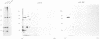Abstract
Class II molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) are composed of two polymorphic glycoprotein chains (alpha and beta), that associate in the ER with a third, non-polymorphic glycoprotein known as the invariant chain (Ii). We have examined the relationship between the intracellular transport and physico-chemical characteristics of various combinations of murine alpha, beta and Ii chains. Biochemical and morphological analyses of transfected fibroblasts expressing class II MHC chains show that both unassembled alpha and beta chains, as well as a large fraction of alpha+beta complexes synthesized in the absence of Ii chain, are retained in the ER in association with the immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein, BiP. Analyses by sedimentation velocity on sucrose gradients show that most incompletely assembled class II MHC species exist as high molecular weight aggregates in both transfected fibroblasts and spleen cells from mice carrying a disruption of the Ii chain gene. This is in contrast to the sedimentation properties of alpha beta Ii complexes from normal mice, which migrate as discrete, stoichiometric complexes of M(r) approximately 200,000-300,000. These observations suggest that assembly with the Ii chain prevents accumulation of aggregated alpha and beta chains in the ER, which might relate to the known ability of the Ii chain to promote exit of class II MHC molecules from the ER.
Full text
PDF
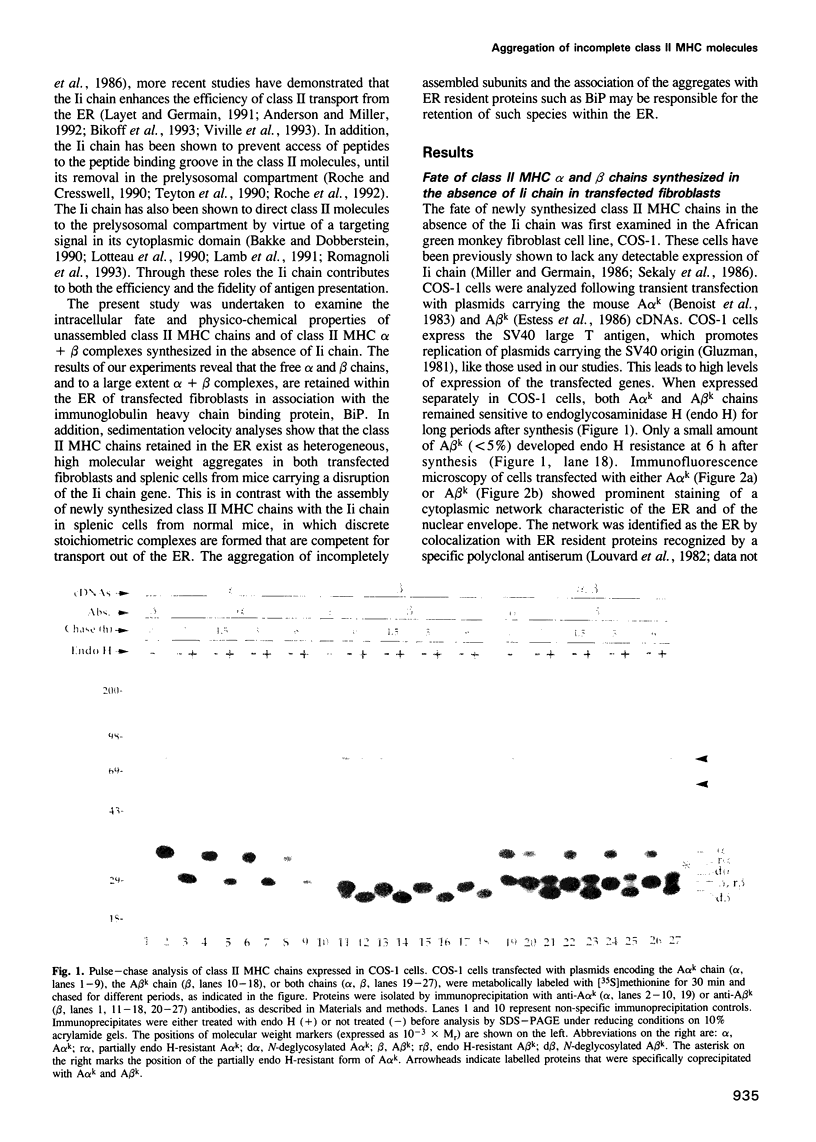
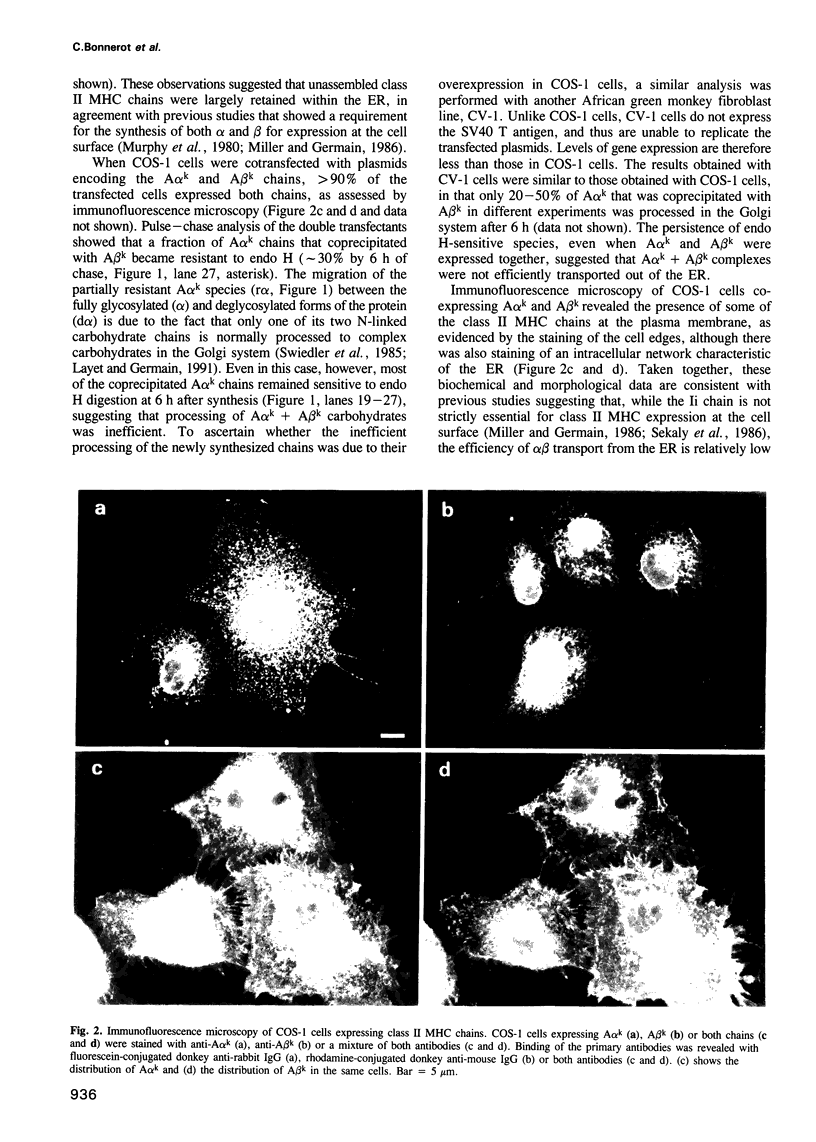








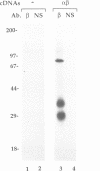
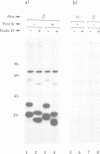
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. S., Cresswell P. A role for calnexin (IP90) in the assembly of class II MHC molecules. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):675–682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. S., Miller J. Invariant chain can function as a chaperone protein for class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakke O., Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. The murine Ia alpha chains, E alpha and A alpha, show a surprising degree of sequence homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikoff E. K., Huang L. Y., Episkopou V., van Meerwijk J., Germain R. N., Robertson E. J. Defective major histocompatibility complex class II assembly, transport, peptide acquisition, and CD4+ T cell selection in mice lacking invariant chain expression. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1699–1712. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. BIP associates with newly synthesized subunits of the mouse muscle nicotinic receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1125–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. S., Cresswell P. Role for intracellular proteases in the processing and transport of class II HLA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3975–3979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Cosson P., Shah N., Klausner R. D. Role of potentially charged transmembrane residues in targeting proteins for retention and degradation within the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2783–2793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Suzuki C. K., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Weissman A. M., Klausner R. D. Pre-Golgi degradation of newly synthesized T-cell antigen receptor chains: intrinsic sensitivity and the role of subunit assembly. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):73–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braakman I., Hoover-Litty H., Wagner K. R., Helenius A. Folding of influenza hemagglutinin in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):401–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Selective degradation of T cell antigen receptor chains retained in a pre-Golgi compartment. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2149–2161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., Bonifacino J. S. Role of transmembrane domain interactions in the assembly of class II MHC molecules. