Abstract
PURPOSE
This pilot study aimed to determine whether raw milk reduces lactose malabsorption and/or lactose intolerance symptoms relative to pasteurized milk.
METHODS
We performed a crossover trial involving 16 adults with self-reported lactose intolerance and lactose malabsorption confirmed by hydrogen (H2) breath testing. Participants underwent 3, 8-day milk phases (raw vs 2 controls: pasteurized, soy) in randomized order separated by 1-week washout periods. On days 1 and 8 of each phase, milk consumption was 473 mL (16 oz); on days 2 to 7, milk dosage increased daily by 118 mL (4 oz), beginning with 118 mL (4 oz) on day 2 and reaching 710 mL (24 oz) on day 7. Outcomes were area under the breath H2 curve (AUC ∆H2) and self-reported symptom severity (visual analog scales: flatulence/gas, audible bowel sounds, abdominal cramping, diarrhea).
RESULTS
AUC ∆H2 (mean ± standard error of the mean) was higher for raw vs pasteurized on day 1 (113 ± 21 vs 71 ± 12 ppm·min·10−2, respectively, P = .01) but not day 8 (72 ± 14 vs 74 ± 15 ppm·min·10−2, respectively, P = .9). Symptom severities were not different for raw vs pasteurized on day 7 with the highest dosage (P >.7). AUC ∆H2 and symptom severities were higher for both dairy milks compared with soy milk.
CONCLUSIONS
Raw milk failed to reduce lactose malabsorption or lactose intolerance symptoms compared with pasteurized milk among adults positive for lactose malabsorption. These results do not support widespread anecdotal claims that raw milk reduces the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Keywords: lactose intolerance, dairy products, soy milk, adult
INTRODUCTION
Lactose malabsorption is an extremely common condition worldwide, and its incidence increases with age and varies between ethnicities.1,2 Bacteria in the colon ferment undigested lactose into short-chain fatty acids, hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide, resulting in such symptoms as bloating, abdominal pain, and/or diarrhea after ingestion of lactose.1 National Institutes of Health (NIH) consensus development panel defined lactose intolerance as a clinical syndrome characterized by the onset of gastrointestinal symptoms following a lactose challenge,3 whereas true lactose malabsorption is identified through a hydrogen breath test (HBT). Many people with lactose malabsorption do not report clinical lactose intolerance.4,5 Conversely, many individuals with perceived lactose intolerance do not experience malabsorption.6 Because of inconsistent definitions in previous studies, the true prevalence of lactose intolerance is unknown.7
Strategies to reduce unpleasant gastrointestinal symptoms associated with lactose intolerance include (1) choosing lactose-free or reduced-lactose dairy foods,8–11 (2) choosing fermented dairy foods,11–13 (3) combining lactose intake with a meal,14–16 (4) taking lactase enzyme tablets,10,11,17 (5) consuming probiotics,11,18–20 (6) colonic adaptation,21–22 and (7) psychological and behavioral approaches.23–25 None of these strategies, however, have been shown to fully eliminate symptoms. A recent review by the NIH highlighted the need for further studies evaluating the effectiveness of interventions addressing lactose intolerance.3,7
Recently, unpasteurized raw milk consumption has increased in popularity and emerged into a nationwide movement despite the acknowledgement of risks associated with foodborne pathogens.26 Raw milk proponents and producers purport that consumption of raw milk is associated with reductions in atopic conditions,27–29 autism, inflammatory bowel disease, and lactose intolerance; these claims currently lack definitive scientific evidence. In the case of raw vs pasteurized yogurt, it has been shown repeatedly that compared with pasteurized yogurt, unpasteurized yogurt containing live bacterial cultures with lactase activity significantly reduces lactose malabsorption.30–34 These findings are apparently due to bacterial lactase activity provided in the small intestine and/or changes in the intestinal milieu.30,34 As in the case of raw yogurt, the omission of pasteurization in the raw milk production process results in a greater number of surviving microflora,26 including naturally occurring strains of lactobacilli.35 It has been hypothesized that these additional microflora may aid in the digestion of lactose, reducing lactose malabsorption for raw milk relative to pasteurized milk. The objective of this pilot study was to examine whether breath hydrogen (H2) (standard measure of lactose malabsorption, primary outcome) and/or symptoms of lactose intolerance (secondary outcomes) would be reduced after consuming raw milk vs pasteurized milk, using soy milk as a negative control.
METHODS
Study Participants
Participants were recruited from the local community near Stanford University through email and radio advertisements and letters to previous study participants. Participants were screened first using an online survey. The initial eligibility criteria were self-reported lactose intolerance symptoms of “moderate” to “severe” severity. Exclusion criteria included self-reported symptoms of “mild” or “extremely severe” severity, recent or planned antibiotic consumption, a history of diarrheal illness within the past month, and a history of any gastrointestinal conditions other than lactose malabsorption. Remaining eligible participants were screened using the standardized HBT. Participants whose peak hydrogen concentrations rose to 25 ppm or higher above baseline and who simultaneously experienced symptoms of lactose intolerance were included in the study. Participants received $150 for completing all 3 milk phases. All participants provided written informed consent, and the study was approved by the Stanford University Human Subjects Committee.
