Abstract
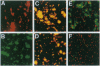
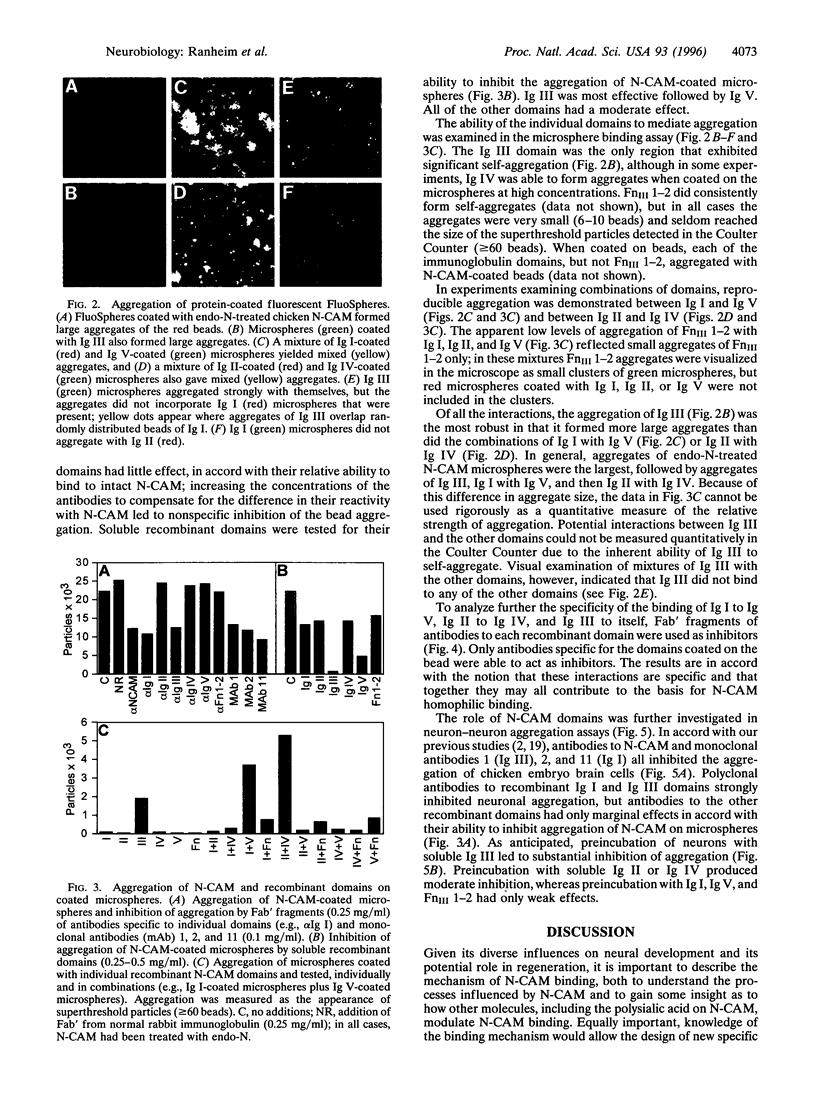
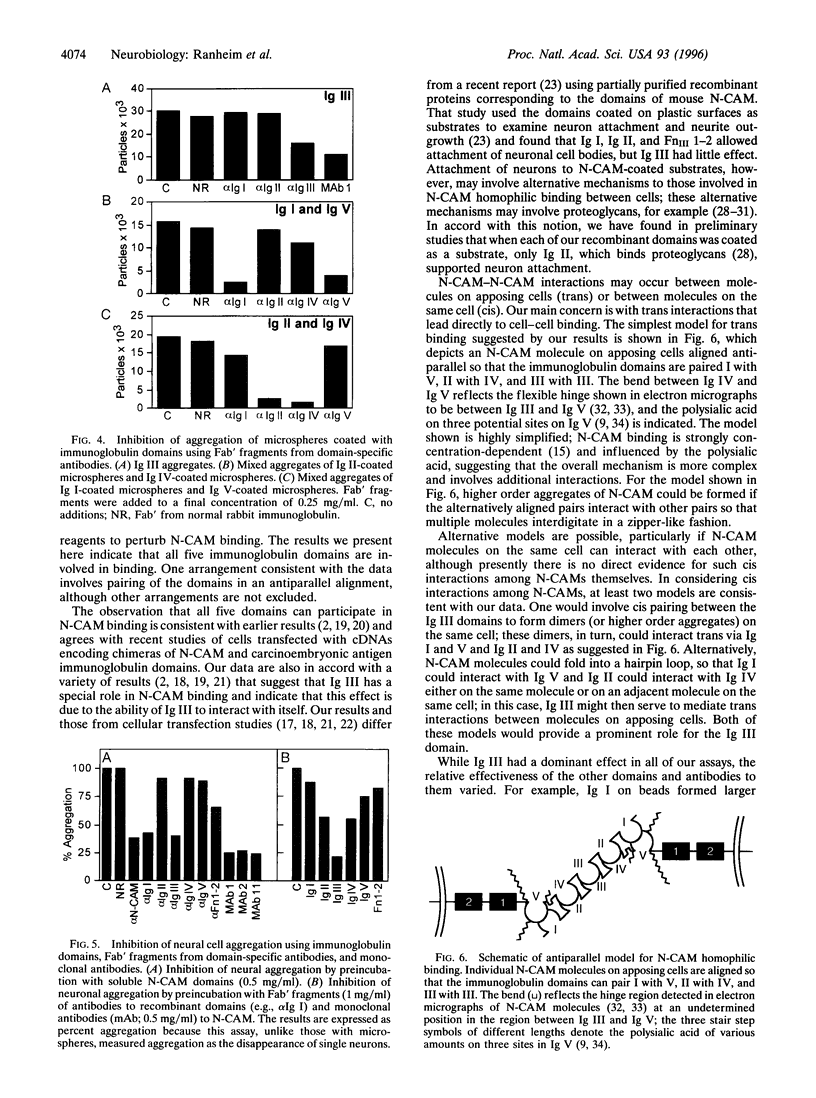
The neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) mediates homophilic binding between a variety of cell types including neurons, neurons and glia, and neurons and muscle cells. The mechanism by which N-CAM on one cell interacts with N-CAM on another, however, is unknown. Attempts to identify which of the five immunoglobulin-like domains (Ig I-V) and the two fibronectin type III repeats (FnIII 1-2) in the extracellular region of N-CAM are involved in this process have led to ambiguous results. We have generated soluble recombinant proteins corresponding to each of the individual immunoglobulin domains and the combined FnIII 1-2 and prepared polyclonal antibodies specific for each. The purified proteins and antibodies were used in aggregation experiments with fluorescent microspheres and chicken embryo brain cells to determine possible contributions of each domain to homophilic adhesion. The recombinant domains were tested for their ability to bind to purified native N-CAM, to bind to each other, and to inhibit the aggregation of N-CAM on microspheres and the aggregation of neuronal cells. Each of the immunoglobulin domains bound to N-CAM, and in solution all of the immunoglobulin domains inhibited the aggregation of N-CAM-coated microspheres. Soluble Ig II, Ig III, and Ig IV inhibited neuronal aggregation; antibodies against whole N-CAM, the Ig III domain, and the Ig I domain all strongly inhibited neuronal aggregation, as well as the aggregation of N-CAM-coated microspheres. Of all the domains, the third immunoglobulin domain alone demonstrated the ability to self-aggregate, whereas Ig I bound to Ig V and Ig II bound to Ig IV. The combined FnIII 1-2 exhibited a slight ability to self-aggregate but did not bind to any of the immunoglobulin-like domains. These results suggest that N-CAM-N-CAM binding involves all five immunoglobulin domains and prompt the hypothesis that in homophilic cell-cell binding mediated by N-CAM these domains may interact pairwise in an antiparallel orientation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker J. W., Erickson H. P., Hoffman S., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Topology of cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1088–1092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Distinct calcium-independent and calcium-dependent adhesion systems of chicken embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):387–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenbury R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. I. An immunological assay for molecules involved in cell-cell binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6835–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. J., Akeson R. Identification of a heparin binding domain of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM using synthetic peptides. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1157–1165. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covault J., Sanes J. R. Neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) accumulates in denervated and paralyzed skeletal muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Mapping of three carbohydrate attachment sites in embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1848–1855. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hoffman S., Rutishauser U., Hemperly J. J., Edelman G. M. Molecular topography of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM: surface orientation and location of sialic acid-rich and binding regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniloff J. K., Levi G., Grumet M., Rieger F., Edelman G. M. Altered expression of neuronal cell adhesion molecules induced by nerve injury and repair. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):929–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Chuong C. M. Embryonic to adult conversion of neural cell adhesion molecules in normal and staggerer mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):7036–7040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.7036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Finne U., Deagostini-Bazin H., Goridis C. Occurrence of alpha 2-8 linked polysialosyl units in a neural cell adhesion molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei T., von Bohlen und Halbach F., Wille W., Schachner M. Different extracellular domains of the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) are involved in different functions. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(1):177–194. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander D. R., Milev P., Karthikeyan L., Margolis R. K., Margolis R. U., Grumet M. The neuronal chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan neurocan binds to the neural cell adhesion molecules Ng-CAM/L1/NILE and N-CAM, and inhibits neuronal adhesion and neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):669–680. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gower H. J., Barton C. H., Elsom V. L., Thompson J., Moore S. E., Dickson G., Walsh F. S. Alternative splicing generates a secreted form of N-CAM in muscle and brain. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):955–964. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Edelman G. M. Neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule interacts with neurons and astroglia via different binding mechanisms. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):487–503. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. K., Rutishauser U. Visualization of neural cell adhesion molecule by electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1579–1586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. C., Vimr E. R., Yu F., Bassler B., Troy F. A. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage-induced endo-N-acetylneuraminidase specific for poly-alpha-2,8-sialosyl carbohydrate units. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3553–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. cDNA clones of the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) lacking a membrane-spanning region consistent with evidence for membrane attachment via a phosphatidylinositol intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9822–9826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the polysialic acid-rich and cytoplasmic domains of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Kinetics of homophilic binding by embryonic and adult forms of the neural cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5762–5766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstkorte R., Schachner M., Magyar J. P., Vorherr T., Schmitz B. The fourth immunoglobulin-like domain of NCAM contains a carbohydrate recognition domain for oligomannosidic glycans implicated in association with L1 and neurite outgrowth. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1409–1421. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilhauer G., Faissner A., Schachner M. Differential inhibition of neurone-neurone, neurone-astrocyte and astrocyte-astrocyte adhesion by L1, L2 and N-CAM antibodies. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):728–730. doi: 10.1038/316728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege R. M., Matsuzaki F., Gallin W. J., Goldberg J. I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Construction of epithelioid sheets by transfection of mouse sarcoma cells with cDNAs for chicken cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7274–7278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. A., Jensen J. J. Evidence for heterophilic adhesion of embryonic retinal cells and neuroblastoma cells to substratum-adsorbed NCAM. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1311–1320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. A., Owens G. C., Prediger E. A., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Cell surface modulation of the neural cell adhesion molecule resulting from alternative mRNA splicing in a tissue-specific developmental sequence. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1431–1439. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. W., Bates P. A., Rutishauser U. Protein determinants for specific polysialylation of the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 21;270(29):17171–17179. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.29.17171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao Y., Wu X. F., Gariepy J., Rutishauser U., Siu C. H. Identification of a peptide sequence involved in homophilic binding in the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):937–949. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao Y., Wu X. F., Yip P., Gariepy J., Siu C. H. Structural characterization of a homophilic binding site in the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20630–20638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Akeson R., Brezina L., Cole G. J. Structural requirements for neural cell adhesion molecule-heparin interaction. Cell Regul. 1990 Jul;1(8):567–576. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.8.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. Binding properties of a cell adhesion molecule from neural tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandig M., Rao Y., Siu C. H. The homophilic binding site of the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM is directly involved in promoting neurite outgrowth from cultured neural retinal cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14841–14848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoni M. J., Barthels D., Vopper G., Boned A., Goridis C., Wille W. Differential exon usage involving an unusual splicing mechanism generates at least eight types of NCAM cDNA in mouse brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):385–392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Rutishauser U. Topography of N-CAM structural and functional determinants. I. Classification of monoclonal antibody epitopes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1721–1727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou H., Fuks A., Alcaraz G., Bolling T. J., Stanners C. P. Homophilic adhesion between Ig superfamily carcinoembryonic antigen molecules involves double reciprocal bonds. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):951–960. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]