Abstract
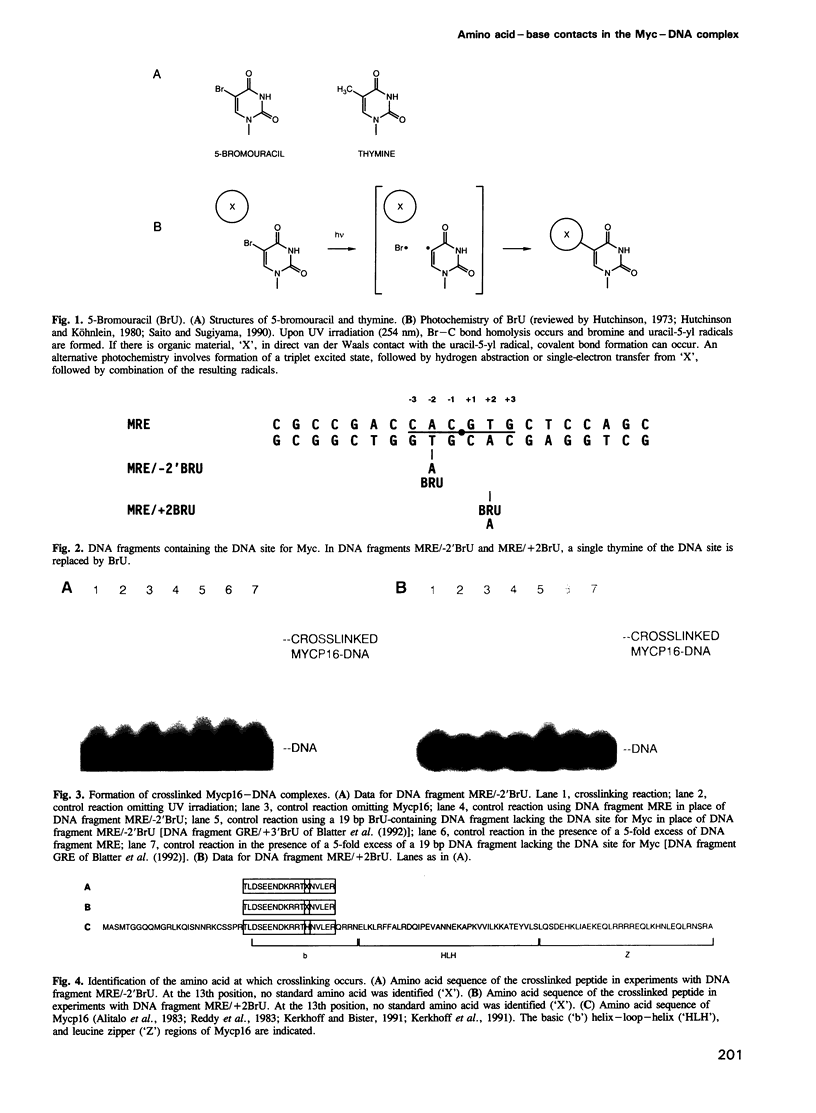
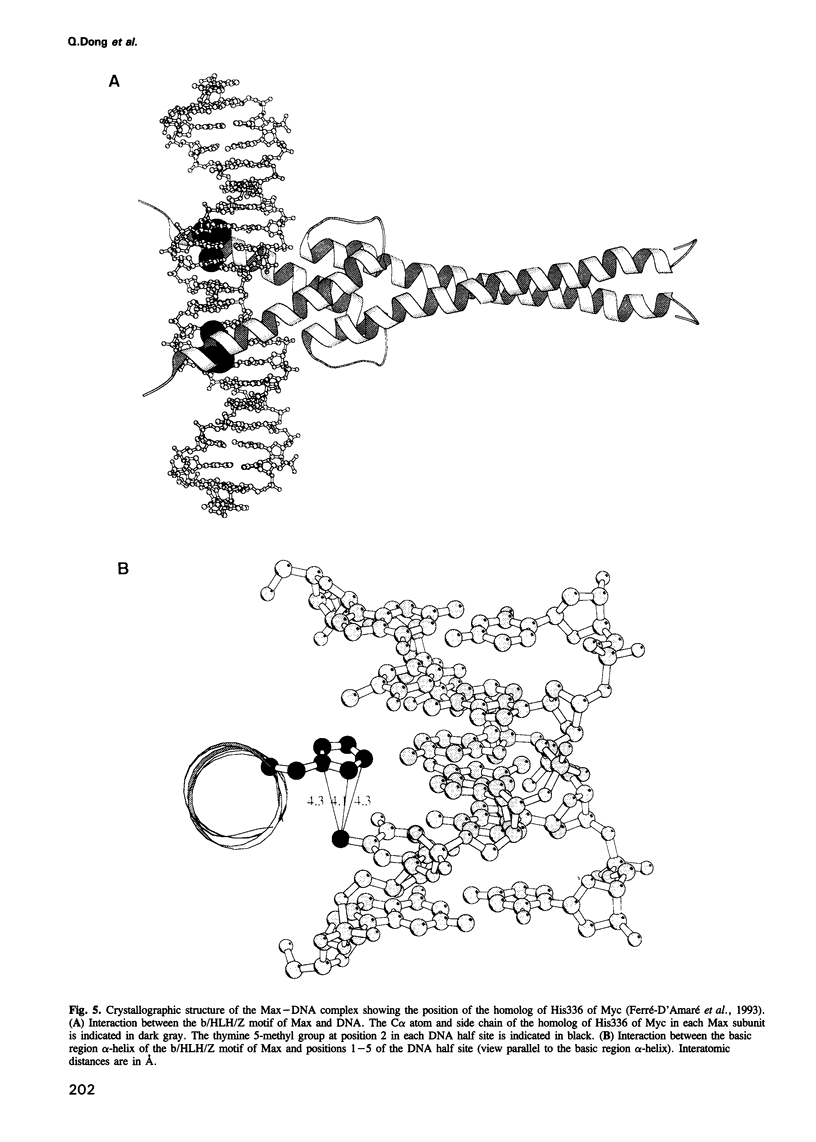
Myc binds to a 6 bp 2-fold symmetric DNA site: 5'-C-3A-2C-1G+1T+2G+3-3'. Using site-specific 5-bromouracil mediated photocrosslinking, we show that His336 of Myc contacts, or is close to, the thymine 5-methyl group at 2-fold symmetry-related positions -2 and +2 of the DNA site in the Myc-DNA complex. Our results strongly suggest that homologous amino acids of Myc and Max make equivalent contacts in the respective protein-DNA complexes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Bishop J. M., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Nucleotide sequence to the v-myc oncogene of avian retrovirus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen T. D., Wick K. L., Matthews K. S. Identification of amino acids in lac repressor protein cross-linked to operator DNA specifically substituted with bromodeoxyuridine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6113–6119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony-Cahill S. J., Benfield P. A., Fairman R., Wasserman Z. R., Brenner S. L., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L., DeGrado W. F. Molecular characterization of helix-loop-helix peptides. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):979–983. doi: 10.1126/science.1312255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Identification of an amino acid-base contact in the GCN4-DNA complex by bromouracil-mediated photocrosslinking. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):650–652. doi: 10.1038/359650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Gunasekera A. Consensus DNA site for the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): CAP exhibits a 450-fold higher affinity for the consensus DNA site than for the E. coli lac DNA site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10295–10305. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. High affinity DNA-binding Myc analogs: recognition by an alpha helix. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. Myc/Max and other helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper proteins bend DNA toward the minor groove. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11779–11783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H. Studies on gene control regions XII. The functional significance of a lac operator constitutive mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):401–416. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekera A., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. DNA sequence determinants for binding of the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14713–14720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Determination of the c-MYC DNA-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6162–6166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Predicted structural similarities of the DNA binding domains of c-Myc and endonuclease Eco RI. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.1734524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. The lesions produced by ultraviolet light in DNA containing 5-bromouracil. Q Rev Biophys. 1973 May;6(2):201–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff E., Bister K., Klempnauer K. H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by Myc proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4323–4327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkhoff E., Bister K. Myc protein structure: localization of DNA-binding and protein dimerization domains. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. H., Cheng S. Y. An efficient method to purify active eukaryotic proteins from the inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):748, 750, 752-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoulas O., Williams N. G., Kingston R. E. DNA binding activities of c-Myc purified from eukaryotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10470–10480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Lawe D., Ziff E. B. Association of Myn, the murine homolog of max, with c-Myc stimulates methylation-sensitive DNA binding and ras cotransformation. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90457-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B. Methylation-sensitive sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc basic region. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):186–189. doi: 10.1126/science.1987636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Watson D. K., Schultz R. A., Lautenberger J., Papas T. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the proviral genome of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Garcia K. C. Molecular model for DNA recognition by the family of basic-helix-loop-helix-zipper proteins. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):396–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. S., Dang C. V. Opposite orientations of DNA bending by c-Myc and Max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7635–7639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]