Study Design
We used a randomized, double-blind, 3-way crossover design. The protocol required each participant to consume 3 types of milk for 8 days each: organic whole raw milk (R), organic whole pasteurized milk (P), and plain (unflavored) soy milk (S). Each 8-day treatment phase was separated by a washout phase of 1 week. Participants were instructed to avoid consuming all dairy and lactose-containing products (other than study products) throughout the treatment and washout phases, as well as during a 1-week run-in period that preceded the first treatment week.
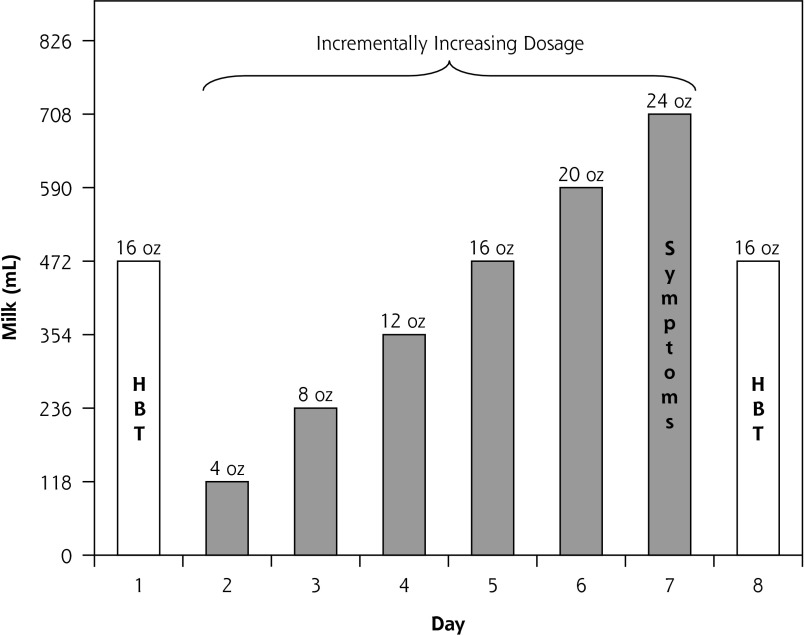
Milk dosage for each 8-day phase is displayed in Figure 1. Eight-day milk phases were selected to explore potential adaptation to each of the milk products resulting in possible changes in the intestinal milieu.30,34 Each 8-day phase was anchored on days 1 and 8 by a dosage of 473 mL (16 oz) to allow for examination of potential adaptation. Each phase included an incrementally increasing dosage on days 2 to 7 to explore participant tolerance to doses ranging from small to substantial. Participants had the option of consuming less than the assigned dose at any point if their symptoms were unbearable. The amount of milk consumed was confirmed verbally twice during each phase, and participants were asked to return leftover milk, which was measured by study staff to corroborate verbal accounts.
Figure 1.
Milk dosage protocol and outcome measures for each 8-day milk phase: full amount of milk was consumed in 1 sitting on each day.
HBT = hydrogen breath test; Symptoms = self-reported severity of 4 symptoms: flatulence/gas, diarrhea, audible bowel sounds, and abdominal cramping.
The 8-day treatment duration, escalating dosage (4 to 24 oz), and compensation amount ($150) were selected in the design phase of the project and informed by 2 focus groups conducted among lactose intolerant individuals. Dosage and duration were selected to lead to symptoms sufficiently severe to allow for a detectable difference in treatment arms but sufficiently bearable to allow for successful recruitment of typical lactose intolerant individuals, thereby allowing for a reasonable level of generalizability of the findings. Participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 6 possible sequences of the 3 milks: RPS, RSP, PRS, PSR, SRP, or SPR. Randomization was done in blocks of 12 (ie, 2 of each of the 6 possible sequences) and was performed by a researcher (S.M.) who was blinded to the study assignments and who selected pieces of paper with order assignments from an envelope.
Milk Products
The raw milk was an organic, grade A, whole milk produced by Organic Pastures, which follows state mandated testing for human pathogens. The pasteurized milk was an organic, grade A, whole milk produced by Horizon Organic. Among 12 different types of soy milk taste tested by a panel of study staff, the soy milk that most resembled the taste and appearance of the cow’s milk was selected: an organic, Soy Dream Original Classic brand produced by The Hain Celestial Group. Energy content and macronutrient composition of the milk products were obtained from label information (Table 1).
Table 1.
Composition of Milk Products per 237 mL (8 oz)
| Component | Raw Milk | Pasteurized Milk | Soy (Nondairy) Milk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 145 | 145 | 126 |
| Macronutrients (g) | |||
| Fat | 7.8 | 7.8 | 3.9 |
| Protein | 7.8 | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Carbohydrate | 11.6 | 11.6 | 15.5 |
| Sugars | 11.6 | 11.6 | 8.7 |
| Lactose | 11.6 | 11.6 | 0 |
Note: All milk products included sugar-free vanilla syrup flavoring in a flavoring to milk ratio of 1:31.
