Abstract
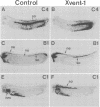
We have identified a novel homeobox gene, Xvent-1, that is differentially expressed in the ventral marginal zone of the early Xenopus gastrula. Evidence is presented from mRNA microinjection experiments for a role for this gene in dorsoventral patterning of mesoderm. First, Xvent-1 is induced by BMP-4, a gene known to be a key regulator of ventral mesoderm development. Second, Xvent-1 and the organizer-specific gene goosecoid are able to interact, directly or indirectly, in a cross-regulatory loop suppressing each other's expression, consistent with their mutually exclusive expression in the marginal zone. Third, microinjection of Xvent-1 mRNA ventralizes dorsal mesoderm. The results suggest that Xvent-1 functions in a ventral signaling pathway that maintains the ventral mesodermal state and antagonizes the Spemann organizer.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaya E., Stein P. A., Musci T. J., Kirschner M. W. FGF signalling in the early specification of mesoderm in Xenopus. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):477–487. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arendt D., Nübler-Jung K. Inversion of dorsoventral axis? Nature. 1994 Sep 1;371(6492):26–26. doi: 10.1038/371026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitz I. L., Cho K. W. Anterior neurectoderm is progressively induced during gastrulation: the role of the Xenopus homeobox gene orthodenticle. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):993–1004. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M., Cho K. W. Organizer-specific homeobox genes in Xenopus laevis embryos. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.1677215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candia A. F., Kovalik J. P., Wright C. V. Amino acid sequence of Mox-2 and comparison to its Xenopus and rat homologs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Oct 25;21(21):4982–4982. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.21.4982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candia A. F., Wright C. V. The expression pattern of Xenopus Mox-2 implies a role in initial mesodermal differentiation. Mech Dev. 1995 Jul;52(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)00384-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Blumberg B., Steinbeisser H., De Robertis E. M. Molecular nature of Spemann's organizer: the role of the Xenopus homeobox gene goosecoid. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90288-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Morita E. A., Wright C. V., De Robertis E. M. Overexpression of a homeodomain protein confers axis-forming activity to uncommitted Xenopus embryonic cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90407-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. L., Moon R. T. Interactions between Xwnt-8 and Spemann organizer signaling pathways generate dorsoventral pattern in the embryonic mesoderm of Xenopus. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):13–28. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cribbs D. L., Pultz M. A., Johnson D., Mazzulla M., Kaufman T. C. Structural complexity and evolutionary conservation of the Drosophila homeotic gene proboscipedia. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1437–1449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Howes G., Price B. M., Smith J. C. Bone morphogenetic protein 4: a ventralizing factor in early Xenopus development. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):573–585. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Slack J. M. Fate map for the 32-cell stage of Xenopus laevis. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):527–551. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale L., Slack J. M. Regional specification within the mesoderm of early embryos of Xenopus laevis. Development. 1987 Jun;100(2):279–295. doi: 10.1242/dev.100.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Polson A. G., Klymkowsky M. W. A whole-mount immunocytochemical analysis of the expression of the intermediate filament protein vimentin in Xenopus. Development. 1989 Jan;105(1):61–74. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainsod A., Steinbeisser H., De Robertis E. M. On the function of BMP-4 in patterning the marginal zone of the Xenopus embryo. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5015–5025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François V., Bier E. Xenopus chordin and Drosophila short gastrulation genes encode homologous proteins functioning in dorsal-ventral axis formation. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):19–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gont L. K., Steinbeisser H., Blumberg B., de Robertis E. M. Tail formation as a continuation of gastrulation: the multiple cell populations of the Xenopus tailbud derive from the late blastopore lip. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):991–1004. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J. M., Thies R. S., Song J. J., Celeste A. J., Melton D. A. Studies with a Xenopus BMP receptor suggest that ventral mesoderm-inducing signals override dorsal signals in vivo. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90409-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. E., Ho R. K., Walker C., Kimmel C. B. Induction of muscle pioneers and floor plate is distinguished by the zebrafish no tail mutation. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):99–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M. In situ hybridization: an improved whole-mount method for Xenopus embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:685–695. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M. The transforming growth factor beta family and induction of the vertebrate mesoderm: bone morphogenetic proteins are ventral inducers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10243–10246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Microinjection of synthetic Xhox-1A homeobox mRNA disrupts somite formation in developing Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):687–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley S. A., Jackson P. D., Sasai Y., Lu B., De Robertis E. M., Hoffmann F. M., Ferguson E. L. A conserved system for dorsal-ventral patterning in insects and vertebrates involving sog and chordin. Nature. 1995 Jul 20;376(6537):249–253. doi: 10.1038/376249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Lyons K. M., Lapan P. M., Wright C. V., Hogan B. L. DVR-4 (bone morphogenetic protein-4) as a posterior-ventralizing factor in Xenopus mesoderm induction. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):639–647. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. M., Smith J. C. Inductive signals. Revolving vertebrates. Curr Biol. 1995 Jun 1;5(6):574–576. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. R., Elinson R. P. The entire mesodermal mantle behaves as Spemann's organizer in dorsoanterior enhanced Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):64–77. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K., Danilchik M. Generation of body plan phenotypes in early embryogenesis. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:271–284. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Winklbauer R. Cellular basis of amphibian gastrulation. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1992;27:39–89. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Christian J. L., Moon R. T. Synergistic principles of development: overlapping patterning systems in Xenopus mesoderm induction. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):1–9. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.Supplement.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köster M., Plessow S., Clement J. H., Lorenz A., Tiedemann H., Knöchel W. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4), a member of the TGF-beta family, in early embryos of Xenopus laevis: analysis of mesoderm inducing activity. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Brennan S., Dathan N., Fairman S., Gurdon J. B. Cell type-specific activation of actin genes in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):716–721. doi: 10.1038/311716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody S. A. Fates of the blastomeres of the 32-cell-stage Xenopus embryo. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):300–319. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehrs C., De Robertis E. M. Ectopic expression of a homeobox gene changes cell fate in Xenopus embryos in a position-specific manner. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3621–3629. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehrs C., Keller R., Cho K. W., De Robertis E. M. The homeobox gene goosecoid controls cell migration in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehrs C., Steinbeisser H., De Robertis E. M. Mesodermal patterning by a gradient of the vertebrate homeobox gene goosecoid. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):817–820. doi: 10.1126/science.7905664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimatsu S., Suzuki A., Shoda A., Murakami K., Ueno N. Genes for bone morphogenetic proteins are differentially transcribed in early amphibian embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1487–1495. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81574-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop J. L., Kimelman D. Dorsal-ventral differences in Xcad-3 expression in response to FGF-mediated induction in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):490–503. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannese M., Polo C., Andreazzoli M., Vignali R., Kablar B., Barsacchi G., Boncinelli E. The Xenopus homologue of Otx2 is a maternal homeobox gene that demarcates and specifies anterior body regions. Development. 1995 Mar;121(3):707–720. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.3.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Bimodal and graded expression of the Xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 during embryonic development. Development. 1989 May;106(1):173–183. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Involvement of the Xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 in pattern formation along the anterior-posterior axis. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Snider L., Weintraub H. Xenopus embryos regulate the nuclear localization of XMyoD. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1311–1323. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasai Y., Lu B., Steinbeisser H., Geissert D., Gont L. K., De Robertis E. M. Xenopus chordin: a novel dorsalizing factor activated by organizer-specific homeobox genes. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90068-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. R., Gerhart J. C. Axis determination in eggs of Xenopus laevis: a critical period before first cleavage, identified by the common effects of cold, pressure and ultraviolet irradiation. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. E., Suzuki A., Ueno N., Kimelman D. Localized BMP-4 mediates dorsal/ventral patterning in the early Xenopus embryo. Dev Biol. 1995 May;169(1):37–50. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe C. R., Fritz A., De Robertis E. M., Gurdon J. B. A homeobox-containing marker of posterior neural differentiation shows the importance of predetermination in neural induction. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):749–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Gulisano M., Acampora D., Stornaiuolo A., Rambaldi M., Boncinelli E. Two vertebrate homeobox genes related to the Drosophila empty spiracles gene are expressed in the embryonic cerebral cortex. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2541–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L. The frog prince-ss: a molecular formula for dorsoventral patterning in Xenopus. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Embryonic induction. Mech Dev. 1993 May;41(2-3):91–107. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Green J. B., Weigel D., Herrmann B. G. Expression of a Xenopus homolog of Brachyury (T) is an immediate-early response to mesoderm induction. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90573-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Slack J. M. Dorsalization and neural induction: properties of the organizer in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1983 Dec;78:299–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Harland R. M. Injected Xwnt-8 RNA acts early in Xenopus embryos to promote formation of a vegetal dorsalizing center. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):753–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90070-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbeisser H., Fainsod A., Niehrs C., Sasai Y., De Robertis E. M. The role of gsc and BMP-4 in dorsal-ventral patterning of the marginal zone in Xenopus: a loss-of-function study using antisense RNA. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5230–5243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Thies R. S., Yamaji N., Song J. J., Wozney J. M., Murakami K., Ueno N. A truncated bone morphogenetic protein receptor affects dorsal-ventral patterning in the early Xenopus embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10255–10259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Jamrich M., Good P. J., Dawid I. B. The LIM domain-containing homeo box gene Xlim-1 is expressed specifically in the organizer region of Xenopus gastrula embryos. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):356–366. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Otani H., Saint-Jeannet J. P., Dawid I. B. Role of the LIM class homeodomain protein Xlim-1 in neural and muscle induction by the Spemann organizer in Xenopus. Nature. 1994 Dec 15;372(6507):677–679. doi: 10.1038/372677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winklbauer R. Mesodermal cell migration during Xenopus gastrulation. Dev Biol. 1990 Nov;142(1):155–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90159-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witta S. E., Agarwal V. R., Sato S. M. XIPOU 2, a noggin-inducible gene, has direct neuralizing activity. Development. 1995 Mar;121(3):721–730. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.3.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Ratcliffe A., Watt F. M. Two subpopulations of differentiated chondrocytes identified with a monoclonal antibody to keratan sulfate. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):53–59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dassow G., Schmidt J. E., Kimelman D. Induction of the Xenopus organizer: expression and regulation of Xnot, a novel FGF and activin-regulated homeo box gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):355–366. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]