Abstract
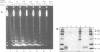
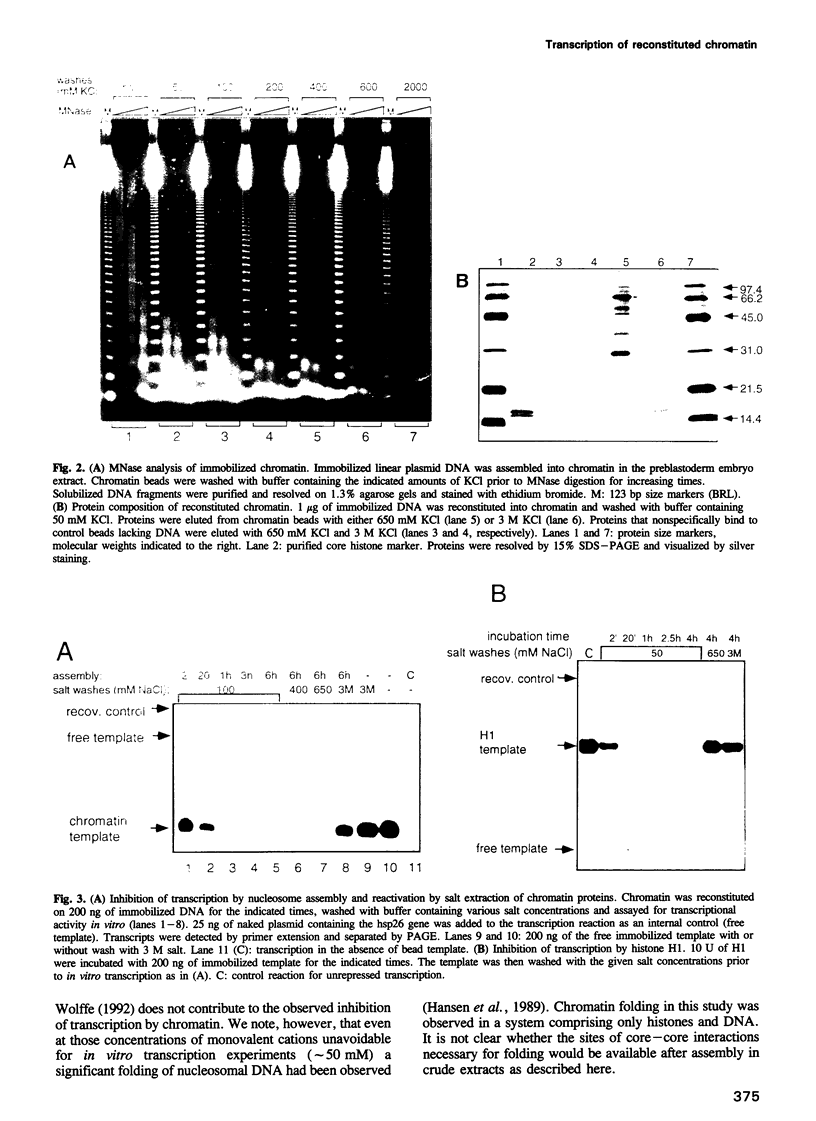
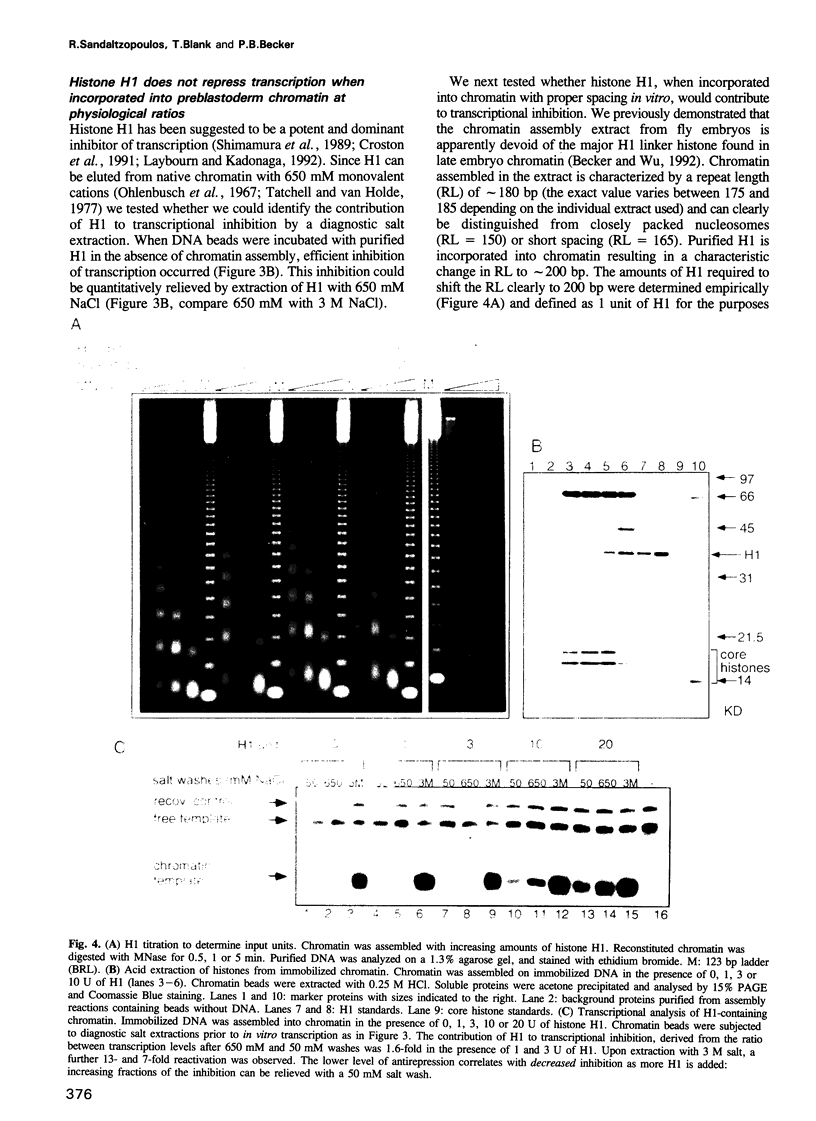
Chromatin reconstituted in an extract from preblastoderm Drosophila embryos represses transcription by RNA polymerase II. We have assembled regularly spaced nucleosomes on DNA attached to paramagnetic beads enabling the efficient purification of chromatin templates for transcription studies. We have used diagnostic salt extractions to establish that transcriptional repression of immobilized chromatin was largely due to nucleosome cores. When purified H1 was incorporated into chromatin, resulting in increased repeat lengths to 200-220 bp, the contribution of H1 to transcriptional repression was negligible. If more H1 was added no regularly spaced chromatin was obtained and only under these conditions was transcriptional inhibition by H1 apparent. We conclude that efficient repression of transcription by polymerase II in this system does not require the presence of histone H1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almouzni G., Méchali M. Assembly of spaced chromatin promoted by DNA synthesis in extracts from Xenopus eggs. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):665–672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02861.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Changing rates of DNA and RNA synthesis in Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90434-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. V., Lengyel J. A. Rates of synthesis of major classes of RNA in Drosophila embryos. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Thomas J. O. Histones H1 and H5: one or two molecules per nucleosome? Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5883–5894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Rabindran S. K., Wu C. Heat shock-regulated transcription in vitro from a reconstituted chromatin template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4109–4113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Wu C. Cell-free system for assembly of transcriptionally repressed chromatin from Drosophila embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Bustin M., Marsaud V., Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. The transcriptionally-active MMTV promoter is depleted of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):273–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kadonaga J. T. Role of chromatin structure in the regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90006-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Lira L. M., Kadonaga J. T. A general method for purification of H1 histones that are active for repression of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Protein Expr Purif. 1991 Apr-Jun;2(2-3):162–169. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(91)90066-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S., Almouzni G., Dasso M., Wolffe A. P. Chromatin transitions during early Xenopus embryogenesis: changes in histone H4 acetylation and in linker histone type. Dev Biol. 1993 Nov;160(1):214–227. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar B. A., Schubiger G. Parameters controlling transcriptional activation during early Drosophila development. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):871–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Hood L. E. Chromosomal proteins of Drosophila embryos. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4984–4991. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. C., Ausio J., Stanik V. H., van Holde K. E. Homogeneous reconstituted oligonucleosomes, evidence for salt-dependent folding in the absence of histone H1. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9129–9136. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. C., Wolffe A. P. Influence of chromatin folding on transcription initiation and elongation by RNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 1;31(34):7977–7988. doi: 10.1021/bi00149a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Wolffe A. P. Preferential and asymmetric interaction of linker histones with 5S DNA in the nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6415–6419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T. Assembly and disassembly of the Drosophila RNA polymerase II complex during transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2624–2631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure of transcriptionally competent and repressed genes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3997–4006. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07621.