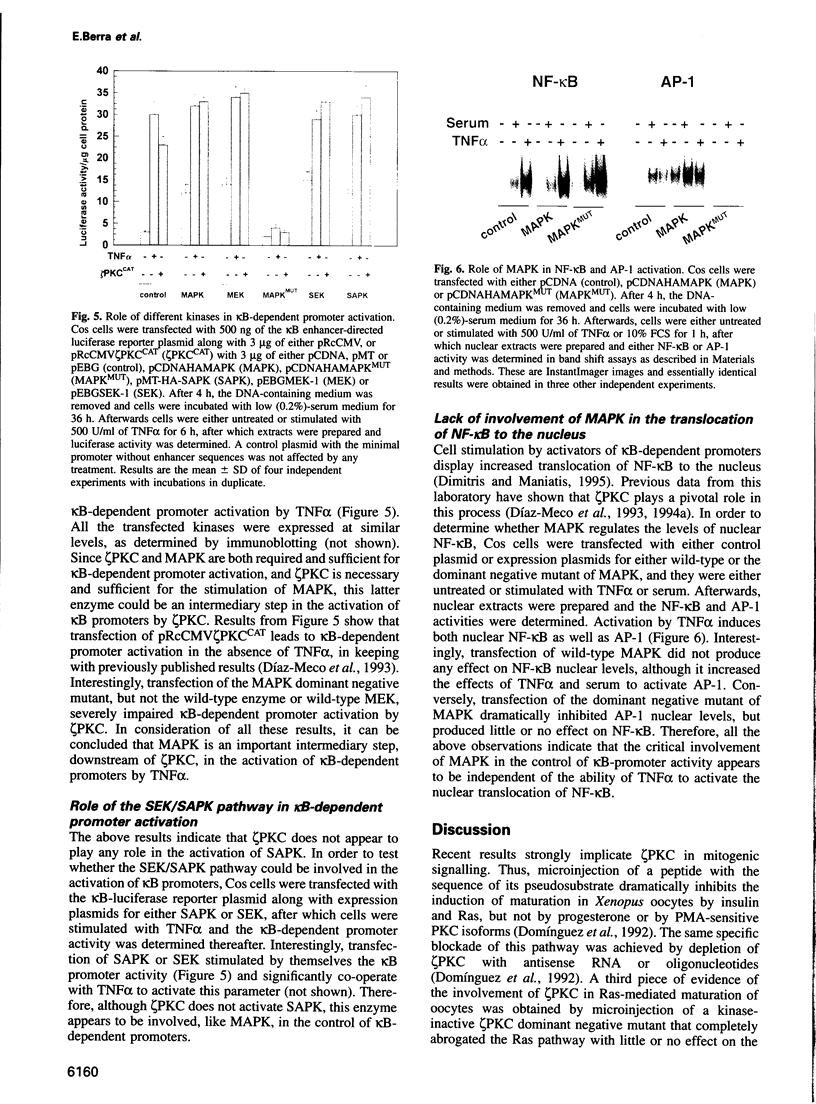
Protein kinase C zeta (zeta PKC) is critically involved in the control of a number of cell functions, including proliferation and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) activation. Previous studies indicate that zeta PKC is an important step downstream of Ras in the mitogenic cascade. The stimulation of Ras initiates a kinase cascade that culminates in the activation of MAP kinase (MAPK), which is required for cell growth. MAPK is activated by phosphorylation by another kinase named MAPK kinase (MEK), which is the substrate of a number of Ras-activated serine/threonine kinases such as c-Raf-1 and B-Raf. We show here that MAPK and MEK are activated in vivo by an active mutant of zeta PKC, and that a kinase-defective dominant negative mutant of zeta PKC dramatically impairs the activation of both MEK and MAPK by serum and tumour necrosis factor (TNF alpha). The stimulation of other kinases, such as stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) or p70S6K, is shown here to be independent of zeta PKC. The importance of MEK/MAPK in the signalling mechanisms activated by zeta PKC was addressed by using the activation of a kappa B-dependent promoter as a biological read-out of zeta PKC.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Fernandez B., Dominguez I., Jacqué J. M., Thomas D., Diaz-Meco M. T., Moscat J., Virelizier J. L. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis activates NF-kappa B and increases human immunodeficiency virus replication in human monocytes and T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6596–6604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6596-6604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Israël N., Bachelerie F., Hazan U., Alcami J., Dautry F., Virelizier J. L. c-Ha-ras transfection induces human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transcription through the HIV-enhancer in human fibroblasts and astrocytes. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berra E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Dominguez I., Municio M. M., Sanz L., Lozano J., Chapkin R. S., Moscat J. Protein kinase C zeta isoform is critical for mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):555–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80056-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørkøy G., Overvatn A., Diaz-Meco M. T., Moscat J., Johansen T. Evidence for a bifurcation of the mitogenic signaling pathway activated by Ras and phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 8;270(36):21299–21306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.36.21299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. Y., Satterberg B., Lyons D. M., Elion E. A. Ste5 tethers multiple protein kinases in the MAP kinase cascade required for mating in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):499–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Rosette C., DiDonato J. A., Karin M. NF-kappa B activation by ultraviolet light not dependent on a nuclear signal. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1442–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.8367725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Meco M. T., Berra E., Municio M. M., Sanz L., Lozano J., Dominguez I., Diaz-Golpe V., Lain de Lera M. T., Alcamí J., Payá C. V. A dominant negative protein kinase C zeta subspecies blocks NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4770–4775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Meco M. T., Dominguez I., Sanz L., Dent P., Lozano J., Municio M. M., Berra E., Hay R. T., Sturgill T. W., Moscat J. zeta PKC induces phosphorylation and inactivation of I kappa B-alpha in vitro. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2842–2848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Meco M. T., Lozano J., Municio M. M., Berra E., Frutos S., Sanz L., Moscat J. Evidence for the in vitro and in vivo interaction of Ras with protein kinase C zeta. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31706–31710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez I., Diaz-Meco M. T., Municio M. M., Berra E., García de Herreros A., Cornet M. E., Sanz L., Moscat J. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C zeta subspecies in maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3776–3783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez I., Sanz L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Diaz-Meco M. T., Virelizier J. L., Moscat J. Inhibition of protein kinase C zeta subspecies blocks the activation of an NF-kappa B-like activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1290–1295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 14;1212(1):26–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco T. S., Baldwin A. S., Jr Kappa B site-dependent induction of gene expression by diverse inducers of nuclear factor kappa B requires Raf-1. