Abstract
Objectives
This article reviews the prevalence of lumbarisation, sacralisation and lumbar ribs, and their morphological relevance by evaluating multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT) images. These segment variations can cause miscounting of vertebrae at the lumbar spinal level.
Methods
A retrospective radiographic analysis of 226 cases scanned by MSCT prior to forensic autopsy was undertaken. MSCT scans of the entire spine were obtained. Radiological data were evaluated on a three-dimensional image workstation. Vertebral levels were determined by counting downward from the first cervical vertebra, based on the assumption of seven cervical, 12 thoracic and five lumbar vertebrae. The prevalence of lumbarisation, sacralisation and lumbar ribs was assessed.
Results
Lumbar ribs were observed in 13 of the 226 cases (5.8 %). Lumbarisation and sacralisation were observed in 14 cases (6.2 %) and six cases (2.7 %), respectively. Lumbar ribs were present in 11 of the 14 cases with lumbarisation, and in two of the 206 cases with normal lumbar vertebral configuration. Lumbarisation had a statistically significant association with lumbar ribs (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
There was a strong association between lumbar ribs and lumbarisation, with a resulting miscount rate for the lumbar spine of slightly less than 10 %.
Teaching points
Lumbarisation and sacralisation are observed 6.2 % and 2.7 %, respectively.
Thoracolumbar segment variations can cause a miscount rate for the lumbar spine of less than 10 %.
Lumbar rib is significantly associated to lumbarisation.
Keywords: Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae, Lumbarisation, Sacralisation, Lumbar rib, Multi-slice computed tomography
Introduction
Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV) are congenital spinal anomalies. LSTV associated with the fifth lumbar vertebra may show assimilation to the sacrum (sacralisation), and those affecting the first sacral vertebra may show transition to a lumbar configuration (lumbarisation) [1], causing misinterpretation as four or six lumbar vertebrae, respectively. LSTV are common in the general population, with a reported prevalence of 4–35.9 % [1–17]. Inaccurate identification of an LSTV may lead to surgical and procedural errors and poor correlation with clinical symptoms [18].
Identification of LSTV and accurate numeric identification of vertebral segments on conventional lumbar radiographs or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are essential to ensure that interventional procedures or surgery are performed at the intended level [19]. However, establishing whether an LSTV is a lumbarised S1 or a sacralised L5 on MRI alone can be problematic. Conventional spine radiographs are often unavailable at the time of imaging, and cervicothoracic localisers may not be routinely obtained. Konin et al. [18] reported that radiographs of the entire spine allowed the radiologist not only to count from C2 inferiorly but also to differentiate hypoplastic ribs from lumbar transverse processes. This approach allows accurate counting of thoracic segments, correct identification of the L1 vertebral body and correct numeric assignment of the LSTV. They also reported that patients undergoing lumbar spinal MRI commonly had radiographs of the lumbar spine alone, rather than of the entire spine. Correct enumeration was often achieved in these cases, but there remained cases in which the presence of thoracolumbar transitions as well as segmentation anomalies complicated evaluation [18].
Thirteenth ribs, known as lumbar ribs, may also cause miscounting at the lumbar spinal level. The lumbar level is usually identified on radiographs by noting T12, which is defined as the lowest vertebra with ribs. However, in some cases, transverse processes of the first lumbar vertebra resemble 12th ribs and have an articular surface. These transverse processes are termed lumbar ribs. Lumbar ribs can complicate identification of the first lumbar vertebra in frontal lumbar radiographs. In cases with both lumbar ribs and lumbarisation, lumbar spinal configuration might be interpreted as normal (Fig. 1). Cases with lumbar ribs and normal lumbar spinal configuration might be interpreted as sacralisation (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1.
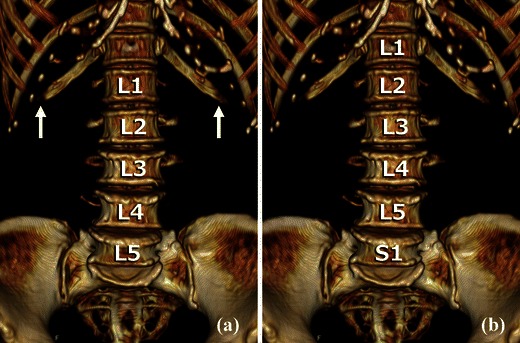
Volume rendering (VR) reconstruction images of the anterior aspect of the lumbar vertebrae. This case has lumbar ribs and lumbarisation. a If the lowest ribs are interpreted as 12th ribs (white arrows), the lumbar spinal configuration might be identified as normal. b By counting inferiorly from C1 or C2, the lowest ribs are identified as lumbar ribs and the lowest non-fused vertebra as S1
Fig. 2.
