Abstract
Mutations have been created in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 18S rRNA gene that correspond to those known to be involved in the control of translational fidelity or antibiotic resistance in prokaryotes. Yeast strains, in which essentially all chromosomal rDNA repeats are deleted and all cellular rRNAs are encoded by plasmid, have been constructed that contain only mutant 18S rRNA. In Escherichia coli, a C-->U substitution at position 912 of the small subunit rRNA causes streptomycin resistance. Eukaryotes normally carry U at the corresponding position and are naturally resistant to streptomycin. We show that a U-->C transition (rdn-4) at this position of the yeast 18S rRNA gene decreases resistance to streptomycin. The rdn-4 mutation also increases resistance to paromomycin and G-418, and inhibits nonsense suppression induced by paromomycin. The same phenotypes, as well as a slow growth phenotype, are also associated with rdn-2, whose prokaryotic counterpart, 517 G-->A, manifests itself as a suppressor rather than an antisuppressor. Neither rdn-2- nor rdn-4-related phenotypes could be detected in the presence of the normal level of wild-type rDNA repeats. Our data demonstrate that eukaryotic rRNA is involved in the control of translational fidelity, and indicate that rRNA features important for interactions with aminoglycosides have been conserved throughout evolution.
Full text
PDF
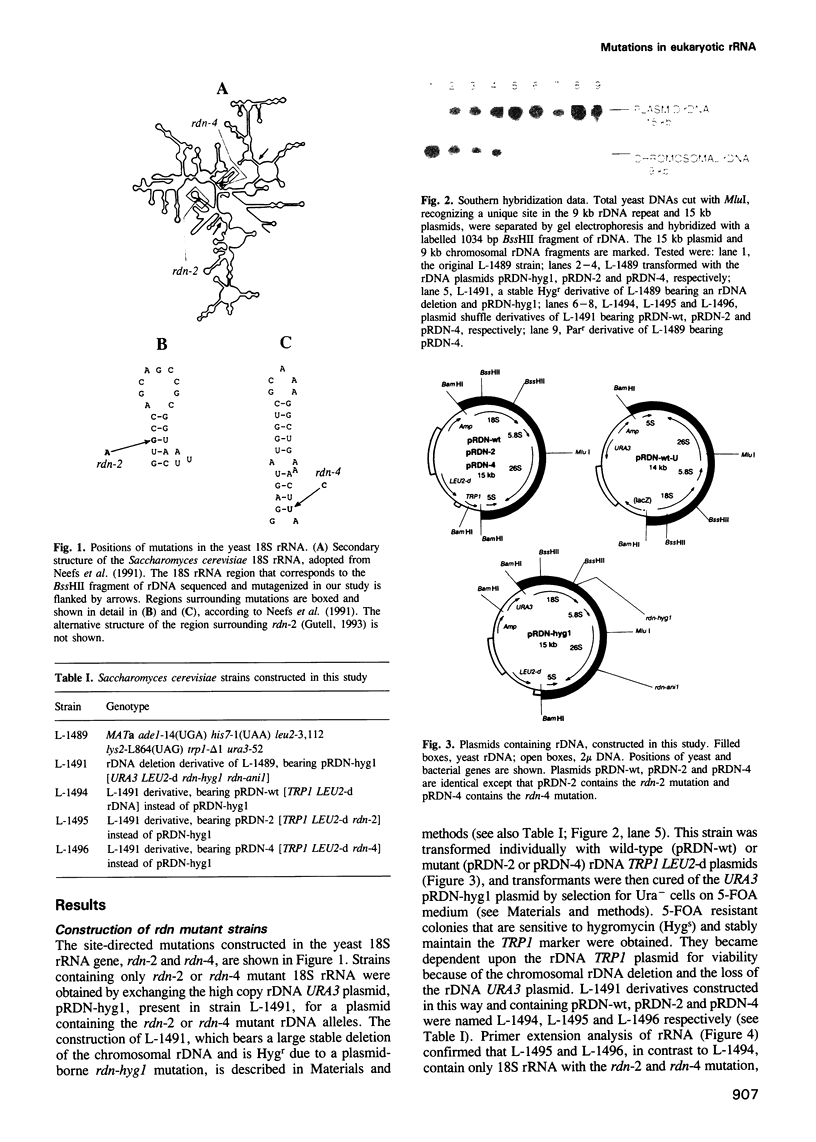

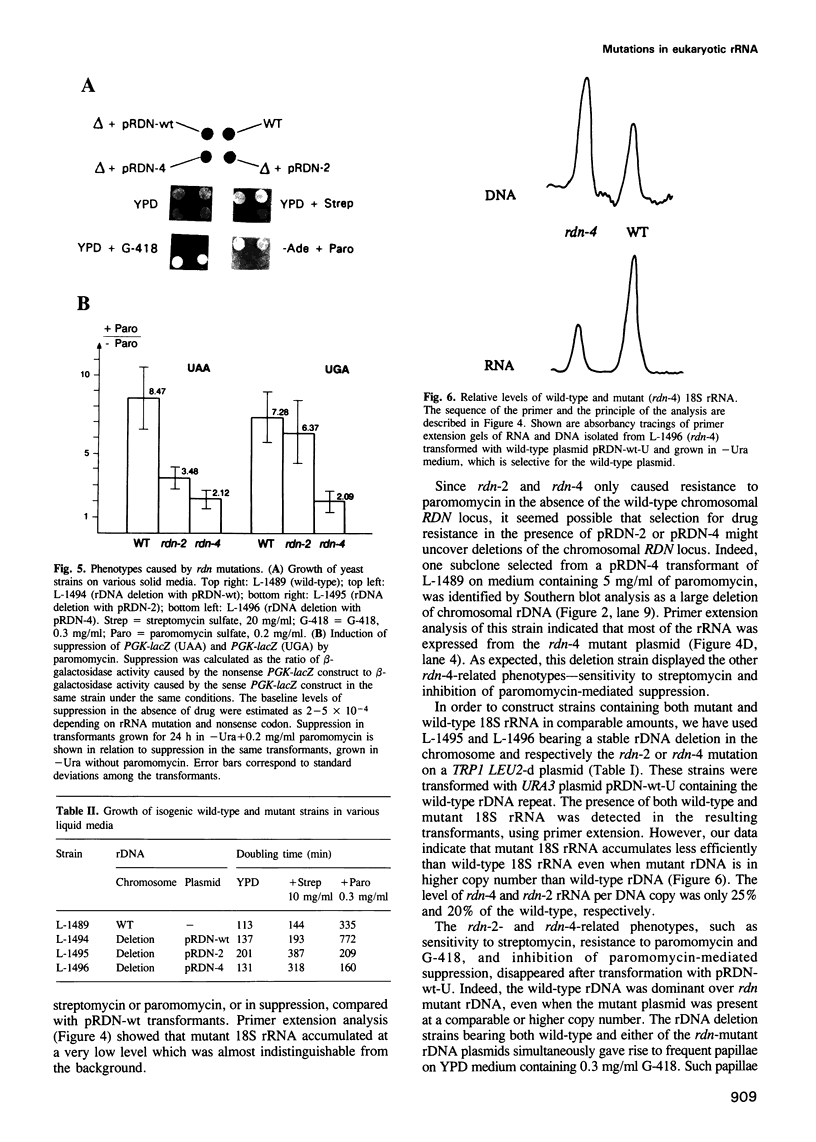




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alksne L. E., Anthony R. A., Liebman S. W., Warner J. R. An accuracy center in the ribosome conserved over 2 billion years. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9538–9541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss F. T., Vinopal R. T. Selection of ribosomal mutants by antibiotic suppression in yeast. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dontsova O., Dokudovskaya S., Kopylov A., Bogdanov A., Rinke-Appel J., Jünke N., Brimacombe R. Three widely separated positions in the 16S RNA lie in or close to the ribosomal decoding region; a site-directed cross-linking study with mRNA analogues. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3105–3116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firoozan M., Grant C. M., Duarte J. A., Tuite M. F. Quantitation of readthrough of termination codons in yeast using a novel gene fusion assay. Yeast. 1991 Feb;7(2):173–183. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. Mapping of chloroplast mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics in Chlamydomonas: evidence for a novel site of streptomycin resistance in the small subunit rRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):192–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00337710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R. Collection of small subunit (16S- and 16S-like) ribosomal RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3051–3054. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel H., Böck A. 23S ribosomal RNA mutations in halobacteria conferring resistance to the anti-80S ribosome targeted antibiotic anisomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2431–2443. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IERUSALIMSKII N. D., SHEVCHENKO L. A., GRISHANKOVA E. V. [Change of some physiological requirements of yeasts as a result of adaptation to streptomycin]. Mikrobiologiia. 