Blinding
Preparation and distribution of each of the milk types was made as comparable as possible so study participants and researchers were blinded to the type of milk they received. To maximize palatability and masking of milk taste, sugar-free vanilla syrup flavoring (Torani brand) was added to all milks in a flavoring to milk ratio of 1:31. To maintain staff blinding, milk containers were prepared and coded by a researcher (S.M.) who did not have participant contact, while separate researchers (Q.V. and J.H.) distributed milks to participants and remained blinded to assignment phase for the duration of the study. All milks were provided in standardized, unlabeled containers. Participants were asked at the end of each treatment phase to try to identify their milk assignment.
Data Collection
Hydrogen Breath Test
The primary study outcome was breath H2 excretion as measured by HBT.36 The increase in H2 production after the consumption of lactose corresponds to the degree of lactose malabsorption. Those determined eligible after the initial online survey screening were invited to complete a 3-hour HBT: after an overnight fast, end-alveolar air samples containing 20 mL or more were collected before and at 9 consecutive 20-minute intervals after an oral load of 25 g of lactose dissolved in water, with continued fasting throughout the 3-hour test. Expired H2 concentrations were stored in plastic syringes with stopcocks and measured within 12 hours, in parts per million, using gaseous chromatography (Breath Tracker Digital Microlyzer, model SC; Quintron Instruments). Participants whose H2 levels rose 25 ppm or more above baseline and who experienced any symptom(s) of lactose intolerance during the test were included in the study.
Once enrolled, on days 1 and 8 of each phase, participants completed a similar 4-hour HBT after consumption of the assigned milk. Samples were collected for 4 rather than 3 hours during the tests conducted with study milks to account for the longer digestion time of milk relative to the lactose solution used for the screening HBT. H2 concentrations were expressed as area under the H2 curve above baseline (AUC ∆H2) in parts per million per minute per 10−2 (ppm · min · 10−2), calculated according to the linear trapezoidal rule ignoring any area below the baseline,37 and as maximal increase over baseline concentration (peak ∆H2) in parts per million.38
Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
To assess the incidence and severity of symptoms, a validated gastrointestinal symptom log39 was used asking participants to mark on a 10-cm visual analog scale of 0 to 10 the severity of 4 symptoms: flatulence/gas, diarrhea, audible bowel sounds, and abdominal cramping. Symptom logs were completed at 52 time points: 4 times during the screening HBT (at baseline and at 3 consecutive 1-hour intervals); 5 times during the HBT on days 1 and 8 of each phase (at baseline and at 4 consecutive 1-hour intervals); and once per day on days 2 through 7 of each phase.
Statistical Methods
Sample size was determined based on the selection of a 25% decrease in AUC ∆H2 as the minimal difference that would be clinically significant—a projected effect size of 1.0. With a crossover design, it was determined that 15 subjects would yield 95% power using α = .05 to detect a 25% decrease. Differences in AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations (primary outcomes) among milk phases were examined by repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). Repeated-measures ANOVA was also used to test for differences within each of the symptom categories (secondary outcomes) on day 7. For both the H2 and symptom levels, when statistical significance was reached by ANOVA, pairwise differences were examined using matched pairs t tests. Matched pairs t tests were also used to test for differences in AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations between days 1 and 8 of each phase. In each analysis, only those study participants with complete data were included in the statistical testing. All statistical tests were 2-tailed using α <.05.
RESULTS
Study Population
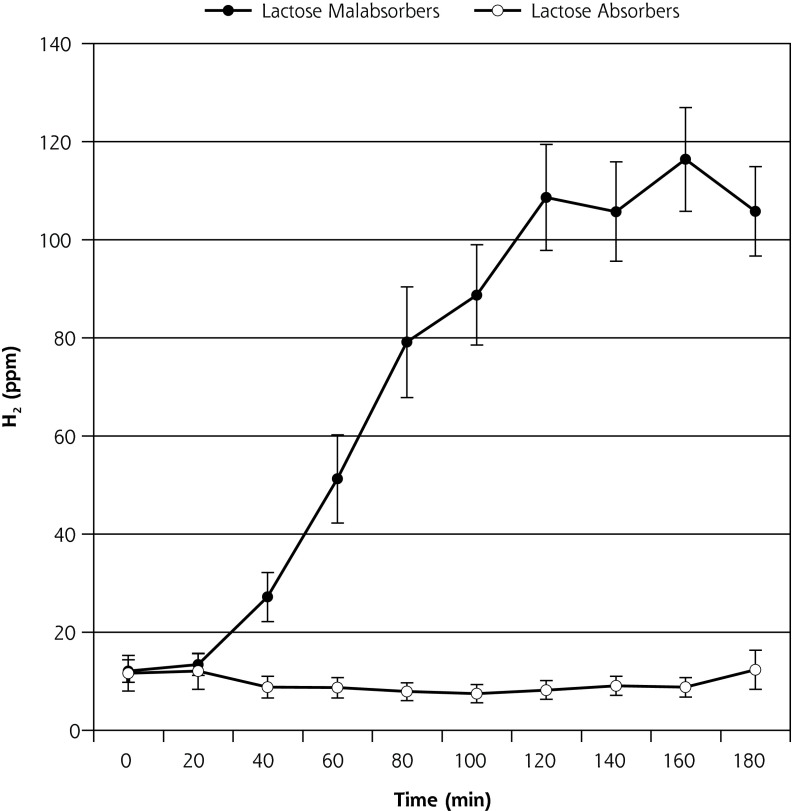
Participant enrollment began in May 2010, and the study ended in September 2010. Of 63 potential participants screened using the HBT, 27 (43%) tested positive for lactose malabsorption (Figure 2), all of whom reported symptoms of lactose intolerance during the HBT. Among these 27 individuals, 11 chose not to continue. Among the 16 participants who were randomized, 2 to 4 were assigned to each of the 6 possible orders of study milks. Randomized participants were aged a mean of 40 years (SD = 14 years), had a mean of 16 years (SD = 3 years) of education, and had a mean body mass index of 24 kg/m2 (SD = 2 kg/m2).