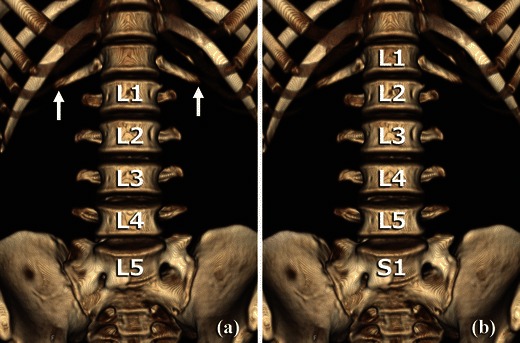
VR reconstruction images of the anterior aspect of the lumbar vertebrae. This case has lumbar ribs and normal lumbar spinal configuration. a If the lowest ribs are interpreted as 12th ribs (white arrows), the lumbar spinal configuration might be identified as sacralisation. b By counting inferiorly from C1 or C2, the lowest ribs are identified as lumbar ribs and the lowest non-fused vertebra as L5
In the present study, we investigated the prevalence of LSTV (lumbarisation and sacralisation) and lumbar ribs and their morphological relevance, by evaluating computed tomography (CT) images. We highlight the importance of accurate enumeration of LSTV and of communication with the referring clinician to avoid severe complications such as wrong-level spine surgery.
Materials and methods
Materials
We performed a retrospective radiographic analysis of 226 cases (148 men, 78 women; age range, 17–94 years; mean age, 59.2 years) scanned from October 2009 to June 2011 by multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT) before forensic autopsy. Cases under 10 years of age, and cases with bodies severely damaged by fire, traffic accident or putrefaction were excluded from the study.
CT machines
MSCT scanning was performed on an eight-channel scanner (Aquilion; Toshiba Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan). Volumetric helical scans were obtained from the head to the proximal femur at 120 kV with variable mAs, a beam pitch of 0.875 and 2.0-mm collimation. The volumetric data allow observation of the whole spine in all directions and differentiation of the presence of rib articular facets. Evaluation of the radiological data was based on a combination of axial images, multi-planar reconstructions (MPRs), and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction using a 3D image workstation (ziostation2 ver. 2.1.0.3; Ziosoft, Tokyo, Japan).
Vertebrae numbering
The vertebral levels were counted craniocaudally, starting from C1, based on the assumption of seven cervical, 12 thoracic, and five lumbar vertebrae. The 20th and 25th vertebrae were defined as L1 and S1, respectively.
Lumbar ribs were defined as ribs articulating with L1 (Fig. 3). Lumbarisation was defined as non-fusion of S1 and S2 (26th vertebra), meaning that there was one additional articulated vertebra (Fig. 4). Sacralisation was defined as anomalous fusion of L5 (24th vertebra) and S1 (Fig. 5).
Fig. 3.
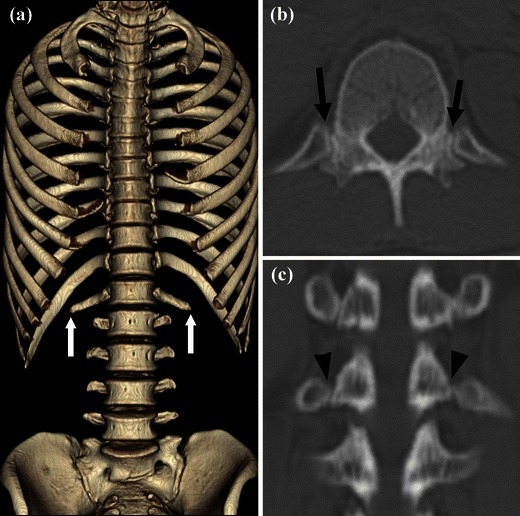
CT images of the lumbar ribs. a VR image of the thoracolumbar spine and ribs with the sternum removed. Lumbar ribs are clearly shown (white arrows). b Axial multi-planar reconstruction (MPR) image of L1. Articulations between L1 and the lumbar ribs are well demonstrated (black arrows). c Coronal MPR image of the thoracolumbar vertebrae. L1 has bilateral costal articular facets for lumbar ribs (black arrowheads), unlike the characteristic transverse processes typically seen at this lower level
Fig. 4.