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):659–662. doi: 10.1126/science.1329208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David V., Hochstenbach F., Rajagopalan S., Brenner M. B. Interaction with newly synthesized and retained proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum suggests a chaperone function for human integral membrane protein IP90 (calnexin). J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9585–9592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Williams D. B. Participation of a novel 88-kD protein in the biogenesis of murine class I histocompatibility molecules. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Krane M. G., Kaufman R. J. Reduction of endogenous GRP78 levels improves secretion of a heterologous protein in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4063–4070. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Begovich A. B., Koo M., Jones P. P., McDevitt H. O. Sequence analysis and structure-function correlations of murine q, k, u, s, and f haplotype I-A beta cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsayeth J. R., Gu Y., Hall Z. W. BiP forms stable complexes with unassembled subunits of the acetylcholine receptor in transfected COS cells and in C2 muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):841–847. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Hendrix L. R. MHC class II structure, occupancy and surface expression determined by post-endoplasmic reticulum antigen binding. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):134–139. doi: 10.1038/353134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Rinker A. G., Jr Peptide binding inhibits protein aggregation of invariant-chain free class II dimers and promotes surface expression of occupied molecules. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):725–728. doi: 10.1038/363725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas I. G., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):387–389. doi: 10.1038/306387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstenbach F., David V., Watkins S., Brenner M. B. Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein of 90 kilodaltons associates with the T- and B-cell antigen receptors and major histocompatibility complex antigens during their assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Bole D. G., Hoover-Litty H., Helenius A., Copeland C. S. Interactions of misfolded influenza virus hemagglutinin with binding protein (BiP). J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2117–2126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Cooperative interaction of B lymphocytes with antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes is MHC restricted. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):547–549. doi: 10.1038/292547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., Hewgill D., McDevitt H. O. Detection of a common polypeptide chain in I--A and I--E sub-region immunoprecipitates. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E., Sheetz M. P., Schindler M. Matrix control of protein diffusion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. A., Cresswell P. Assembly and transport properties of invariant chain trimers and HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3478–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. A., Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R., Cresswell P. Invariant chain targets HLA class II molecules to acidic endosomes containing internalized influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5998–6002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layet C., Germain R. N. Invariant chain promotes egress of poorly expressed, haplotype-mismatched class II major histocompatibility complex A alpha A beta dimers from the endoplasmic reticulum/cis-Golgi compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S. L., Quaranta V., Peterson P. A. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):600–605. doi: 10.1038/348600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Cresswell P. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the invariant chain associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2564–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Vesicular stomatitis virus G proteins with altered glycosylation sites display temperature-sensitive intracellular transport and are subject to aberrant intermolecular disulfide bonding. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5955–5960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Blum J. S., Cresswell P. Invariant chain trimers are sequestered in the rough endoplasmic reticulum in the absence of association with HLA class II antigens. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):839–855. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt T., Helenius A. Misfolding and aggregation of newly synthesized proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):505–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., Kühn L. C., Ruddle F. H. The human transferrin receptor gene: genomic organization, and the complete primary structure of the receptor deduced from a cDNA sequence. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehringer J. H., Harris M. R., Kindle C. S., McCourt D. W., Cullen S. E. Characterization of fragments of the murine Ia-associated invariant chain. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):920–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J., Aviel S., Argon Y. The endoplasmic reticulum stress protein GRP94, in addition to BiP, associates with unassembled immunoglobulin chains. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21303–21306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Germain R. N. Efficient cell surface expression of class II MHC molecules in the absence of associated invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1478–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Jones P. P., Loken M. R., McDevitt H. O. Interaction between I region loci influences the expression of a cell surface Ia antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5404–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Q. V., Humphreys R. E. Time course of intracellular associations, processing, and cleavages of Ii forms and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1631–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. H., Law D. T., Williams D. B. Binding protein BiP is required for translocation of secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1565–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Neefjes J. J., Oorschot V., Ploegh H. L., Geuze H. J. Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):669–676. doi: 10.1038/349669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Kourilsky F. M., Rebouah J. P., Dosseto M., Caillol D. Distinct epitopes of Ik gene products identified by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Dec;10(12):950–957. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Cresswell P. Invariant chain association with HLA-DR molecules inhibits immunogenic peptide binding. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):615–618. doi: 10.1038/345615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Marks M. S., Cresswell P. Formation of a nine-subunit complex by HLA class II glycoproteins and the invariant chain. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):392–394. doi: 10.1038/354392a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Teletski C. L., Karp D. R., Pinet V., Bakke O., Long E. O. Stable surface expression of invariant chain prevents peptide presentation by HLA-DR. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2841–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli P., Layet C., Yewdell J., Bakke O., Germain R. N. Relationship between invariant chain expression and major histocompatibility complex class II transport into early and late endocytic compartments. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):583–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Myers J., Holowka D., Baird B., Webb W. W. Molecular crowding on the cell surface. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):61–64. doi: 10.1126/science.2962287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Hendrix L. R., Coligan J. E., Maloy W. L., Germain R. N. Defective intracellular transport as a common mechanism limiting expression of inappropriately paired class II major histocompatibility complex alpha/beta chains. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):799–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. The effect of mobile obstacles. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):989–997. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83291-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaiff W. T., Hruska K. A., Jr, McCourt D. W., Green M., Schwartz B. D. HLA-DR associates with specific stress proteins and is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum in invariant chain negative cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):657–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekaly R. P., Tonnelle C., Strubin M., Mach B., Long E. O. Cell surface expression of class II histocompatibility antigens occurs in the absence of the invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1490–1504. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh I., Doms R. W., Wagner K. R., Helenius A. Intracellular transport of soluble and membrane-bound glycoproteins: folding, assembly and secretion of anchor-free influenza hemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):631–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfrè G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Monoclonal xenogeneic antibodies to murine cell surface antigens: identification of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Aug;8(8):539–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. J., Wiley D. C. The human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 assembles as empty alpha beta heterodimers in the absence of antigenic peptide. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90184-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki C. K., Bonifacino J. S., Lin A. Y., Davis M. M., Klausner R. D. Regulating the retention of T-cell receptor alpha chain variants within the endoplasmic reticulum: Ca(2+)-dependent association with BiP. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):189–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiedler S. J., Freed J. H., Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Hart G. W. Oligosaccharide microheterogeneity of the murine major histocompatibility antigens. Reproducible site-specific patterns of sialylation and branching in asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4046–4054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., O'Sullivan D., Dickson P. W., Lotteau V., Sette A., Fink P., Peterson P. A. Invariant chain distinguishes between the exogenous and endogenous antigen presentation pathways. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):39–44. doi: 10.1038/348039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viville S., Neefjes J., Lotteau V., Dierich A., Lemeur M., Ploegh H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Mice lacking the MHC class II-associated invariant chain. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):635–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90081-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel J. P., Misra L. M., Rose M. D. Loss of BiP/GRP78 function blocks translocation of secretory proteins in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1885–1895. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva A. M., Balch W. E., Helenius A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: folding and misfolding of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein in cells and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):857–866. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva A., Braakman I., Helenius A. Posttranslational folding of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein in the ER: involvement of noncovalent and covalent complexes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):647–655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]