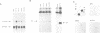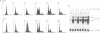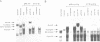Abstract
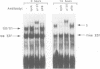
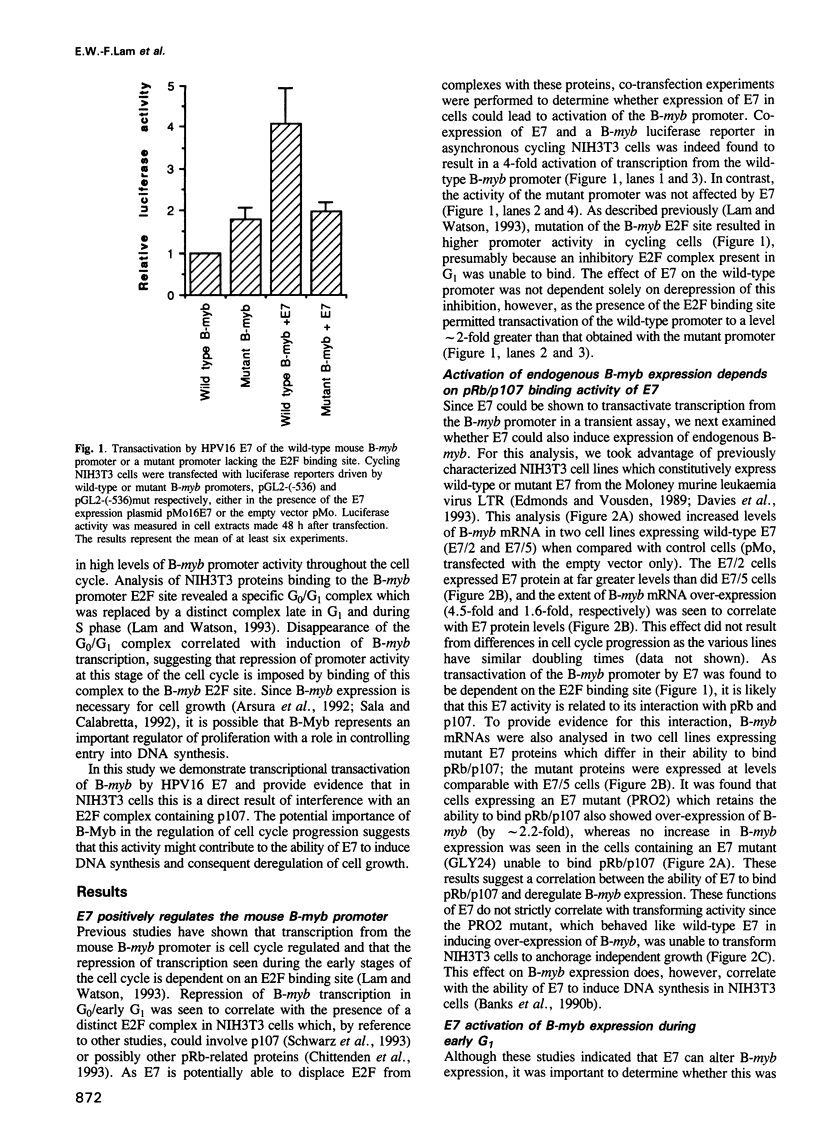
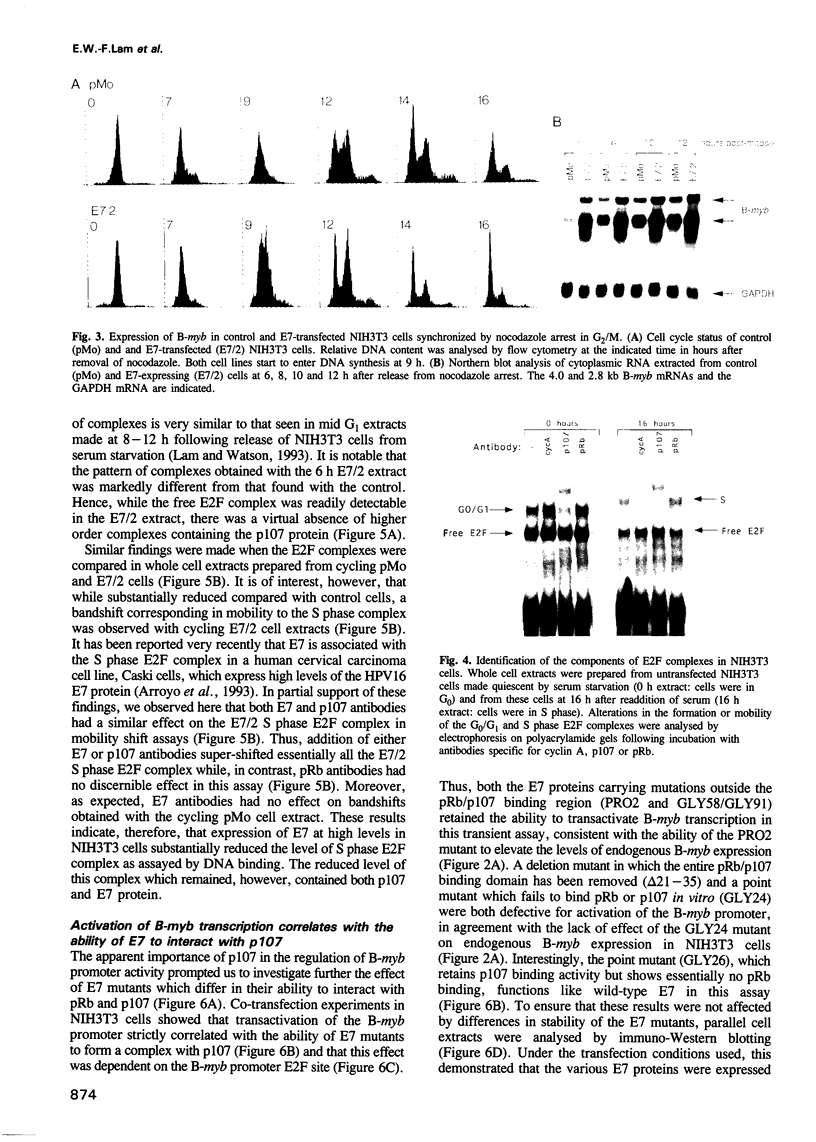
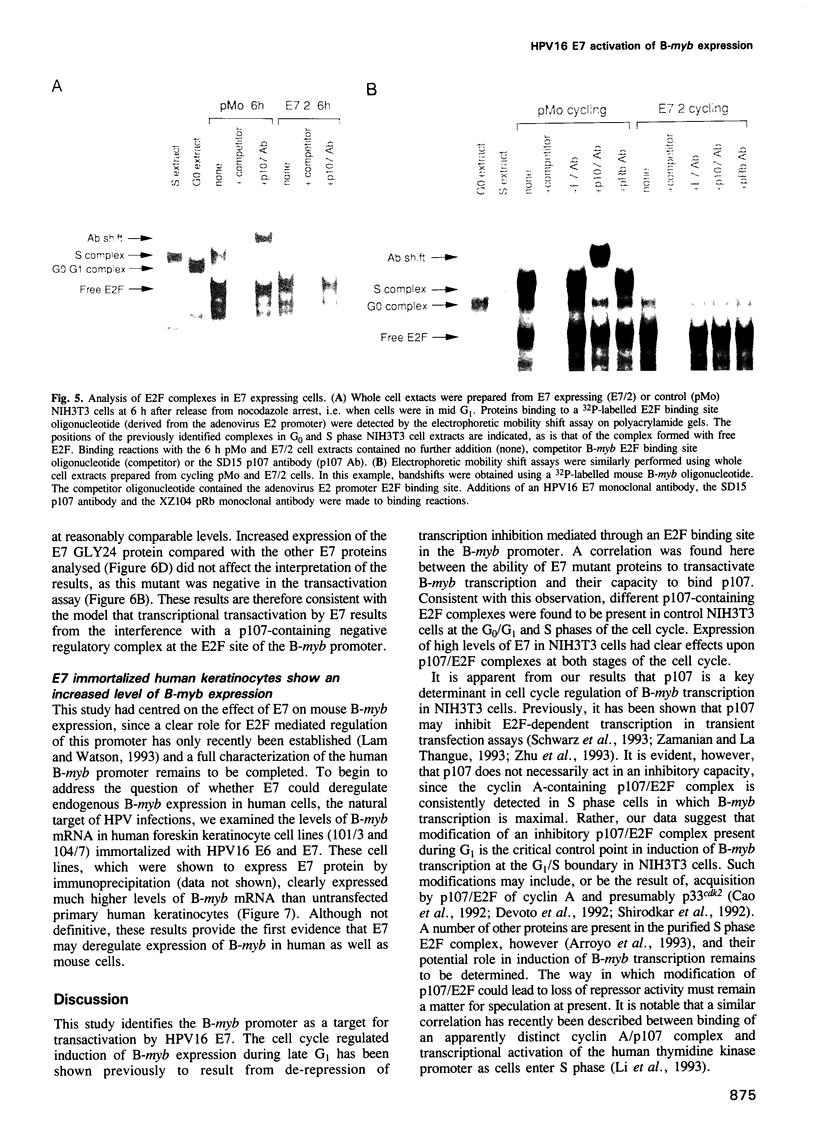
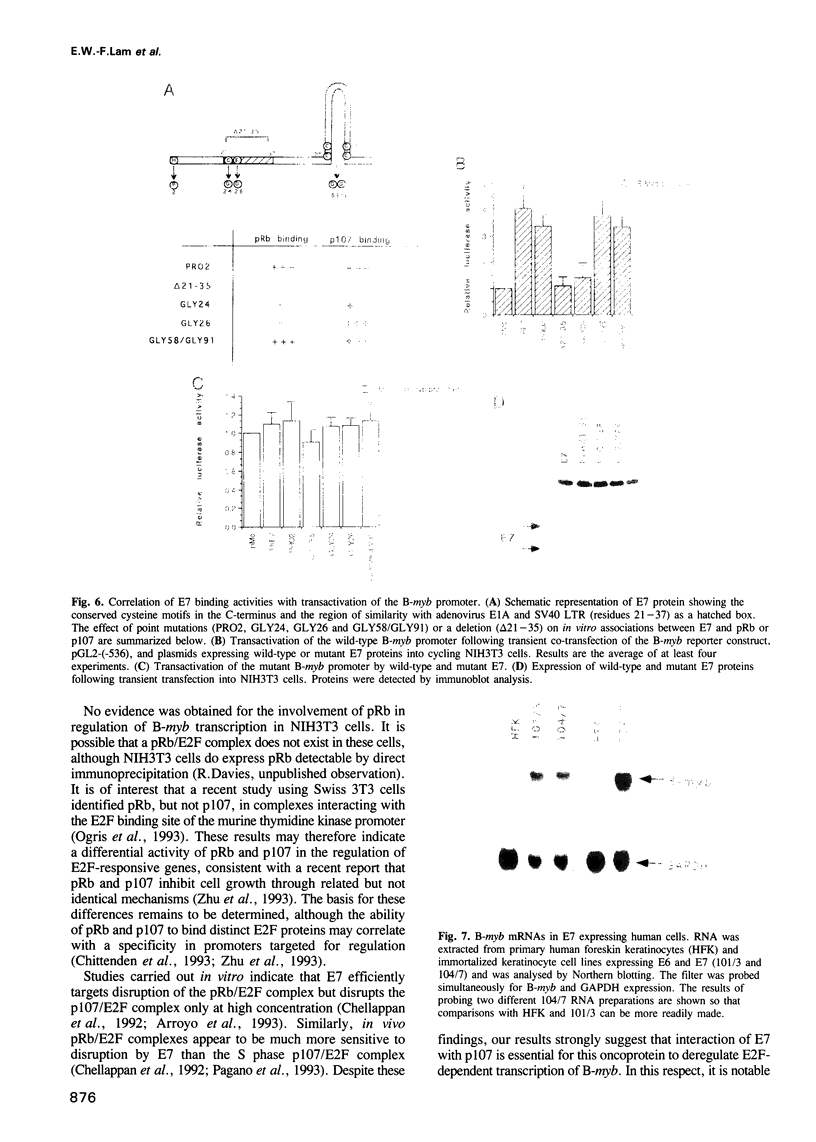
HPV16 is a human tumour virus encoding two principal oncoproteins, E6 and E7. Expression of E7 can induce DNA synthesis in quiescent cells and this property coincides with its ability to bind to the cell proteins pRb and p107. As these cell proteins are regulators of the transcription factor E2F, we have investigated whether the interaction with E7 could result in induction of cell cycle regulated genes. We show that B-myb, whose induction at the G1/S boundary is regulated by release from E2F mediated transcriptional repression, is a target for transcriptional activation by E7 and is the first E7 responsive cell gene to be identified. E7 transactivation leads to both inappropriate transcription of B-myb during G1 and constitutive over-expression in cycling cells. B-Myb plays an essential role in cell cycle progression, and activation by E7 is likely to contribute to the mitogenic activity of the viral oncoprotein. Regulation of the B-myb promoter in NIH3T3 cells correlates with binding of distinct p107-containing complexes at the E2F binding site, and analysis of E7 mutants confirms that B-myb transcription in these cells is regulated through interactions with p107 rather than pRb. These results provide the first example of a potentially specific role for p107 in the regulation of the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arroyo M., Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P. Association of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein with the S-phase-specific E2F-cyclin A complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6537–6546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsura M., Introna M., Passerini F., Mantovani A., Golay J. B-myb antisense oligonucleotides inhibit proliferation of human hematopoietic cell lines. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2708–2716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Barnett S. C., Crook T. HPV-16 E7 functions at the G1 to S phase transition in the cell cycle. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):833–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. Ability of the HPV16 E7 protein to bind RB and induce DNA synthesis is not sufficient for efficient transforming activity in NIH3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1383–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J. L., Yang Z. H., Barthold S. W., Johnson E. A. Use of a rapid, efficient inoculation method to induce papillomas by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus DNA shows that the E7 gene is required. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4816–4820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S., Kraus V. B., Kroger B., Munger K., Howley P. M., Phelps W. C., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen, and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. Cell cycle analysis of E2F in primary human T cells reveals novel E2F complexes and biochemically distinct forms of free E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3975–3983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R., Hicks R., Crook T., Morris J., Vousden K. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 associates with a histone H1 kinase and with p107 through sequences necessary for transformation. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2521–2528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2521-2528.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defeo-Jones D., Vuocolo G. A., Haskell K. M., Hanobik M. G., Kiefer D. M., McAvoy E. M., Ivey-Hoyle M., Brandsma J. L., Oliff A., Jones R. E. Papillomavirus E7 protein binding to the retinoblastoma protein is not required for viral induction of warts. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):716–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.716-725.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golay J., Capucci A., Arsura M., Castellano M., Rizzo V., Introna M. Expression of c-myb and B-myb, but not A-myb, correlates with proliferation in human hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1991 Jan 1;77(1):149–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Chellappan S. P., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Bautista C., Edwards G. M., Defeo-Jones D., Jones R. E., Harlow E. Antibodies specific for the human retinoblastoma protein identify a family of related polypeptides. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5792–5799. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. S., Patrick D. R., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Huber H. E., Miles L., Garsky V. M., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Protein domains governing interactions between E2F, the retinoblastoma gene product, and human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):953–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewers R. J., Hildebrandt P., Ludlow J. W., Kell B., McCance D. J. Regions of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein required for immortalization of human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1329-1335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Robinson C., Watson R. J. Characterization and cell cycle-regulated expression of mouse B-myb. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1885–1890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Watson R. J. An E2F-binding site mediates cell-cycle regulated repression of mouse B-myb transcription. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. J., Naeve G. S., Lee A. S. Temporal regulation of cyclin A-p107 and p33cdk2 complexes binding to a human thymidine kinase promoter element important for G1-S phase transcriptional regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3554–3558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. D., Crook T., Bandara L. R., Davies R., LaThangue N. B., Vousden K. H. Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 regulates E2F and contributes to mitogenic signalling. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Yee C. L., Phelps W. C., Pietenpol J. A., Moses H. L., Howley P. M. Biochemical and biological differences between E7 oncoproteins of the high- and low-risk human papillomavirus types are determined by amino-terminal sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3943–3948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3943-3948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Takahashi M., Matsui M., Ishii S., Date T., Sasamoto S., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human cDNA clones of myb-related genes, A-myb and B-myb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11075–11089. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogris E., Rotheneder H., Mudrak I., Pichler A., Wintersberger E. A binding site for transcription factor E2F is a target for trans activation of murine thymidine kinase by polyomavirus large T antigen and plays an important role in growth regulation of the gene. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1765–1771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1765-1771.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Dürst M., Joswig S., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Binding of the human E2F transcription factor to the retinoblastoma protein but not to cyclin A is abolished in HPV-16-immortalized cells. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1681–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Bagchi S., Barnes J. A., Raychaudhuri P., Kraus V., Münger K., Howley P. M., Nevins J. R. Analysis of trans activation by human papillomavirus type 16 E7 and adenovirus 12S E1A suggests a common mechanism. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6922–6930. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6922-6930.