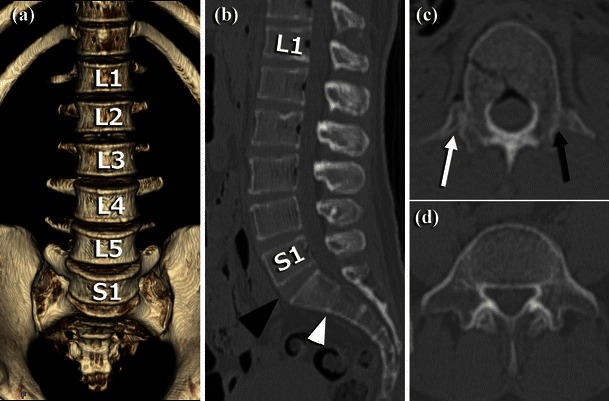
CT images of lumbarisation and unilateral lumbar rib. a VR image of the anterior aspect of the lumbar vertebrae showing lumbarised S1 segment. b Sagittal MPR image of the lumbar vertebrae showing a lumbar-type disk at S1-S2 (black arrowhead) and a sacrum-type disk at S2-S3 (white arrowhead). c Axial MPR image of L1 vertebra showing an articulated lumbar rib on the right side (white arrow) and a non-articulated transverse process on the left side (black arrow). d Axial MPR image of S1 with transverse processes, resembling L5
Fig. 5.
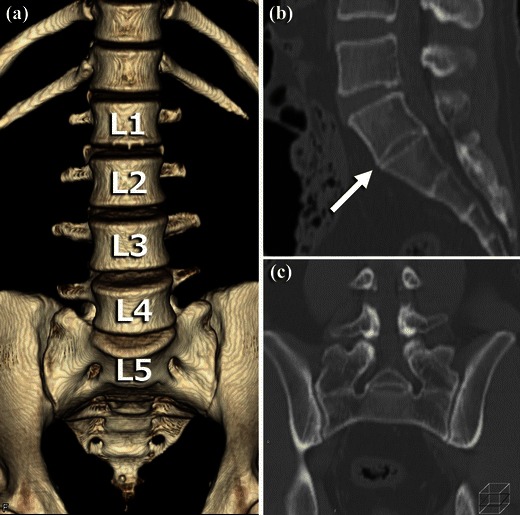
CT images of sacralisation. a VR image of the lumbar vertebrae and sacrum showing anomalous fusion of the transverse processes of L5 with the sacrum. b Sagittal MPR image of sacralised L5 vertebral body. There is no disk between L5 and S1 (white arrow). c Coronal MPR image of L5. Anomalous fusion of the transverse processes of L5 with the sacrum
Statistical analysis
Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical variables. Differences were assessed with an alpha level of 0.05.
Results
Lumbar ribs were observed in 13 of the 226 cases (5.8 %: unilateral rib, 3; bilateral ribs, 10). Agenesis of the 12th ribs was observed in two cases. Lumbarisation was observed in 14 of 226 cases (6.2 %) and sacralisation in six of 226 cases (2.7 %; Table 1). There was no gender difference in the incidence of lumbar LSTV or lumbar ribs.
Table 1.
