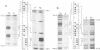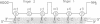Abstract
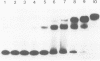
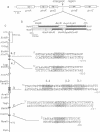
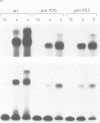
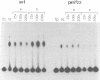
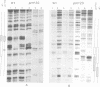
CREA is the negative regulator mediating carbon catabolism repression in Aspergillus nidulans. We have determined all the sites in the DNA region between the prnD and prnB genes of the proline degradation cluster of this organism which are able to bind a fusion protein containing the zinc finger domain of CREA. The consensus sequence derived for CREA binding is 5'-SYGGRG-3', but not all possible sites derived from this consensus do in fact bind. The binding of at least some sequences of the form 5'-SYGGAG-3' is context dependent. Two different and divergent sites, separated by one base pair (5'-GCGGAGACCCCAG-3'), contain the previously sequenced derepressed mutations and are essential for carbon catabolite repression in vivo. We have studied the binding of CREA to the region by DNase I and methylation protection, and by methylation and depurination interference. We propose that this pair of sites is the physiological, cis-acting element responsible for the carbon catabolite repression of prnB transcription.
Full text
PDF
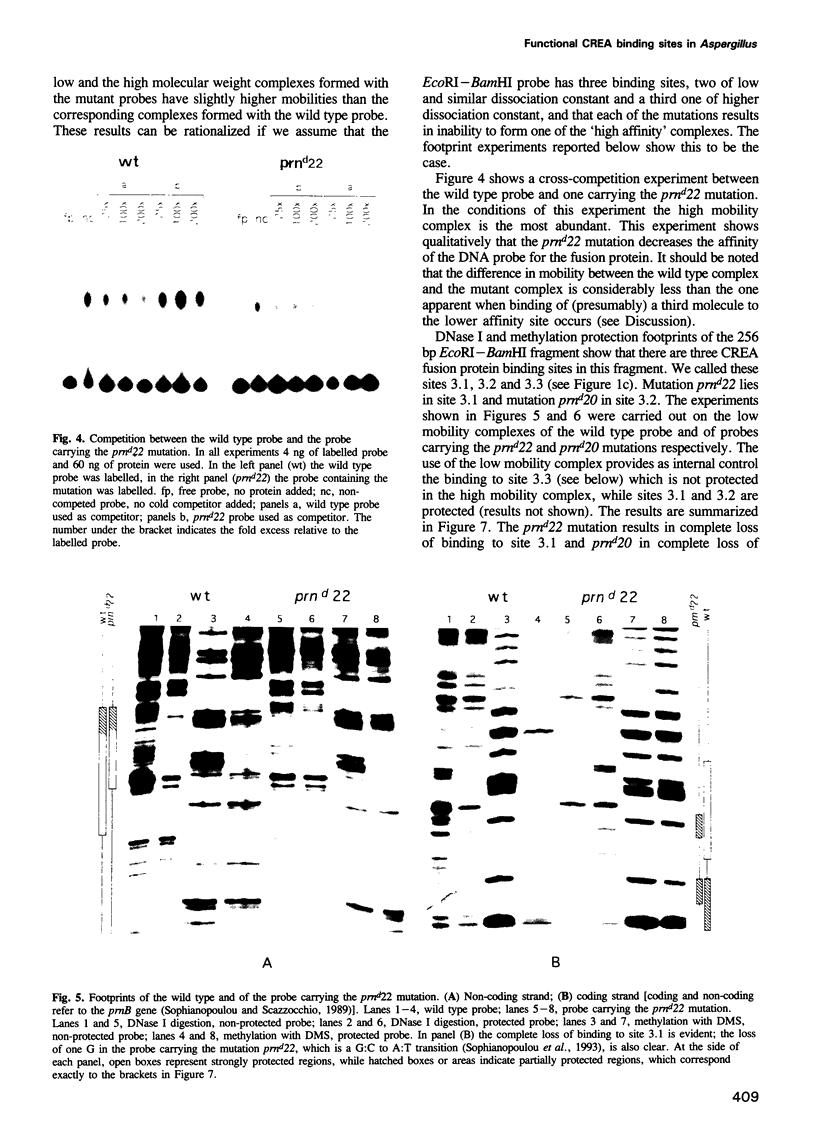



Images in this article
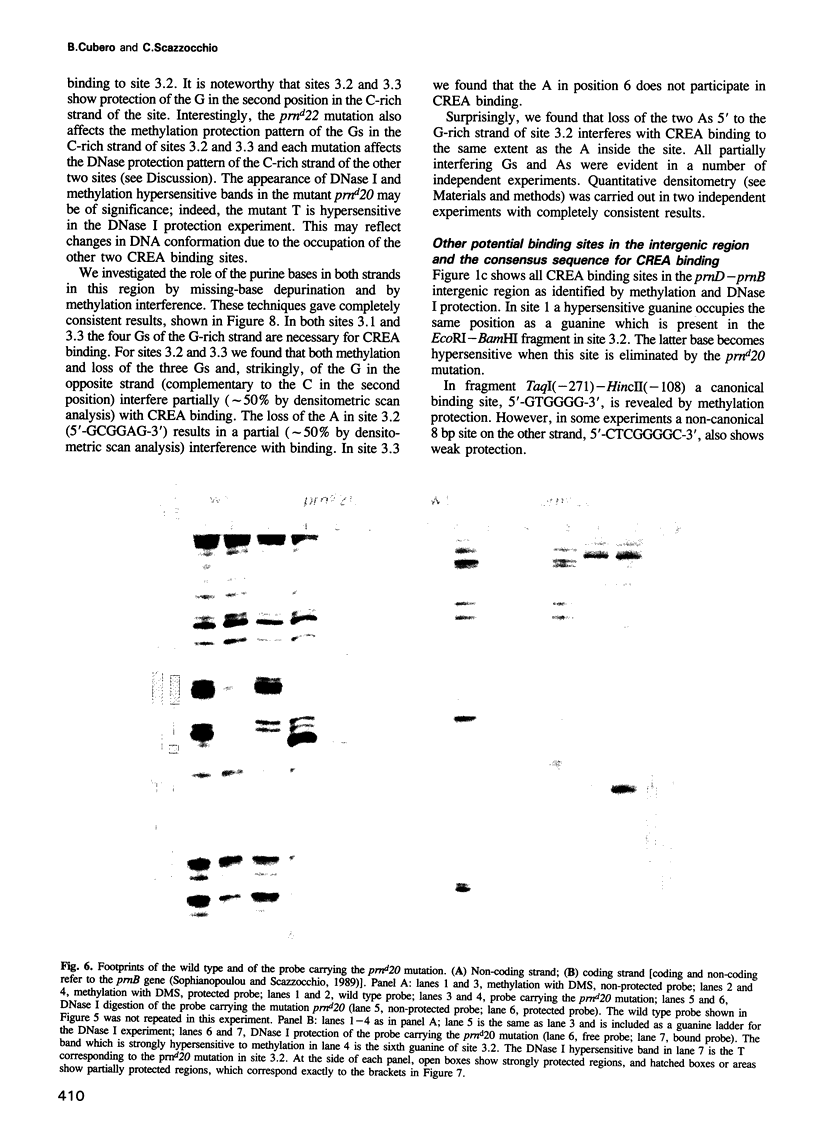
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
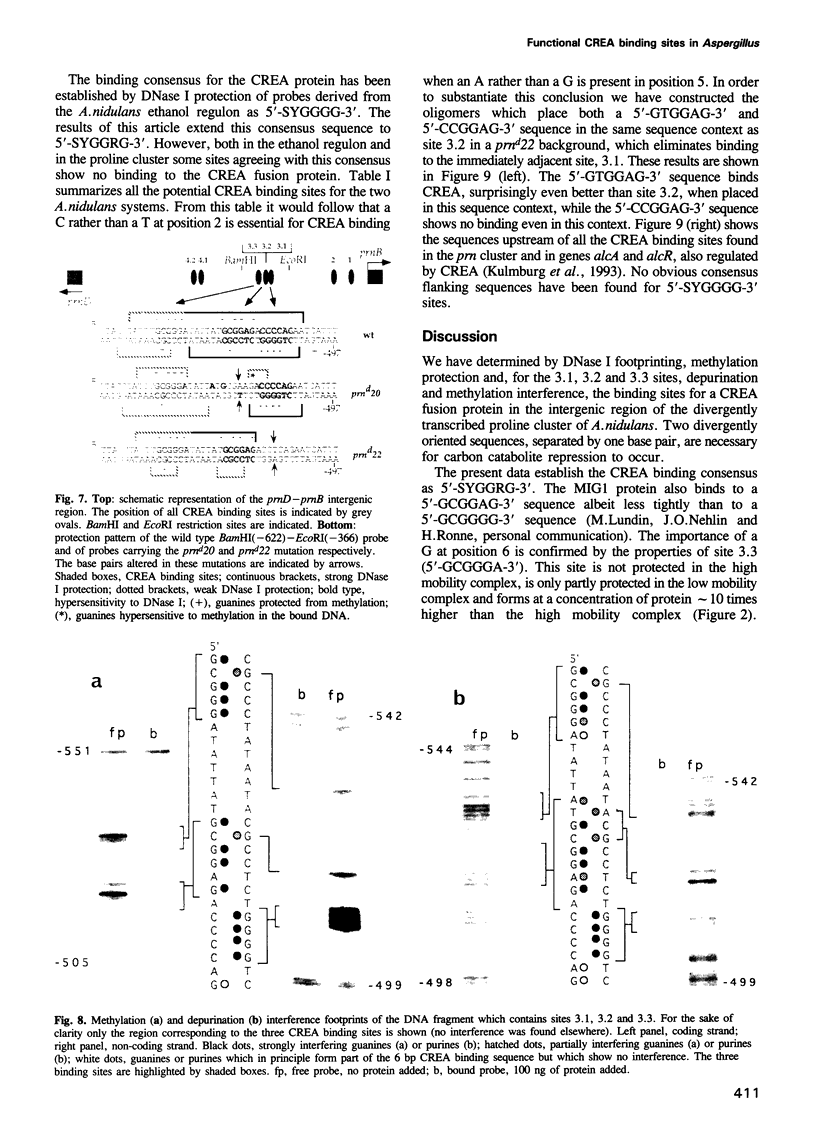
- Adams T. H., Boylan M. T., Timberlake W. E. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr, Cove D. J. Nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 2;126(2):111–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00330988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
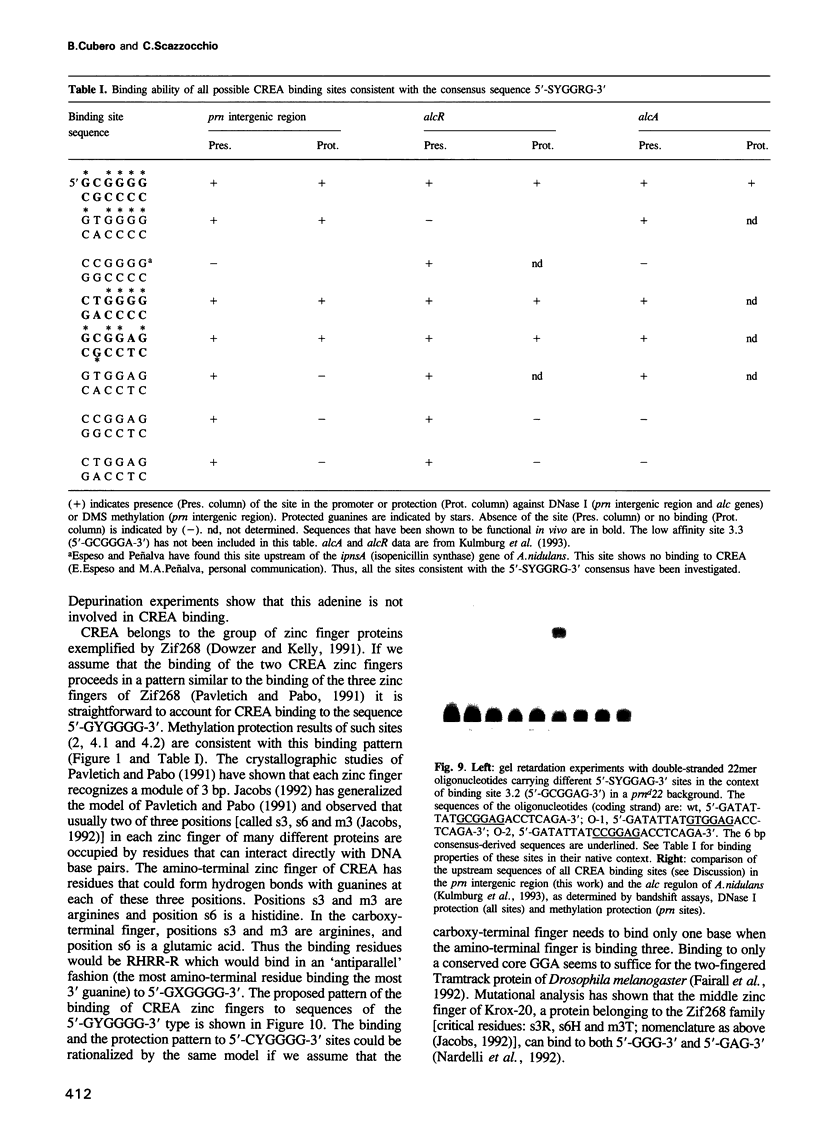