Figure 2.
Breath H2 results for 63 participants with self-reported lactose intolerance (mean ± SEM).
H2 = hydrogen; SEM = standard error of the mean.
Note: of 63 participants, 27 (43%) tested positive for lactose malabsorption, as evidenced by a rise in H2 ≥25 ppm, and 36 (57%) tested negative.
Retention and Adherence
All 16 participants completed all 3 milk phases. There was 100% adherence on day 1 of all 3 milk phases. Four participants failed to adhere to the full 8-day protocol during 1 of the 3 milk phases: 3 participants opted to consume less than the assigned dosage during 1 of the phases due to unbearable symptoms, and 1 participant accidentally did not consume milk on day 6 of the R phase.
There was no significant difference in adherence to the milk consumption protocol among the 3 milk phases (P = .3), and 90% or more of the total assigned milk intake was consumed by 88%, 94%, and 100% of the participants during the R, P, and S phases, respectively.
Blinding
Of the 16 participants, 12 (80%) correctly guessed assignment to the soy milk phase, whereas 6 (40%) correctly identified both dairy milks. Successful identification of milk assignment increased with each successive milk phase from 43% to 69% to 88% during the first, second, and third phases, respectively.
H2 Outcomes
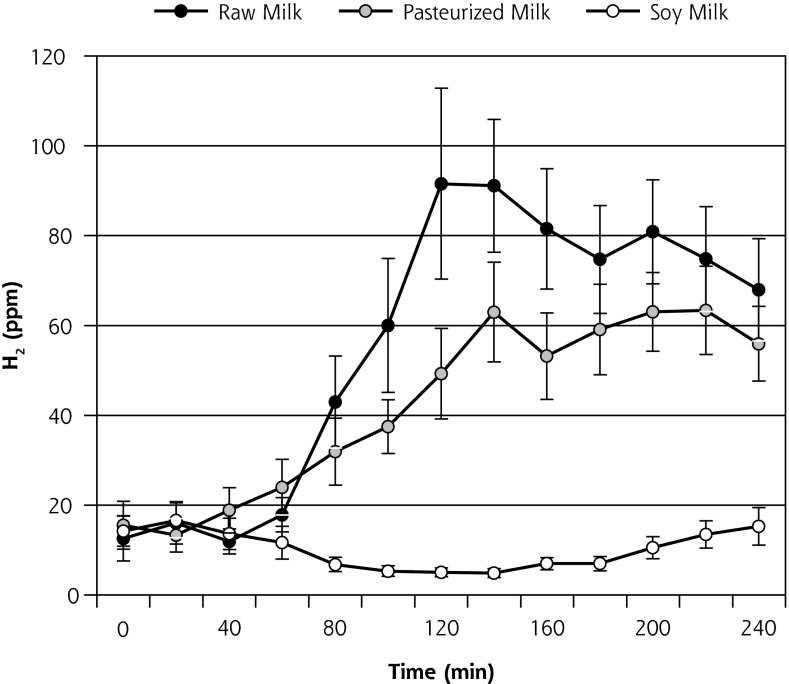
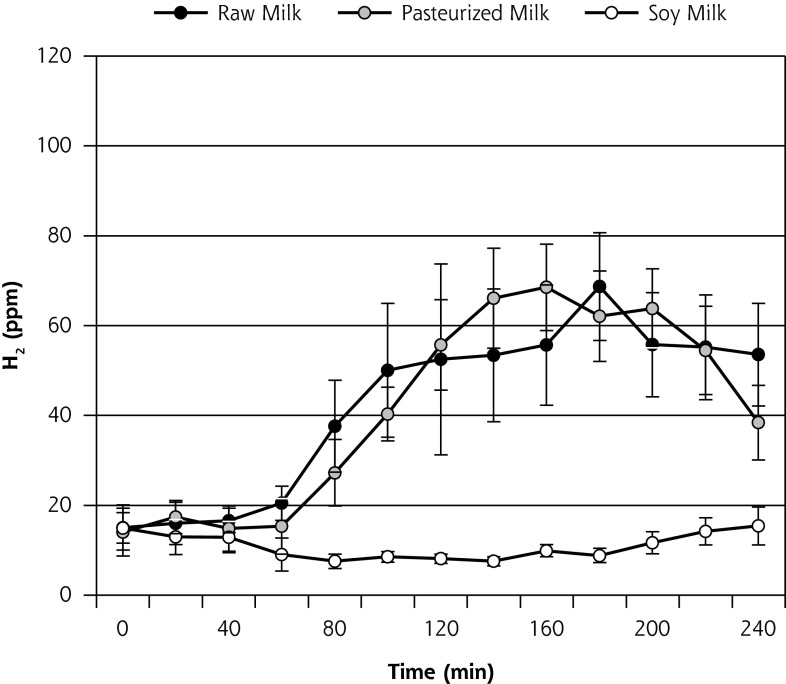
Mean H2 production (± standard error of the mean [SEM]) during the course of the HBT on day 1 is displayed in Figure 3a and on day 8 is displayed in Figure 3b. AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations for both days 1 and 8 are shown in Table 2. Contrary to what was hypothesized, on day 1, both AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations were significantly higher for R relative to P (P = .01). In contrast, on day 8, no significant difference was observed between R and P (P = .9). On both days 1 and 8, AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations were significantly higher for the 2 dairy milks (R and P) relative to the soy milk (P ≤.001). AUC ∆H2 and peak ∆H2 concentrations between days 1 and 8 indicated a borderline significant reduction in H2 production during the course of the R phase (P = .05, and .06, respectively) (Table 2). No significant change was observed for the P phase (P >.6) or S phase (P = .7).