The prevalence of rib anomalies and lumbosacral transitional vertebrae (LSTV), including lumbarisation and sacralisation. Vertebral segments were counted inferiorly from C1
| Male | Female | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 134 (90.5 %) | 72 (92.3 %) | 206 (91.2 %) | |
| LSTV | Lumbarisation (6 lumbar type vertebrara) | 11 (7.4 %) | 3 (3.8 %) | 14 (6.2 %) |
| Sacralisation (4 lumbar type vertebra) | 3 (2.0 %) | 3 (3.8 %) | 6 (2.7 %) | |
| Normal | 137 (92.6 %) | 74 (94.9 %) | 211 (93.4 %) | |
| Rib anomalies | Lumber ribs (interpreted as 13 pairs of ribs) | 11 (7.4 %) | 2 (2.6 %) | 13 (5.8 %) |
| Agenesis of 12th ribs (interpreted as 11 pairs of ribs) | 0 - | 2 (2.6 %) | 2 (0.9 %) | |
| No. of cases | 148 | 78 | 226 | |
As shown in Table 2, lumbar ribs were found in 11 of 14 cases with lumbarisation (79 %: unilateral rib, two; bilateral, nine), and in two of 206 cases with normal lumbar vertebral configuration (1.0 %: unilateral, one; bilateral, one). No lumbar ribs were observed in the six cases with sacralisation. Agenesis of the 12th ribs was observed in one of the six cases with sacralisation. Another case of 12th rib agenesis was observed among the 206 cases with normal vertebral configuration. Lumbarisation was found in 11 of the 13 cases with lumbar ribs. Three cases with lumbarisation were observed among 211 cases with normal rib configuration (12 pairs of ribs). Of the six cases with sacralisation, one had concurrent agenesis of the 12th ribs, while the other five had normal rib configuration. We combined cases of 12th rib agenesis with the normal rib configuration group due to the small number of cases (agenesis of 12th ribs, n = 2). Similarly, we combined the sacralisation with normal rib configuration group (n = 5) with the normal rib configuration group. We compared the prevalence of lumbar ribs in the lumbarisation group with those in the non-lumbarisation groups using Fisher’s exact test. Lumbarisation and lumbar ribs had a statistically significant association (p < 0.01).
Table 2.
The prevalence of different rib configurations by vertebral configuration type, subdivided into lumbarisation, normal and sacralisation
| Rib configuration | Lumbarisation | Vertebral configuration Normal configuration | Sacralisation | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agenesis of 12th ribs | 0 - | 1 (0.5 %) | 1 (16.7 %) | 2 (0.9 %) |
| Normal configuration | 3 (21.4 %) | 203 (98 5 %) | 5 (83.3 %) | 211 (93.4 %) |
| Lumbar ribs | 11 (78.6 %) | 2 (1.0 %) | 0 - | 13 (5.8 %) |
| Unilareral | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| Bilateral | 9 | 1 | 10 | |
| No. of cases | 14 | 206 | 6 | 226 |
Discussion
Our vertebral counting method using whole-spine CT images revealed a strong association between lumbar ribs and lumbarisation. Eleven of 14 cases with lumbarisation also had lumbar ribs. Eleven of 13 cases with lumbar ribs also had lumbarisation. In cases with lumbar ribs and lumbarisation, lumbar spinal configuration might be interpreted as normal, based on lumbar spinal radiographs (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
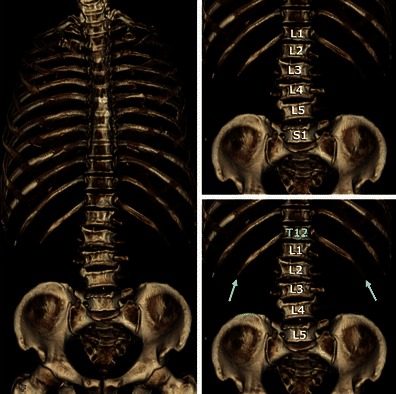
CT images from a case with lumbar ribs and lumbarisation. a VR image of thoracolumbar spine and ribs with removal of the sternum. Lumbar ribs are clearly shown (white arrows). b Counting inferiorly from C1 or C2, the lowest ribs are lumbar ribs and the lowest non-fused vertebra is identified as S1. c If the lowest ribs are interpreted as 12th ribs, the lumbar spinal configuration might be identified as normal
In a study by Carrino et al. [19], 4.1 % of subjects had transitional thoracolumbar segments, defined as lumbar ribs in our study, and two-thirds of those also had LSTV. These results were consistent with those of our study.
The cause of lumbar rib formation has not been clearly determined. However, genetic factors are thought to play a role in the segmental development of the spine [13]. The number of cervical vertebrae is extremely stable at seven. The number of thoracic vertebrae may be reduced to 11 or increased to 13, and the number of lumbar vertebrae may range from four to six [20]. Variations in the thoracolumbar segment have the potential to promote morphological shifts in the lumbosacral segment, because the thoracic spine, lumbar spine and sacral spine develop craniocaudally in early fetal life [21]. If ribs form on L1 (20th vertebrae), then S1 (25th vertebra) might separate from S2, resulting in lumbarisation.
The incidence of lumbarisation was 6.2 % and of sacralisation was 2.7 % in the present study. Widely variable incidences of LSTV have been reported in the literature, ranging from 4 % to 35.9 % [1–17]. This variation may be explained by differences in diagnostic criteria, imaging techniques and confounding factors among the investigated populations.