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17676–17679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A. The sphingomyelin cycle and the second messenger function of ceramide. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3125–3128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R., Golde D. W. The sphingomyelin pathway in tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 signaling. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Johnson G. L. Ras-dependent growth factor regulation of MEK kinase in PC12 cells. Science. 1994 Sep 2;265(5177):1458–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.8073291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange-Carter C. A., Pleiman C. M., Gardner A. M., Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):315–319. doi: 10.1126/science.8385802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrodera P., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Lopez-Barahona M., Diaz-Laviada I., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Moscat J. Phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine is an important step in PDGF-stimulated DNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1113–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90074-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barahona M., Kaplan P. L., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Larrodera P., Diaz-Laviada I., Municio A. M., Moscat J. Kinetic evidence of a rapid activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by Ki-ras oncogene. Possible involvement in late steps of the mitogenic cascade. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9022–9026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozano J., Berra E., Municio M. M., Diaz-Meco M. T., Dominguez I., Sanz L., Moscat J. Protein kinase C zeta isoform is critical for kappa B-dependent promoter activation by sphingomyelinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19200–19202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming X. F., Burgering B. M., Wennström S., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H., Bos J. L., Kozma S. C., Thomas G. Activation of p70/p85 S6 kinase by a pathway independent of p21ras. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):426–429. doi: 10.1038/371426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H., Brewer K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of the zeta isozyme of protein kinase C by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H., Exton J. H. Purification and characterization of the zeta isoform of protein kinase C from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16347–16354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacktor T. C., Osten P., Valsamis H., Jiang X., Naik M. U., Sublette E. Persistent activation of the zeta isoform of protein kinase C in the maintenance of long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8342–8346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Ballard D. W., Greene W. C., Angel P., Herrlich P. Cross-coupling of the NF-kappa B p65 and Fos/Jun transcription factors produces potentiated biological function. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3879–3891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. NF-kappa B: a lesson in family values. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaillancourt R. R., Gardner A. M., Johnson G. L. B-Raf-dependent regulation of the MEK-1/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in PC12 cells and regulation by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6522–6530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Cook P. P., Webster C., Parker P. J. Effect of phorbol esters on protein kinase C-zeta. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4799–4805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Posekany K., deVente J., Garris T., Chen J., Hooker J., Qin W., Cook P., Fletcher D., Parker P. Overexpression of protein kinase C-zeta stimulates leukemic cell differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Nov;5(11):1195–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooten M. W., Zhou G., Seibenhener M. L., Coleman E. S. A role for zeta protein kinase C in nerve growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Apr;5(4):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Robbins D., Frost J., Dang A., Lange-Carter C., Cobb M. H. MEKK1 phosphorylates MEK1 and MEK2 but does not cause activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6808–6812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. X., Tessner T. G., Rock C. O., Jackowski S. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and c-myc expression are in collaborating mitogenic pathways activated by colony-stimulating factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1522–1533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]