Figure 3a.
Breath H2 results for day 1 of each 8-day crossover phase (n = 16) (mean ± SEM).
H2 = hydrogen; SEM = standard error of the mean.
Note: End-alveolar air samples collected before and at 12 consecutive 20-minute intervals after ingestion of 473 mL (16 oz) of milk.
Figure 3b.
Breath H2 results for day 8 of each 8-day crossover phase (n = 14) (mean ± SEM).
H2 = hydrogen; SEM = standard error of the mean.
Note: End-alveolar air samples collected before and at 12 consecutive 20-minute intervals after ingestion of 473 mL (16 oz) of milk. All data for 2 participants who did not undergo the day-8 hydrogen breath test during one of the milk phases were omitted from this analysis.
Table 2.
Breath H2 Results for Each 8-Day Crossover Phase, n = 16 (mean ± SEM)
| Phase | Milk Consumption Phases | P Valuea | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| Raw (R) | Pasteurized (P) | Soy (S) | R vs P | R vs S | P vs S | |
| AUC ∆H2b | ||||||
| Day 1 | 113 ± 21 | 71 ± 12 | 5 ± 2 | 0.01 | <.001 | <.001 |
| Day 8 | 72 ± 14c | 74 ± 15 | 5 ± 2 | 0.9 | <.001 | <.001 |
| Peak ∆H2 | ||||||
| Day 1 | 117 ± 20 | 75 ± 11 | 11 ± 4 | 0.01 | <.001 | <.001 |
| Day 8 | 79 ± 14d | 80 ± 13 | 12 ± 3 | 0.9 | <.001 | <.001 |
ANOVA = analysis of variance; AUC ∆H2 = area under the H2 curve above baseline; Peak ∆H2 = highest H2 concentration after milk ingestion, minus baseline concentration (ppm); H2 = hydrogen; HBT = hydrogen breath test.
Notes: End-alveolar air samples collected before and at 12 consecutive 20-minute intervals after ingestion of 473 mL (16 oz) of milk. All data for 2 participants who did not undergo the day-8 HBT during one of the milk phases were omitted from the day-8 analysis (n = 14). In the analysis comparing days 1 and 8, all data were omitted for 1 participant in the R phase and 1 participant in the P phase analyses who did not complete the day-8 HBT in each respective phase (n = 15).
Group differences were tested by repeated-measures ANOVA, showing significant differences among the 3 milks in all instances (P <.001). Pairwise differences were subsequently calculated using matched pairs t tests.
AUC ∆H2 calculated by the linear trapezoidal method (ppm · min · 10−2).
Matched pair t test for day 1 vs day 8 for raw milk (n = 15): P = .05.
Matched pair t test for day 1 vs day 8 for raw milk (n = 15): P = .06.
