Abstract
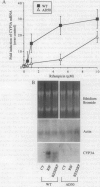
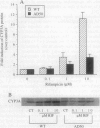
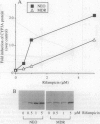
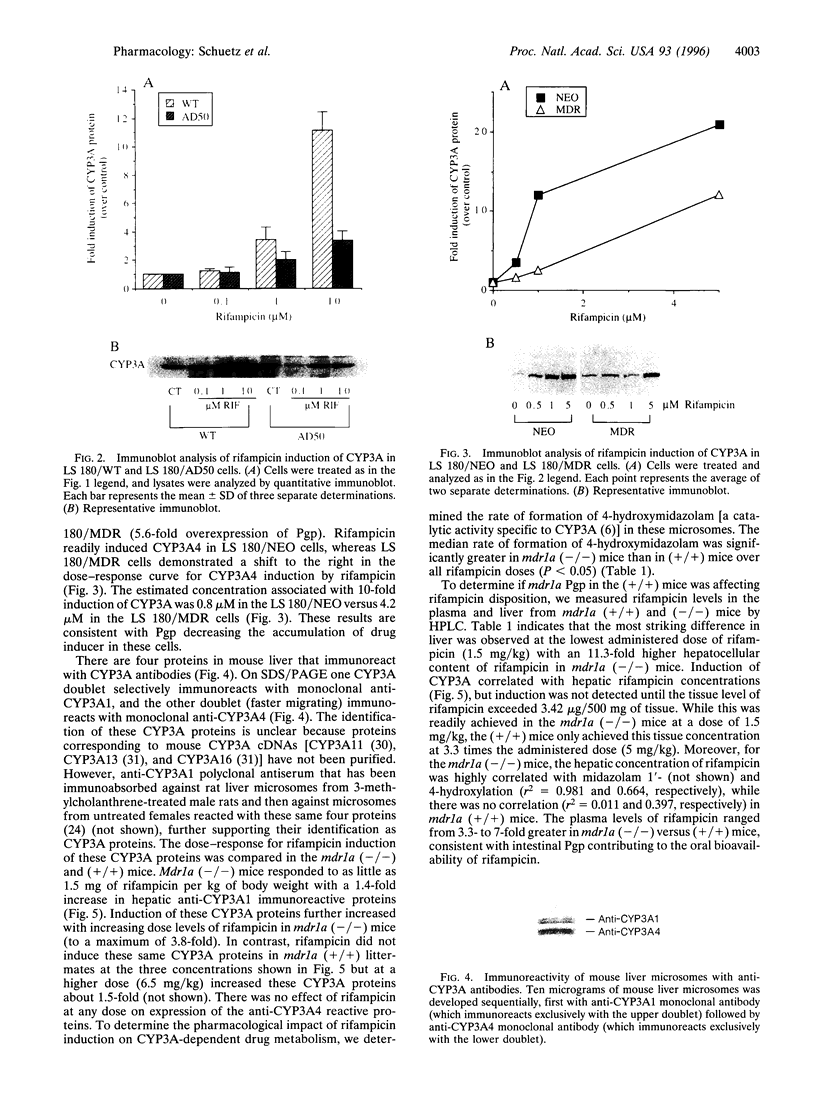
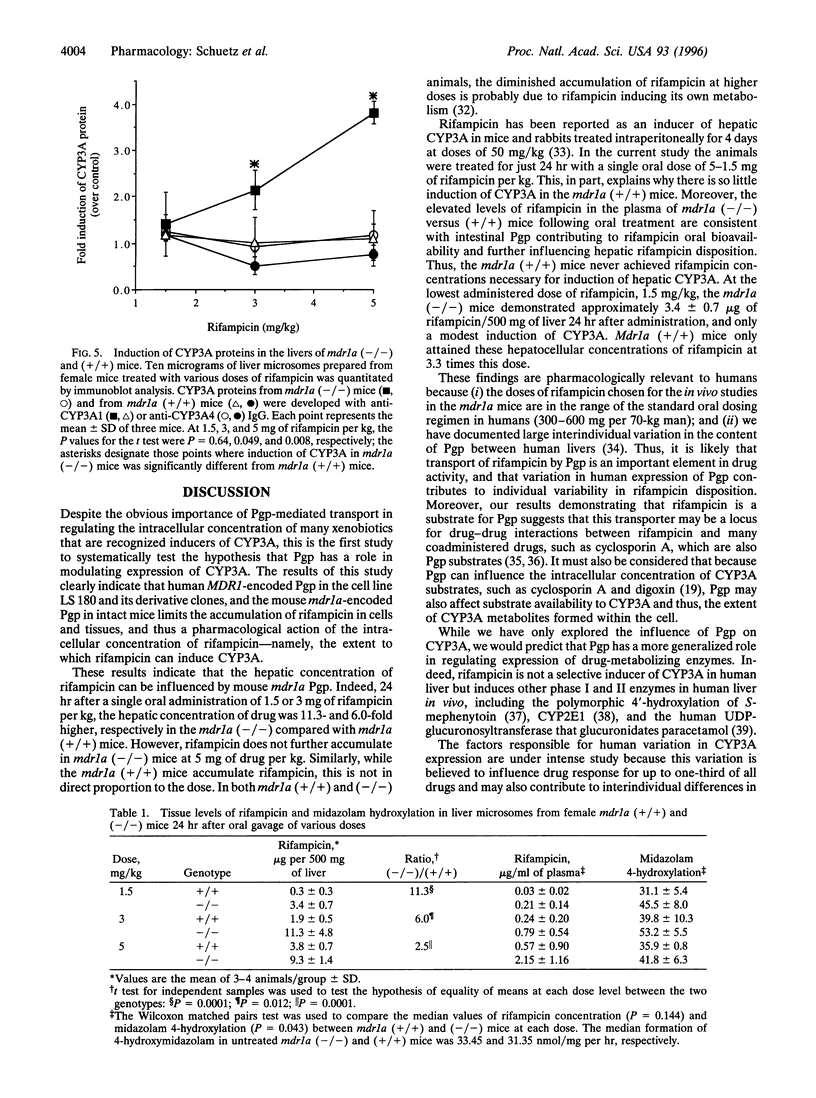
The P-glycoprotein (Pgp) efflux pump can influence the hepatocellular concentration of xenobiotics that are modulators and substrates of cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A). We tested the hypothesis that Pgp is a determinant of drug-inducible expression of CYP3A. The magnitude of CYP3A induction by rifampicin was compared in the human parental colon carcinoma cell line LS 180/WT (wild type) and in two derivative clones overexpressing the human multidrug resistance gene MDR1 (also designated PGY1) because of either drug selection (LS 180/ADR) or transfection with MDRI cDNA (LS 180/MDR). In both MDR1 cDNA-overexpressing clones, rifampicin induction of CYP3A mRNA and protein was decreased and required greater rifampicin concentrations compared with parental cells. The role of Pgp in regulation of CYP3A expression in vivo was analyzed in mice carrying a targeted disruption of the mdr1a mouse gene. Oral treatment with increasing doses of rifampicin resulted in elevated drug levels in the livers of mdr1a (-/-) mice compared with mdr1a (+/+) mice at all doses. Consistent with the enhanced accumulation of rifampicin in mdr1a (-/-) mice, lower doses of rifampicin were required for induction of CYP3A proteins, and the magnitude of CYP3A induction was greater at all doses of rifampicin in mdr1a (-/-) mice compared with mdr1a (+/+) mice. We conclude that Pgp-mediated transport is a critical element influencing the CYP3A inductive response.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaune P., Kremers P., Letawe-Goujon F., Gielen J. E. Monoclonal antibodies against human liver cytochrome P-450. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 1;34(19):3547–3552. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90732-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borcherding S. M., Baciewicz A. M., Self T. H. Update on rifampin drug interactions. II. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Apr;152(4):711–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin K. V., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Function and regulation of the human multidrug resistance gene. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;60:157–180. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60825-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croop J. M., Raymond M., Haber D., Devault A., Arceci R. J., Gros P., Housman D. E. The three mouse multidrug resistance (mdr) genes are expressed in a tissue-specific manner in normal mouse tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1346–1350. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Gros P. Two members of the mouse mdr gene family confer multidrug resistance with overlapping but distinct drug specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1652–1663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. M., Hait W. N. Pharmacologic circumvention of multidrug resistance. Cytotechnology. 1993;12(1-3):171–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00744664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert M. F., Roberts J. P., Prueksaritanont T., Benet L. Z. Bioavailability of cyclosporine with concomitant rifampin administration is markedly less than predicted by hepatic enzyme induction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Nov;52(5):453–457. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog C. E., Tsokos M., Bates S. E., Fojo A. T. Increased mdr-1/P-glycoprotein expression after treatment of human colon carcinoma cells with P-glycoprotein antagonists. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2946–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. A., Wrighton S. A., Kremers P., Guzelian P. S. Immunochemical evidence for multiple steroid-inducible hepatic cytochromes P-450 in the rat. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):27–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2450027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii M., Ogata H. Determination of rifampicin and its main metabolites in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1988 Apr 29;426(2):412–416. