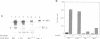Abstract
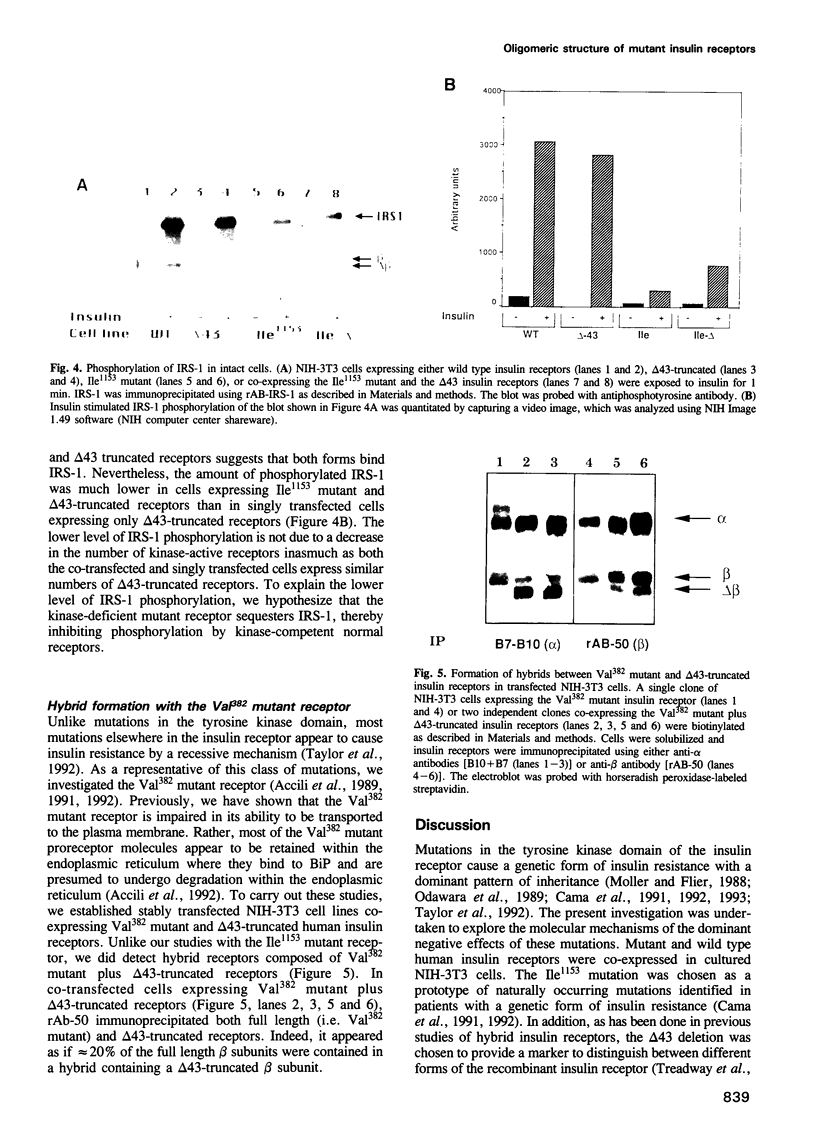
Mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor cause insulin resistance in a dominant fashion. It has been proposed that formation of hybrid dimers between normal and mutant receptors may explain the dominant negative effect of these mutations. To investigate this mechanism, we expressed two types of human insulin receptors in NIH-3T3 cells; wild type and the tyrosine kinase-deficient Ile1153 mutant. To distinguish the two types of receptors, 43 amino acids were deleted from the C-terminus of the wild type receptor (delta 43 truncation). If mutant and wild type receptors assemble in a random fashion, 50% of the receptors would be hybrid oligomers (alpha 2 beta beta mut). However, alpha 2 beta beta mut hybrids were undetectable. Nevertheless, insulin stimulated the kinase competent delta 43 receptors to transphosphorylate the kinase-deficient Ile1153 mutant receptor in co-transfected cells via an intermolecular mechanism. Furthermore, transphosphorylation of the Ile1153 mutant receptor is sufficient to trigger insulin-stimulated endocytosis. Despite the absence of alpha 2 beta beta mut hybrids, expression of the Ile1153 mutant receptor inhibited the ability of the delta 43 truncated receptor to mediate insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Evidence is presented to support the hypothesis that the Ile1153 mutant receptor retains the ability to bind IRS-1, and that sequestration of substrate may explain the dominant negative effect of the mutant receptor to inhibit phosphorylation of IRS-1.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accili D., Frapier C., Mosthaf L., McKeon C., Elbein S. C., Permutt M. A., Ramos E., Lander E., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. A mutation in the insulin receptor gene that impairs transport of the receptor to the plasma membrane and causes insulin-resistant diabetes. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2509–2517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accili D., Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Mosthaf L., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. Immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein binds to misfolded mutant insulin receptors with mutations in the extracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Accili D., Mosthaf L., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. A mutation in the extracellular domain of the insulin receptor impairs the ability of insulin to stimulate receptor autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):434–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Chin D. J., Shoelson S. E., Miralpeix M., White M. F. Association of IRS-1 with the insulin receptor and the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Formation of binary and ternary signaling complexes in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8204–8212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Kaligian A., DelVecchio R., Pilch P. F. Ligand-dependent intersubunit association within the insulin receptor complex activates its intrinsic kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6822–6828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cama A., Marcus-Samuels B., Taylor S. I. Immunological abnormalities in insulin receptors on cultured EBV-transformed lymphocytes from insulin-resistant patient with leprechaunism. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):982–988. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cama A., Quon M. J., de la Luz Sierra M., Taylor S. I. Substitution of isoleucine for methionine at position 1153 in the beta-subunit of the human insulin receptor. A mutation that impairs receptor tyrosine kinase activity, receptor endocytosis, and insulin action. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8383–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cama A., de la Luz Sierra M., Ottini L., Kadowaki T., Gorden P., Imperato-McGinley J., Taylor S. I. A mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor associated with insulin resistance in an obese woman. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Oct;73(4):894–901. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-4-894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cama A., de la Luz Sierra M., Quon M. J., Ottini L., Gorden P., Taylor S. I. Substitution of glutamic acid for alanine 1135 in the putative "catalytic loop" of the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor. A mutation that impairs proteolytic processing into subunits and inhibits receptor tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8060–8069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier J. L., Paccaud J. P., Gorden P., Rutter W. J., Orci L. Insulin-induced surface redistribution regulates internalization of the insulin receptor and requires its autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):162–166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. E., Tavaré J. M., Ellis L., Roth R. A. Evidence for hybrid rodent and human insulin receptors in transfected cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15587–15590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frattali A. L., Treadway J. L., Pessin J. E. Transmembrane signaling by the human insulin receptor kinase. Relationship between intramolecular beta subunit trans- and cis-autophosphorylation and substrate kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19521–19528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki H., Kadowaki T., Cama A., Marcus-Samuels B., Rovira A., Bevins C. L., Taylor S. I. Mutagenesis of lysine 460 in the human insulin receptor. Effects upon receptor recycling and cooperative interactions among binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21285–21296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Bevins C. L., Cama A., Ojamaa K., Marcus-Samuels B., Kadowaki H., Beitz L., McKeon C., Taylor S. I. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):787–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2834824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Accili D., Taylor S. I. Substitution of lysine for asparagine at position 15 in the alpha-subunit of the human insulin receptor. A mutation that impairs transport of receptors to the cell surface and decreases the affinity of insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19143–19150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Accili D., Yazaki Y., Taylor S. I. Substitution of arginine for histidine at position 209 in the alpha-subunit of the human insulin receptor. A mutation that impairs receptor dimerization and transport of receptors to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21224–21231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Taylor S. I. A nonsense mutation causing decreased levels of insulin receptor mRNA: detection by a simplified technique for direct sequencing of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Yarden Y., Fischer R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A dominant negative mutation suppresses the function of normal epidermal growth factor receptors by heterodimerization. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Van Obberghen E., Ballotti R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Transphosphorylation as a possible mechanism for insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16886–16890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Toledano R., Caro L. H., Hindman N., Taylor S. I. Streptavidin blotting: a sensitive technique to study cell surface proteins; application to investigate autophosphorylation and endocytosis of biotin-labeled insulin receptors. Endocrinology. 1993 Oct;133(4):1803–1808. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.4.8404622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa H., McClain D. A., Freidenberg G., Olefsky J. M., Napier M., Lipari T., Dull T. J., Lee J., Ullrich A. Properties of a human insulin receptor with a COOH-terminal truncation. II. Truncated receptors have normal kinase activity but are defective in signaling metabolic effects. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8912–8917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa H., Olefsky J. M., Thies S., Boyd D., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Insulin receptors with defective tyrosine kinase inhibit normal receptor function at the level of substrate phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12629–12637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Levy J., Huecksteadt T., Dull T. J., Lee J., Ullrich A., Olefsky J. M. Properties of a human insulin receptor with a COOH-terminal truncation. I. Insulin binding, autophosphorylation, and endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8904–8911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Flier J. S. Detection of an alteration in the insulin-receptor gene in a patient with insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans, and the polycystic ovary syndrome (type A insulin resistance). N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 8;319(23):1526–1529. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812083192306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Backer J. M., Siddle K., White M. F. The insulin receptor functions normally in Chinese hamster ovary cells after truncation of the C terminus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10616–10623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odawara M., Kadowaki T., Yamamoto R., Shibasaki Y., Tobe K., Accili D., Bevins C., Mikami Y., Matsuura N., Akanuma Y. Human diabetes associated with a mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.2544998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T. S., Bamberger M. J., Lane M. D. Post-translational changes in tertiary and quaternary structure of the insulin proreceptor. Correlation with acquisition of function. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7342–7351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann N., Holzmann B., von Rüden T., Wagner E. F., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Anti-oncogenic activity of signalling-defective epidermal growth factor receptor mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):491–498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Morrison B. D., Wilden P. A., Pessin J. E. Insulin-dependent intermolecular subunit communication between isolated alpha beta heterodimeric insulin receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16730–16738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Cama A., Accili D., Barbetti F., Quon M. J., de la Luz Sierra M., Suzuki Y., Koller E., Levy-Toledano R., Wertheimer E. Mutations in the insulin receptor gene. Endocr Rev. 1992 Aug;13(3):566–595. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-3-566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Marcus-Samuels B. Anti-receptor antibodies mimic the effect of insulin to down-regulate insulin receptors in cultured human lymphoblastoid (IM-9) cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Jan;58(1):182–186. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-1-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadway J. L., Morrison B. D., Soos M. A., Siddle K., Olefsky J., Ullrich A., McClain D. A., Pessin J. E. Transdominant inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity in mutant insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Roth R. A. A region of the insulin receptor important for ligand binding (residues 450-601) is recognized by patients' autoimmune antibodies and inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9858–9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]