Symptom Outcomes
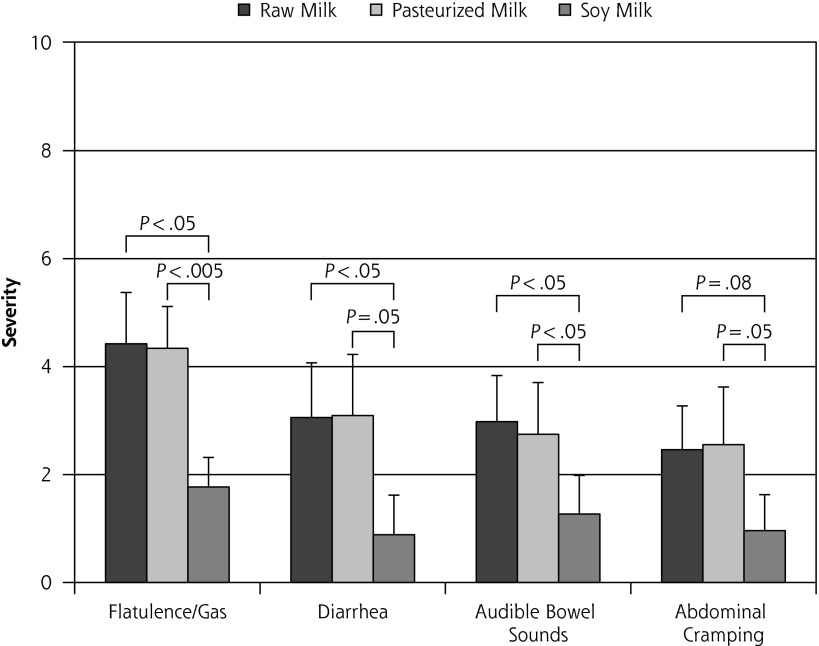
The highest milk dose, 710 mL (24 oz), occurred on day 7 of each milk phase and produced the most severe symptoms relative to all other days, as would be expected. All but 3 participants were able to complete this dose for all 3 milk phases. Mean self-reported symptom severity levels (± SEM) are displayed in Figure 4. There was no significant difference in severity levels between R and P for any of the 4 categories (P >.7).
Figure 4.
Lactose intolerance symptom severity report following ingestion of 710 mL (24 oz) of milk on day 7 of each 8-day crossover phase (n = 13) (mean ± SEM).
Note: Visual analog scale: 0 = no symptoms, 10 = unbearably severe symptoms. All data for 3 participants who were unable to complete one of the 710 mL (24 oz) doses were omitted from this analysis.
DISCUSSION
Our trial was designed to determine whether lactose malabsorption and/or lactose intolerance symptoms experienced by adults positive for lactose malabsorption would be reduced with raw milk vs pasteurized milk. The hypothesis was not supported. To the contrary, H2 results showed higher lactose malabsorption for raw vs pasteurized milk on day 1, and H2 results showed comparable degrees of lactose malabsorption for both milks on day 8. Day 7 symptom severities were similar for raw and pasteurized milk. Inclusion of soy milk as a negative control showed that in all cases both dairy milks induced significantly greater degrees of lactose malabsorption and intolerance symptoms. Overall, this 3-arm crossover trial provided no evidence that raw milk is better tolerated by adults positive for lactose malabsorption, either objectively or subjectively.
Previous studies have shown that in the case of yogurt, the additional microflora in unpasteurized yogurt reduce lactose malabsorption relative to pasteurized yogurt.30–34 One possible reason that a similar effect was not observed in the current study stems from the greater viscosity of yogurt, which prolongs digestion time, potentially allowing more time for the microflora to hydrolyze lactose in the small intestine.30 The current findings for raw milk parallel those of sweet acidophilus milk, which also contains live bacteria but has similarly been shown not to reduce lactose malabsorption.32,40,41
Interestingly, raw milk induced significantly greater H2 production than pasteurized milk on day 1 but not on day 8, despite containing identical amounts of lactose. It is not clear why this was the case. Although the reduced H2 production observed for raw milk on day 8 vs day 1 suggests a degree of adaptation to raw milk, this apparent adaptation led only to levels of lactose malabsorption comparable to those of pasteurized milk. In contrast to raw milk, no adaptation was observed for pasteurized milk. This finding does not support the colonic adaptation hypothesis for conventional milk and parallels findings from other randomized controlled trials.7,21,22 Notably, 57% (36 of 63) of screened individuals in the current study tested negative for lactose malabsorption despite their personal belief they were lactose intolerant. This finding confirms conclusions drawn by a recent NIH review indicating that many who believe they are lactose intolerant are not true lactose malabsorbers.3
There were several strengths in the design of the current study, including each participant serving as his or her own control in the crossover design, the use of both objective (breath H2) and subjective (symptom report) outcome measures, and the use of soy milk as a negative control. Strengths in conduct of the study included 100% retention across all 3 milk phases and high levels of adherence to the incrementally increasing dosage schedule. Double-blind study efforts proved highly effective for study staff and partially effective for participants. The current study also had strong ecological validity as one of the few studies on lactose intolerance that utilized commercially available milk products rather than isolated lactose. We believe it is also the first randomized controlled trial examining the effect of raw milk on symptoms of lactose intolerance. Overall, these strengths in design and conduct address many of the limitations identified in the recent NIH consensus report.3
The study also included several limitations. The sample size was small, the impact of which was mitigated to some degree by using a crossover design. The sample size was too small to examine potential ethnic/ racial differences. The 8-day study phases precluded examining possible responses or adaptation to raw milk that might have occurred after longer periods of time. A requirement to elicit and sustain symptoms of lactose intolerance for longer than 8 days, however, would likely make recruitment substantially more challenging, resulting in a lower percentage of eligible participants enrolling and thus a decrease in generalizability. The study also did not address any questions regarding consumer behavior associated with the higher cost (2-to 3-fold) of raw milk relative to conventional milk.