1963 Jan-Feb;32:13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inge-Vechtomov S. G., Tikhodeev O. N., Karpova T. S. Selektivnye sistemy dlia polucheniia retsessivnykh ribosomnykh supressorov u drozhzhei sakharomitsetov. Genetika. 1988 Jul;24(7):1159–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain V. K., Magrath I. T. A chemiluminescent assay for quantitation of beta-galactosidase in the femtogram range: application to quantitation of beta-galactosidase in lacZ-transfected cells. Anal Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;199(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Prakash L. Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae selectable markers in pUC18 polylinkers. Yeast. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):363–366. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkens T., van der Sande C. A., Dekker A. F., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. A system to study transcription by yeast RNA polymerase I within the chromosomal context: functional analysis of the ribosomal DNA enhancer and the RBP1/REB1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4665–4674. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. Mutations in the 915 region of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA reduce the binding of streptomycin to the ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3973–3977. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. The interaction between streptomycin and ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1991 Dec;73(12):1431–1438. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90175-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Lemieux C., Brakier-Gingras L. A mutation in the 530 loop of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA causes resistance to streptomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9631–9639. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Nicolas P., Schürmann P., Stutz E. Streptomycin-resistance of Euglena gracilis chloroplasts: identification of a point mutation in the 16S rRNA gene in an invariant position. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4299–4310. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgola E. J., Hijazi K. A., Göringer H. U., Dahlberg A. E. Mutant 16S ribosomal RNA: a codon-specific translational suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4162–4165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Venema J., van der Linden G., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. A system for the analysis of yeast ribosomal DNA mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):551–559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., De Rijk P., Goris A., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):1987–2015. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Yano R., Nomura M. Synthesis of large rRNAs by RNA polymerase II in mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3962–3966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Hoffarth V., Zimniak L. Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1416–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1604315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:191–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. tRNA-rRNA interactions and peptidyl transferase. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):87–89. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M., De Stasio E. A., Dahlberg A. E. Interaction between 16S ribosomal RNA and ribosomal protein S12: differential effects of paromomycin and streptomycin. Biochimie. 1991 Dec;73(12):1493–1500. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M., Göringer H. U., Dahlberg A. E. A ribosomal ambiguity mutation in the 530 loop of E. coli 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4221–4227. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Wilhelm J. M., Sherman F. Phenotypic suppression of nonsense mutants in yeast by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):148–150. doi: 10.1038/277148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent S. A., Fenimore C. M., Bostian K. A. Vector systems for the expression, analysis and cloning of DNA sequences in S. cerevisiae. Yeast. 1985 Dec;1(2):83–138. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pel H. J., Maat C., Rep M., Grivell L. A. The yeast nuclear gene MRF1 encodes a mitochondrial peptide chain release factor and cures several mitochondrial RNA splicing defects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6339–6346. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Noller H. F. A functional pseudoknot in 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2203–2214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Planta R. J. Ribosome biogenesis in yeast. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:89–129. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Z. H., Fox T. D. Substitution of an invariant nucleotide at the base of the highly conserved '530-loop' of 15S rRNA causes suppression of yeast mitochondrial ochre mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4535–4539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Borden A., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:673–690. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., Ursic D., Davies J. Phenotypic suppression and misreading Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):146–148. doi: 10.1038/277146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler E. A., Blackburn E. H. The nucleotide sequence of the 17S ribosomal RNA gene of Tetrahymena thermophila and the identification of point mutations resulting in resistance to the antibiotics paromomycin and hygromycin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6334–6340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Vink T., Kraal B., Bosch L. Mutants of the elongation factor EF-Tu, a new class of nonsense suppressors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1049–1052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Liebman S. W. The yeast omnipotent suppressor SUP46 encodes a ribosomal protein which is a functional and structural homolog of the Escherichia coli S4 ram protein. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):375–386. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Petes T. D. Mitotic and meiotic gene conversion of Ty elements and other insertions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):759–772. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chumley F., Fink G. R. Eviction and transplacement of mutant genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:211–228. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]