Previous studies have reported that the presence of LSTV is best identified on a true 30° cranially angled anteroposterior (AP) radiograph of the lumbosacral junction together with frontal AP and lateral views that include the thoracolumbar junction, enabling assessment of the vertebral level [10]. The lumbar spinal level is easily defined on radiographs by counting inferiorly from T12, which is defined as the lowest vertebra with ribs. In this way, Castellvi et al. [3] classified the four types of LSTV according to the form and orientation of the transverse processes (Table 3). They reported a prevalence of lumbarisation and sacralisation of 2 % and 28 %, respectively (Table 4). However, this counting method leads to miscount of the lumbar spinal level when lumbar ribs are present, as mentioned above. In the present study, if the lowest rib was a lumbar rib, we regarded it as the 12th rib. When we recounted the lumbar vertebral level using the lowest ribs as a landmark, the lumbarisation incidence rate fell from 6.2 % to 1.8 %, closely agreeing with Castellvi’s results. It appears that Castellvi et al. did not consider the presence of lumbar ribs in their study. Our definition of sacralisation corresponds to Castellvi types III and IV. Thus, our results agreed with Castellvi’s study, as shown in Table 4. Some studies have reported lumbarisation and sacralisation prevalence using our counting method [2, 15] (Table 5), and these values almost exactly match the lumbar spinal level misdiagnosis rates.
Table 3.
Classification of LSTV according to Castellvi et al. [2]
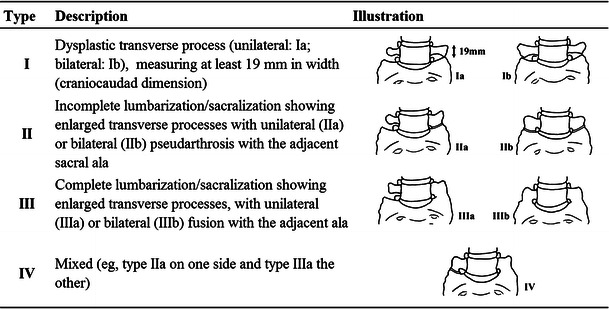
Table 4.
Comparison of LSTV prevalence by counting method, based on different vertebral level landmarks
| LSTV | Lumbarisation | Sacralisation | No. of cases | Landmark | Imaging modality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | ||||||
| Count from C2 | 20 (8.8 %) | 14 (6.2 %) | 6 (2.7 %) | 226 | C2 | Whole-spine MSCT |
| Recount | 11 (4.9 %) | 4 (1.8 %) | 7 (3.1 %) | the lowest rib | ||
| Castellvi et al. [3] | ||||||
| 60 (30.0 %) | 4 (2.0 %) | 56 (28.0 %) | ||||
| Type I | 25 (12.5 %) | AP, LAT and | ||||
| Type II | 23 (11.5 %) | 200 | the lowest rib | 30° cranially angled AP | ||
| Type III | 5 (2.5 %) | lumber radiograph | ||||
| Type IV | 3 (1.5 %) | |||||
C2 second cervical spine, MSCT multi-slice computed tomography, AP anteroposterior, LAT lateral
Table 5.
Comparison of the prevalence of lumbarisation and sacralisation in studies using the same counting method. Vertebral segments were counted from C1 or C2 inferiorly on whole-spine image
| Lumbarisation | Sacralisation | No. of cases | Imaging modality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | 14 (6.2 %) | 6 (2.7 %) | 226 | Whole spine MSCT |
| Hahn et al. [2] | 9 (4.5 %) | 15 (7.5 %) | 200 | TL and LS sagittal MRI |
| Peh et al. [15] | 9 (7.0 %) | 8 (6.2 %) | 129 | TL and LS sagittal MRI |
MSCT multi-slice computed tomography, TL thoracolumber, LS lumbosacral
Hughes et al. [22] reported another technique to correctly number an LSTV by locating the iliolumbar ligaments. Sacralisation was determined by the lack of an iliolumbar ligament at the level above the sacrum. When an iliolumbar ligament was identified above the LSTV, the vertebra with the iliolumbar ligament was considered L5 and the LSTV was termed lumbarisation. However, this technique assumes that there are always seven cervical, 12 thoracic and five lumbar vertebrae. Identification of the iliolumbar ligament in cases with various segmentation anomalies might not accurately identify the L5 vertebral body [18].