Replication of the findings presented here would strengthen the conclusions. To that end, the design and conduct of this pilot study should be useful in informing future studies of a larger scale. In particular, feedback from study participants suggested that escalating the milk dosage over time, with the option to discontinue the escalation at any time because of unbearable symptoms, was an important strategy for addressing concerns about the discomfort level that would arise from participating. Perhaps equally informative, and unexpected by our research team, more than 80% of our participants were willing to complete the full 1-week regimen and consume the highest 24-oz dose in 1 sitting for all 3 milk types. Given that these participants were confirmed lactose intolerant individuals (subjective) who were also determined to suffer from lactose malabsorption (objective), we would not have anticipated such a high rate of adherence to the highest dosage level. These observations and others reported here should prove useful to other investigators designing future trials to test the ability of other products that might diminish the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Among those who report intolerance symptoms because of lactose malabsorption, these data do not support the widespread claim that raw milk confers benefits in reducing the discomfort of lactose intolerance. Primary care physicians and gastroenterologists should be aware that the evidence supporting raw milk consumption remains anecdotal. Although other health benefit claims for raw milk are plausible, such claims remain similarly anecdotal and unsubstantiated and should be subjected to appropriately designed controlled trials.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Soowon Kim, PhD, for her detailed review of the manuscript; the Endoscopy Unit at Stanford Hospital & Clinics for the use of the Quintron gas chromatograph; the staff of the Stanford Prevention Research Center in the Department of Medicine, including Antonella Dewell, MS, RD, and Dana Forks; the staff of the Stanford Human Biology Honors Program, including Katherine Preston, PhD, for her detailed review of the manuscript; Organic Pastures for the donation and delivery of the raw milk; and all study participants for their generous time and effort.
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest; authors report none.
Author contributions: The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: Mummah and Gardner had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Mummah, Oelrich, Hope, and Gardner designed research. Mummah, Hope, and Vu conducted research. Mummah analyzed data. Mummah, Oelrich, and Gardner wrote the paper. Mummah and Gardner had primary responsibility for final content. Gardner provided guidance and consultation throughout. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT-01129791
Funding support: This study was supported by an unrestricted gift from the Weston A. Price Foundation and a student research stipend from the Stanford University Program in Human Biology.
Disclaimer: The funding agencies had no role in the design and conduct of the study; the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of data; or the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Law D, Conklin J, Pimentel M. Lactose intolerance and the role of the lactose breath test. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(8):1726–1728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keith JN, Nicholls J, Reed A, Kafer K, Miller GD. The prevalence of self-reported lactose intolerance and the consumption of dairy foods among African American adults are less than expected. J Natl Med Assoc. 2011;103(1):36–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Suchy FJ, Brannon PM, Carpenter TO, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference: lactose intolerance and health. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(12):792–796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Savaiano DA, Boushey CJ, McCabe GP. Lactose intolerance symptoms assessed by meta-analysis: a grain of truth that leads to exaggeration. J Nutr. 2006;136(4):1107–1113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vesa TH, Korpela RA, Sahi T. Tolerance to small amounts of lactose in lactose maldigesters. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;64(2):197–201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jellema P, Schellevis FG, van der Windt DA, Kneepkens CM, van der Horst HE. Lactose malabsorption and intolerance: a systematic review on the diagnostic value of gastrointestinal symptoms and self-reported milk intolerance. QJM. 2010;103(8):555–572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shaukat A, Levitt MD, Taylor BC, et al. Systematic review: effective management strategies for lactose intolerance. Ann Intern Med. 2010;152(12):797–803 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.McBean LD, Miller GD. Allaying fears and fallacies about lactose intolerance. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998;98(6):671–676 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suarez FL, Savaiano DA, Levitt MD. A comparison of symptoms after the consumption of milk or lactose-hydrolyzed milk by people with self-reported severe lactose intolerance. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(1):1–4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suarez FL, Savaiano D, Arbisi P, Levitt MD. Tolerance to the daily ingestion of two cups of milk by individuals claiming lactose intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65(5):1502–1506 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Onwulata CI, Rao DR, Vankineni P. Relative efficiency of yogurt, sweet acidophilus milk, hydrolyzed-lactose milk, and a commercial lactase tablet in alleviating lactose maldigestion. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49(6):1233–1237 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kolars JC, Levitt MD, Aouji M, Savaiano DA. Yogurt—an autodigesting source of lactose. N Engl J Med. 1984;310(1):1–3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jones DV, Latham MC, Kosikowski FV, Woodward G. Symptom response to lactose-reduced milk in lactose-intolerant adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976;29(6):633–638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dehkordi N, Rao DR, Warren AP, Chawan CB. Lactose malabsorption as influenced by chocolate milk, skim milk, sucrose, whole milk, and lactic cultures. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995;95(4):484–486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martini MC, Savaiano DA. Reduced intolerance symptoms from lactose consumed during a meal. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988;47(1):57–60 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Martini MC, Kukielka D, Savaiano DA. Lactose digestion from yogurt: influence of a meal and additional lactose. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;53(5):1253–1258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tamm A. Management of lactose intolerance. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1994;202:55–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.de Vrese M, Schrezenmeir J. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2008;111:1–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Montes RG, Bayless TM, Saavedra JM, Perman JA. Effect of milks inoculated with Lactobacillus acidophilus or a yogurt starter culture in lactose-maldigesting children. J Dairy Sci. 1995;78(8):1657–1664 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vesa TH, Marteau P, Zidi S, Briet F, Pochart P, Rambaud JC. Digestion and tolerance of lactose from yoghurt and different semi-solid fermented dairy products containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and bifidobacteria in lactose maldigesters—is bacterial lactase important? Eur J Clin Nutr. 1996;50(11):730–733 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Briet F, Pochart P, Marteau P, Flourie B, Arrigoni E, Rambaud JC. Improved clinical tolerance to chronic lactose ingestion in subjects with lactose intolerance: a placebo effect? Gut. 1997;41(5):632–635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hertzler SR, Savaiano DA. Colonic adaptation to daily lactose feeding in lactose maldigesters reduces lactose intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;64(2):232–236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Casellas F, Aparici A, Casaus M, Rodríguez P, Malagelada JR. Subjective perception of lactose intolerance does not always indicate lactose malabsorption. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8(7):581–586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Larson NI, Story M, Wall M, Neumark-Sztainer D. Calcium and dairy intakes of adolescents are associated with their home environment, taste preferences, personal health beliefs, and meal patterns. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006;106(11):1816–1824 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Matlik L, Savaiano D, McCabe G, VanLoan M, Blue CL, Boushey CJ. Perceived milk intolerance is related to bone mineral content in 10-to 13-year-old female adolescents. Pediatrics. 2007;120(3):e669–e677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oliver SP, Boor KJ, Murphy SC, Murinda SE. Food safety hazards associated with consumption of raw milk. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009;6(7):793–806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Riedler J, Braun-Fahrländer C, Eder W, et al. ; ALEX Study Team Exposure to farming in early life and development of asthma and allergy: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2001;358(9288):1129–1133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alfvén T, Braun-Fahrländer C, Brunekreef B, et al. ; PARSIFAL study group Allergic diseases and atopic sensitization in children related to farming and anthroposophic lifestyle—the PARSIFAL study. Allergy. 2006;61(4):414–421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Braun-Fahrländer C, von Mutius E. Can farm milk consumption prevent allergic diseases? Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41(1):29–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.de Vrese M, Stegelmann A, Richter B, Fenselau S, Laue C, Schrezenmeir J. Probiotics—compensation for lactase insufficiency. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73(2)(Suppl):421S–429S [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Marteau P, Flourie B, Pochart P, Chastang C, Desjeux JF, Rambaud JC. Effect of the microbial lactase (EC 3.2.1.23) activity in yoghurt on the intestinal absorption of lactose: an in vivo study in lactase-deficient humans. Br J Nutr. 1990;64(1):71–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Savaiano DA, AbouElAnouar A, Smith DE, Levitt MD. Lactose malabsorption from yogurt, pasteurized yogurt, sweet acidophilus milk, and cultured milk in lactase-deficient individuals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;40(6):1219–1223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lerebours E, N’Djitoyap Ndam C, Lavoine A, Hellot MF, Antoine JM, Colin R. Yogurt and fermented-then-pasteurized milk: effects of short-term and long-term ingestion on lactose absorption and mucosal lactase activity in lactase-deficient subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49(5):823–827 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McDonough FE, Hitchins AD, Wong NP, Wells P, Bodwell CE. Modification of sweet acidophilus milk to improve utilization by lactose-intolerant persons. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987;45(3):570–574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Quirós A, Ramos M, Muguerza B, et al. Determination of the antihypertensive peptide LHLPLP in fermented milk by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Dairy Sci. 2006;89(12):4527–4535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perman JA, Barr RG, Watkins JB. Sucrose malabsorption in children: noninvasive diagnosis by interval breath hydrogen determination. J Pediatr. 1978;93(1):17–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rumessen JJ, Hamberg O, Gudmand-Høyer E. Influence of orocaecal transit time on hydrogen excretion after carbohydrate malabsorption. Gut. 1989;30(6):811–814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Casellas F, Malagelada JR. Applicability of short hydrogen breath test for screening of lactose malabsorption. Dig Dis Sci. 2003;48(7):1333–1338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Beyerlein L, Pohl D, Delco F, Stutz B, Fried M, Tutuian R. Correlation between symptoms developed after the oral ingestion of 50 g lactose and results of hydrogen breath testing for lactose intolerance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(8):659–665 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Payne DL, Welsh JD, Manion CV, Tsegaye A, Herd LD. Effectiveness of milk products in dietary management of lactose malabsorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34(12):2711–2715 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Newcomer AD, Park HS, O’Brien PC, McGill DB. Response of patients with irritable bowel syndrome and lactase deficiency using unfermented acidophilus milk. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983;38(2):25–263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]