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Münger K., Yee C. L., Barnes J. A., Howley P. M. Structure-function analysis of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2418–2427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2418-2427.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Rooney R., Nevins J. R. Identification of an E1A-inducible cellular factor that interacts with regulatory sequences within the adenovirus E4 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4073–4081. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss K., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Growth regulated expression of B-myb in fibroblasts and hematopoietic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Sep;148(3):338–343. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala A., Calabretta B. Regulation of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblast proliferation by B-myb is accompanied by selective activation of cdc2 and cyclin D1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10415–10419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Expression of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene induces DNA synthesis of rat 3Y1 cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky J. E., Li Y., Kaelin W. G., Farnham P. J. A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1610–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Sato H., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 functions. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.207-214.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Sato H., Komiyama N., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. The E7 functions of human papillomaviruses in rat 3Y1 cells. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu E. W., Clemens K. E., Heck D. V., Münger K. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein and the cellular transcription factor E2F bind to separate sites on the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2402-2407.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian M., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from repressing the activity of a cellular transcription factor. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2603–2610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian M., La Thangue N. B. Transcriptional repression by the Rb-related protein p107. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Apr;4(4):389–396. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M. Papillomaviruses in human disease: Part I. Pathogenesis and epidemiology of human papillomavirus infections. Eur J Med. 1992 Nov;1(7):415–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in the pathogenesis of anogenital cancer. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90816-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]