Abstract
Protein introns are recently discovered genetic elements whose intervening sequences are removed from a precursor protein by an unusual protein splicing reaction. This involves the excision of a central spacer molecule, the protein intron, and the religation of the amino- and carboxy-terminal fragments of the precursor. The recA gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis contains one such element and we now show that the other major mycobacterial pathogen, Mycobacterium leprae, also possesses a protein intron in its recA, although other mycobacterial recA genes do not. However, these two protein introns are different in size, sequence and location of insertion of their coding sequences into the recAs of M. tuberculosis and M. leprae, indicating that acquisition of the protein introns has occurred independently in the two species, and thus suggesting that there has been selection for splicing in the maturation of RecA in the pathogenic mycobacteria. The M. leprae protein intron provides an example of conditional protein splicing, splicing occurring in M. leprae itself but not when expressed in Escherichia coli, unlike most previously described protein introns. These observations suggest that protein introns may perform a function for their host, rather than being just selfish elements.
Full text
PDF


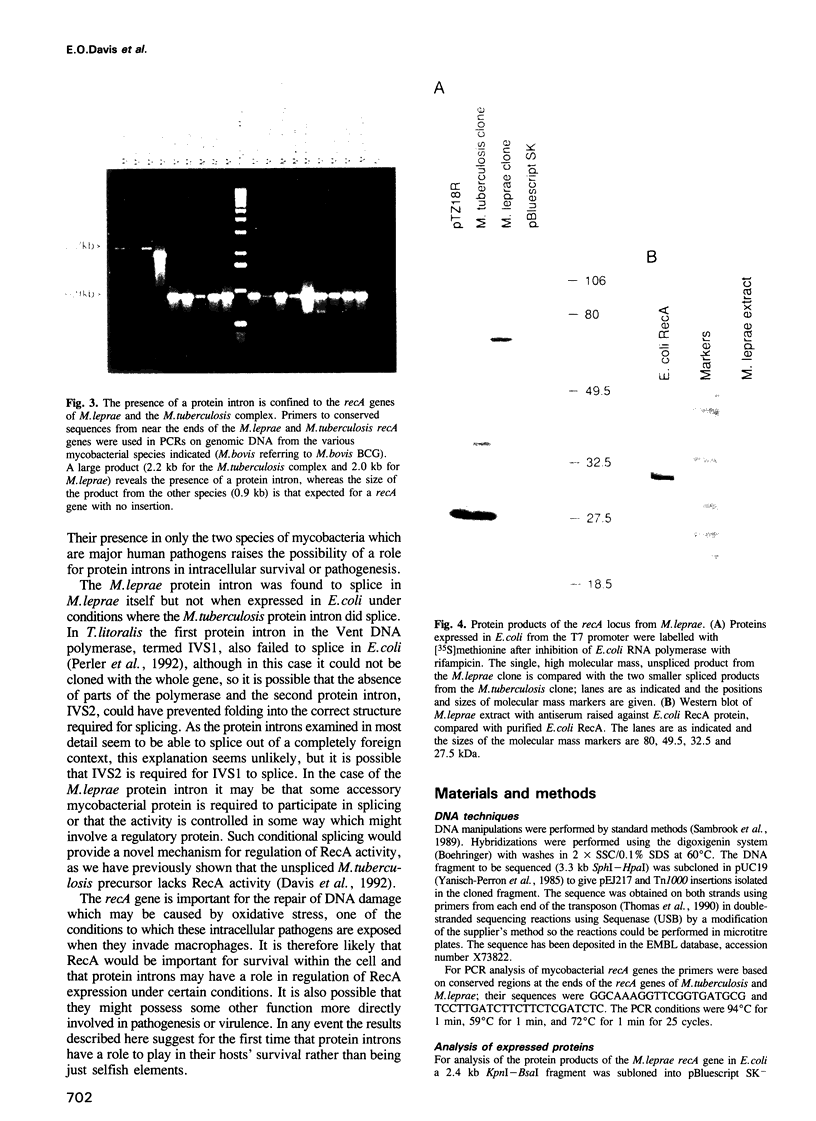

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper A. A., Chen Y. J., Lindorfer M. A., Stevens T. H. Protein splicing of the yeast TFP1 intervening protein sequence: a model for self-excision. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Jenner P. J., Brooks P. C., Colston M. J., Sedgwick S. G. Protein splicing in the maturation of M. tuberculosis recA protein: a mechanism for tolerating a novel class of intervening sequence. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90349-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Sedgwick S. G., Colston M. J. Novel structure of the recA locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis implies processing of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5653–5662. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5653-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. The comings and goings of homing endonucleases and mobile introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5379–5381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiglmeier K., Honoré N., Woods S. A., Caudron B., Cole S. T. Use of an ordered cosmid library to deduce the genomic organization of Mycobacterium leprae. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Thorner J. Homing of a DNA endonuclease gene by meiotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):301–306. doi: 10.1038/357301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H. H., Xu J., Gallagher M., Dean G. E. Peptide splicing in the vacuolar ATPase subunit A from Candida tropicalis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7372–7381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata R., Anraku Y. Mutations at the putative junction sites of the yeast VMA1 protein, the catalytic subunit of the vacuolar membrane H(+)-ATPase, inhibit its processing by protein splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92347-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata R., Ohsumk Y., Nakano A., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Anraku Y. Molecular structure of a gene, VMA1, encoding the catalytic subunit of H(+)-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6726–6733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. A., Perler F. B., Noren C. J., Jack W. E. Protein splicing removes intervening sequences in an archaea DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6153–6157. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim M. A., Lamb F. I., Colston M. J. Analysis of variation in batches of armadillo-derived Mycobacterium leprae by immunoblotting. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1990 Mar;58(1):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane P. M., Yamashiro C. T., Wolczyk D. F., Neff N., Goebl M., Stevens T. H. Protein splicing converts the yeast TFP1 gene product to the 69-kD subunit of the vacuolar H(+)-adenosine triphosphatase. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):651–657. doi: 10.1126/science.2146742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F. B., Comb D. G., Jack W. E., Moran L. S., Qiang B., Kucera R. B., Benner J., Slatko B. E., Nwankwo D. O., Hempstead S. K. Intervening sequences in an Archaea DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5577–5581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Mobile introns and intron-encoded proteins. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1106–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.2479980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Goodrich-Blair H. Protein introns: a new home for endonucleases. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90345-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Crowne H. M., Pidsley S. C., Sedgwick S. G. Structural characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 umu operon. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4979–4987. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4979-4987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. J. The curious case of protein splicing: mechanistic insights suggested by protein semisynthesis. Protein Sci. 1993 May;2(5):697–705. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]