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Luse D. S. The presence of nucleosomes on a DNA template prevents initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Chromatin structure and transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:563–587. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.003023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Threshold phenomena and long-distance activation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1682–1685. doi: 10.1126/science.1388287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Initiation on chromatin templates in a yeast RNA polymerase II transcription system. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2282–2287. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenhaupt K., Cartwright I. L., Keene M. A., Zimmerman J. L., Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure in pre- and postblastula embryos of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. J., Török I., Kiss I., Karch F., Udvardy A. Evolutionary implications of a complex pattern of DNA sequence homology extending far upstream of the hsp70 genes at loci 87A7 and 87C1 in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacheva G. A., Guschin D. Y., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Karpov V. L., Ebralidse K. K., Mirzabekov A. D. Change in the pattern of histone binding to DNA upon transcriptional activation. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. P., Albright S. C., Wiseman J. M., Garrard W. T. Reassociation of histone H1 with nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11751–11760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch H. H., Olivera B. M., Tuan D., Davidson N. Selective dissociation of histones from calf thymus nucleoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):299–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Campos A., Shimamura A., Worcel A. Assembly and properties of chromatin containing histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):135–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5' end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):795–804. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant A., Bohmann D., Zentgraf H., Weiher H., Keller W. A transcription enhancer acts in vitro over distances of hundreds of base-pairs on both circular and linear templates but not on chromatin-reconstituted DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):577–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Sapp M., Rodriguez-Campos A., Worcel A. Histone H1 represses transcription from minichromosomes assembled in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5573–5584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tremethick D., Worcel A. Characterization of the repressed 5S DNA minichromosomes assembled in vitro with a high-speed supernatant of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4257–4269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B. Expression of a histone H1-like protein is restricted to early Xenopus development. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1284–1295. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeller W. C., Poole S. J., Kornberg T. In vitro transcription of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):68–81. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Reconstitution of chromatin core particles. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5295–5303. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P. Chromatin organization of the 87A7 heat shock locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 5;172(4):385–403. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Histone-H1-dependent chromatin superstructures and the suppression of gene activity. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90522-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):527–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. New approaches to chromatin function. New Biol. 1990 Mar;2(3):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Buchman A. R. Multiple functions of nucleosomes and regulatory factors in transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90160-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda G. K., Baker J., Schubiger G. Temporal regulation of gene expression in the blastoderm Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1800–1812. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlatanova J. Histone H1 and the regulation of transcription of eukaryotic genes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90053-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]