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81972-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh S., Satoh M., Abe Y., Hashimoto H., Yanagimoto T., Kamataki T. A novel form of mouse cytochrome P450 3A (Cyp3a-16). Its cDNA cloning and expression in fetal liver. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Dec 15;226(3):877–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.t01-1-00877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Benedict P., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Watkins P. B. Aflatoxin B1-adduct formation in rat and human small bowel enterocytes. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90602-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Schuetz J. D., Fang C., Watkins P. B. Identification of rifampin-inducible P450IIIA4 (CYP3A4) in human small bowel enterocytes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1871–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI116064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce H. L., Safa A. R., Bach N. J., Winter M. A., Cirtain M. C., Beck W. T. Essential features of the P-glycoprotein pharmacophore as defined by a series of reserpine analogs that modulate multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5128–5132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichard L., Fabre I., Fabre G., Domergue J., Saint Aubert B., Mourad G., Maurel P. Cyclosporin A drug interactions. Screening for inducers and inhibitors of cytochrome P-450 (cyclosporin A oxidase) in primary cultures of human hepatocytes and in liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1990 Sep-Oct;18(5):595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Critchley J. A., Balali-Mood M., Pentland B. Effects of microsomal enzyme induction on paracetamol metabolism in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;12(2):149–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relling M. V., Nemec J., Schuetz E. G., Schuetz J. D., Gonzalez F. J., Korzekwa K. R. O-demethylation of epipodophyllotoxins is catalyzed by human cytochrome P450 3A4. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;45(2):352–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Ueda K., Tanigawara Y., Hori R., Komano T. Human P-glycoprotein transports cyclosporin A and FK506. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6077–6080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Smit J. J., van Tellingen O., Beijnen J. H., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., van der Valk M. A., Robanus-Maandag E. C., te Riele H. P. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinkel A. H., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Borst P. Absence of the mdr1a P-Glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone, digoxin, and cyclosporin A. J Clin Invest. 1995 Oct;96(4):1698–1705. doi: 10.1172/JCI118214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Beck W. T., Schuetz J. D. Modulators and substrates of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P4503A coordinately up-regulate these proteins in human colon carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;49(2):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Furuya K. N., Schuetz J. D. Interindividual variation in expression of P-glycoprotein in normal human liver and secondary hepatic neoplasms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Nov;275(2):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Li D., Omiecinski C. J., Muller-Eberhard U., Kleinman H. K., Elswick B., Guzelian P. S. Regulation of gene expression in adult rat hepatocytes cultured on a basement membrane matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):309–323. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041340302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Schuetz J. D., Strom S. C., Thompson M. T., Fisher R. A., Molowa D. T., Li D., Guzelian P. S. Regulation of human liver cytochromes P-450 in family 3A in primary and continuous culture of human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1993 Nov;18(5):1254–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz E. G., Wrighton S. A., Barwick J. L., Guzelian P. S. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by glucocorticoids in rat liver. I. Evidence that glucocorticoids and pregnenolone 16 alpha-carbonitrile regulate de novo synthesis of a common form of cytochrome P-450 in cultures of adult rat hepatocytes and in the liver in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1999–2006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz J. D., Kauma S., Guzelian P. S. Identification of the fetal liver cytochrome CYP3A7 in human endometrium and placenta. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):1018–1024. doi: 10.1172/JCI116607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz J. D., Schuetz E. G. Extracellular matrix regulation of multidrug resistance in primary monolayer cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Jan;4(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Martin M. V., Pruess-Schwartz D., Marnett L. J., Guengerich F. P. Roles of individual human cytochrome P-450 enzymes in the bioactivation of benzo(a)pyrene, 7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo(a)pyrene, and other dihydrodiol derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6304–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Yamazaki H., Mimura M., Inui Y., Guengerich F. P. Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 Caucasians. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jul;270(1):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. A., Jones B. C. Speculations on the substrate structure-activity relationship (SSAR) of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 1;44(11):2089–2098. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90333-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnichsen D. S., Liu Q., Schuetz E. G., Schuetz J. D., Pappo A., Relling M. V. Variability in human cytochrome P450 paclitaxel metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Nov;275(2):566–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strolin Benedetti M., Dostert P. Induction and autoinduction properties of rifamycin derivatives: a review of animal and human studies. Environ Health Perspect. 1994 Nov;102 (Suppl 9):101–105. doi: 10.1289/ehp.94102s9101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tom B. H., Rutzky L. P., Jakstys M. M., Oyasu R., Kaye C. I., Kahan B. D. Human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. I. Establishment and description of a new line. In Vitro. 1976 Mar;12(3):180–191. doi: 10.1007/BF02796440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Okamura N., Hirai M., Tanigawara Y., Saeki T., Kioka N., Komano T., Hori R. Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24248–24252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Murray S. A., Winkelman L. G., Heuman D. M., Wrighton S. A., Guzelian P. S. Erythromycin breath test as an assay of glucocorticoid-inducible liver cytochromes P-450. Studies in rats and patients. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):688–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI113933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Schuetz E. G., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI113156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Schuetz E. G., Watkins P. B., Maurel P., Barwick J., Bailey B. S., Hartle H. T., Young B., Guzelian P. Demonstration in multiple species of inducible hepatic cytochromes P-450 and their mRNAs related to the glucocorticoid-inducible cytochrome P-450 of the rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;28(3):312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimoto T., Itoh S., Muller-Enoch D., Kamataki T. Mouse liver cytochrome P-450 (P-450IIIAM1): its cDNA cloning and inducibility by dexamethasone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H. H., Anthony L. B., Wood A. J., Wilkinson G. R. Induction of polymorphic 4'-hydroxylation of S-mephenytoin by rifampicin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;30(3):471–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]