LSTV is a common benign anatomical variation of the lumbosacral spine. However, the clinical significance of the condition is still unknown and its relationship with low back pain is controversial [1]. The presence of LSTV and rib anomalies can lead to inaccurate identification of vertebral levels. Caution in numbering the lumbosacral vertebrae in patients with LSTV is of the utmost importance in spinal surgery [1]. Our report suggests that evaluating AP radiographs alone could result in miscounting of the lower spinal levels. There is no foolproof method for accurately numbering a transitional segment without high-quality imaging of the entire spine; therefore, communication between radiologists and referring clinicians, and correlation of intraoperative and preoperative imaging, are very important.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. No funding was received for this work. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained, informed patient content was waived.
References
- 1.Bron JL, van Royen BJ, Wuisman PI. The clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional anomalies. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73:678–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hahn PY, Strobel JJ, Hahn FJ. Verification of lumbosacral segments on MR images: identification of transitional vertebrae. Radiology. 1992;182:580–581. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.2.1732988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Castellvi AE, Goldstein LA, Chan DPK. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae and their relationship with lumbar extradural defects. Spine. 1984;9:493–495. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198407000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O’Driscoll CM, Irwin A, Saifuddin A. Variations in morphology of the lumbosacral junction on sagittal MRI: correlation with plain radiography. Skeletal Radiol. 1996;25:225–230. doi: 10.1007/s002560050069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hsieh CY, Vanderford JD, Moreau SR, Prong T. Lumbosacral transitional segments: classification, prevalence, and effect on disk height. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2000;23:483–489. doi: 10.1067/mmt.2000.108817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Erken E, Ozer HT, Gulek B, Durgun B. The association between cervical rib and sacralization. Spine. 2002;27:1659–1664. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200208010-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chang HS, Nakagawa H. Altered function of lumbar nerve roots in patients with transitional lumbosacral vertebrae. Spine. 2004;29:1632–1635. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000132319.43140.D3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Delport EG, Cucuzzella TR, Kim N, et al. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: incidence in a consecutive patient series. Pain Physician. 2006;9:53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Elster AD. Bertolotti’s syndrome revisited: transitional vertebrae of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1989;14:1373–1377. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198912000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hughes RJ, Saifuddin A. Imaging of lumbosacral transitional vertebrae. Clin Radiol. 2004;59:984–991. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2004.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Luoma K, Vehmas T, Raininko R, et al. Lumbosacral transitional vertebra: relation to disc degeneration and low back pain. Spine. 2004;29:200–205. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000107223.02346.A8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taskaynatan MA, Izci Y, Ozgul A, et al. Clinical significance of congenital lumbosacral malformations in young male population with prolonged low back pain. Spine. 2005;30:E210–E213. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000158950.84470.2a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tini PG, Wieser C, Zinn WM. The transitional vertebra of the lumbosacral spine: its radiological classification, incidence, prevalence, and clinical significance. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1977;16:180–185. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/16.3.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Otani K, Konno S, Kikuchi S. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae and nerveroot symptoms. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83-B:1137–1140. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.83B8.11736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Peh WC, Siu TH, Chan JH. Determining the lumbar vertebral segments on magnetic resonance imaging. Spine. 1999;24:1852–1855. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199909010-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Seçer M, Muradov JM, Dalgiç A. Evaluation of congenital lumbosacral malformations and neurological findings in patients with low back pain. Turk Neurosurg. 2009;19:145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wigh RE, Anthony HF., Jr Transitional lumbosacral discs: probability of herniation. Spine. 1981;6:168–171. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198103000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Konin GP, Walz DM. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: classification, imaging findings, and clinical relevance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:1778–1786. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carrino JA, Campbell PD, Jr, Lin DC, Morrison WB, Schweitzer ME, Flanders AE, Eng J, Vaccaro AR. Effect of spinal segment variants on numbering vertebral levels at lumbar MR imaging. Radiology. 2011;259:196–202. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11081511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wigh RE. The thoracolumbar and lumbosacral transitional junctions. Spine. 1980;3:215–222. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Standring S. Development of the back: development of vertebrae. In: Newell RLM, editor. Gray’s Anatomy. 40. London: Elsevier; 2008. pp. 768–769. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hughes RJ, Saifuddin A. Numbering of lumbosacral transitional vertebrae on MRI: role of the iliolumbar ligaments. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187:59–66. doi: 10.2214/AJR.05.0415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