- Arst H. N., Jr, MacDonald D. W. A gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans with an internally located cis-acting regulatory region. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):26–31. doi: 10.1038/254026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr, MacDonald D. W. Reduced expression of a distal gene of the prn gene cluster in deletion mutants of Aspergillus nidulans: genetic evidence for a dicistronic messenger in an eukaryote. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 6;163(1):17–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00268959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C., Arst H. N., Jr Carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillos nidulans. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):573–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowzer C. E., Kelly J. M. Analysis of the creA gene, a regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5701–5709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowzer C. E., Kelly J. M. Cloning of the creA gene from Aspergillus nidulans: a gene involved in carbon catabolite repression. Curr Genet. 1989 Jun;15(6):457–459. doi: 10.1007/BF00376804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estruch F. The yeast putative transcriptional repressor RGM1 is a proline-rich zinc finger protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4873–4877. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Harrison S. D., Travers A. A., Rhodes D. Sequence-specific DNA binding by a two zinc-finger peptide from the Drosophila melanogaster Tramtrack protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):349–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90952-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. W., Johnston M. Regulated expression of the GAL4 activator gene in yeast provides a sensitive genetic switch for glucose repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8597–8601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne T. A., Blumberg H., Young E. T. Sequence homology of the yeast regulatory protein ADR1 with Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):283–287. doi: 10.1038/320283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hromas R., Collins S. J., Hickstein D., Raskind W., Deaven L. L., O'Hara P., Hagen F. S., Kaushansky K. A retinoic acid-responsive human zinc finger gene, MZF-1, preferentially expressed in myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14183–14187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull E. P., Green P. M., Arst H. N., Jr, Scazzocchio C. Cloning and physical characterization of the L-proline catabolism gene cluster of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs G. H. Determination of the base recognition positions of zinc fingers from sequence analysis. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4507–4517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulmburg P., Mathieu M., Dowzer C., Kelly J., Felenbok B. Specific binding sites in the alcR and alcA promoters of the ethanol regulon for the CREA repressor mediating carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):847–857. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Vesque C., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Frank R., Charnay P. The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3456–3467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B. The isoenzymes of glutathione transferase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1985;57:357–417. doi: 10.1002/9780470123034.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T., Charnay P. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: analysis of base specificity by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4137–4144. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Carlberg M., Ronne H. Control of yeast GAL genes by MIG1 repressor: a transcriptional cascade in the glucose response. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3373–3377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehlin J. O., Ronne H. Yeast MIG1 repressor is related to the mammalian early growth response and Wilms' tumour finger proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2891–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst S. M., Harrison D. A., Remington M. P., Spana C., Kelley R. L., Coyne R. S., Corces V. G. The Drosophila su(Hw) gene, which controls the phenotypic effect of the gypsy transposable element, encodes a putative DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1205–1215. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma K. K., Arst H. N., Jr The product of the regulatory gene of the proline catabolism gene cluster of Aspergillus nidulans is a positive-acting protein. Curr Genet. 1985;9(4):299–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00419959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianopoulou V., Scazzocchio C. The proline transport protein of Aspergillus nidulans is very similar to amino acid transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):705–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianopoulou V., Suárez T., Diallinas G., Scazzocchio C. Operator derepressed mutations in the proline utilisation gene cluster of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00277114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Donoviel M. S., Young E. T. Adjacent upstream activation sequence elements synergistically regulate transcription of ADH2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):34–42. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]