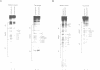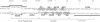Abstract
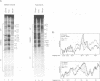
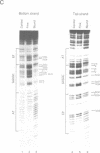
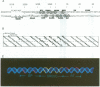
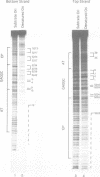
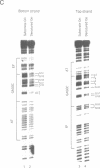
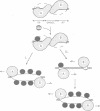
The mechanism by which a replicator (origin of replication) becomes denatured during the initiation of replication is not understood for any prokaryotic or eukaryotic system. To address this question, we chemically probed the molecular contacts on the SV40 origin of replication (ori) that are used by the SV40 large T-antigen and a single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB) during ori denaturation. Prior to the actual denaturation step, the T-antigen double hexamer bound ori utilizing sugar-phosphate contacts that were located on opposite strands in each flanking domain of ori. Each set of flanking phosphate contacts were also located on approximately opposite faces of the ori duplex. While the phosphate contacts had a 2-fold symmetry with respect to the ori center, T-antigen contacts with nucleotide bases were polar with critical interactions detected in only one of the two flanking domains. During origin denaturation catalyzed by T-antigen and a SSB, numerous new contacts to flanking phosphates were observed on the strand not initially bound by T-antigen, suggesting movement of each T-antigen hexamer outward from ori. These data suggest that T-antigen initially binds ori in a manner that facilitates transfer of each T-antigen hexamer to opposite strands during the initiation of SV40 replication.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker T. A., Sekimizu K., Funnell B. E., Kornberg A. Extensive unwinding of the plasmid template during staged enzymatic initiation of DNA replication from the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Differential induction of structural changes in the simian virus 40 origin of replication by T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1228–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1228-1235.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. ATP stimulates the binding of simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen to the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3149–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A. Inhibition of structural changes in the simian virus 40 core origin of replication by mutation of essential origin sequences. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5248–5255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5248-5255.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):743–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Stillman B. Yeast replication factor-A functions in the unwinding of the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):92–95. doi: 10.1038/342092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle A., Schleif R. F. Missing contact probing of DNA-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6673–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Borowiec J. A., Eki T., Hurwitz J. The simian virus 40 T antigen double hexamer assembles around the DNA at the replication origin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14129–14137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Borowiec J. A., Ishimi Y., Deb S., Tegtmeyer P., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen requires three core replication origin domains for DNA unwinding and replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8267–8271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Dodson M., Echols H., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent formation of a specialized nucleoprotein structure by simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen at the SV40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8981–8985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 large T antigen untwists DNA at the origin of DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5062–5071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. ATP enhances the binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3649–3654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3649-3654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Baur C. P., Koff A., Tegtmeyer P. Domain structure of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1663–1670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Tsui S., Koff A., DeLucia A. L., Parsons R., Tegtmeyer P. The T-antigen-binding domain of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2143–2149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2143-2149.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Echols H., Wickner S., Alfano C., Mensa-Wilmot K., Gomes B., LeBowitz J., Roberts J. D., McMacken R. Specialized nucleoprotein structures at the origin of replication of bacteriophage lambda: localized unwinding of duplex DNA by a six-protein reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7638–7642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Erdile L. F., Gilbert I. U., von Winkler D., Kelly T. J., Fanning E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):769–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz G. S., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J., Matson S. W. The unwinding of duplex regions in DNA by the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-associated DNA helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Torsional rigidity of DNA and length dependence of the free energy of DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J., Dean F. B., Kwong A. D., Lee S. H. The in vitro replication of DNA containing the SV40 origin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18043–18046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Rich A. Chemical probes of DNA conformation: detection of Z-DNA at nucleotide resolution. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9757–9761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C., Snyder R. O., Wold M. S. Binding properties of replication protein A from human and yeast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3050–3059. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Eki T., Hurwitz J. Synthesis of DNA containing the simian virus 40 origin of replication by the combined action of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7361–7365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wall J. S., Dodson M., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):658–662. doi: 10.1038/338658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wilson V. G., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Tegtmeyer P. Monomers through trimers of large tumor antigen bind in region I and monomers through tetramers bind in region II of simian virus 40 origin of replication DNA as stable structures in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3626–3630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. E., Stenger J. E., Ray S., Welker R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Cooperative assembly of simian virus 40 T-antigen hexamers on functional halves of the replication origin. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2798–2806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2798-2806.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Three domains in the simian virus 40 core origin orchestrate the binding, melting, and DNA helicase activities of T antigen. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):509–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.509-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnos M., Zahn K., Inman R. B., Blattner F. R. Initiation protein induced helix destabilization at the lambda origin: a prepriming step in DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):385–395. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. J., Blackwell L. J., Gillette T., Borowiec J. A. Recognition of model DNA replication forks by the SV40 large tumor antigen. Chromosoma. 1992;102(1 Suppl):S46–S51. doi: 10.1007/BF02451785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. J., Borowiec J. A. Strand-specific recognition of a synthetic DNA replication fork by the SV40 large tumor antigen. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1656–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigman D. S., Kuwabara M. D., Chen C. H., Bruice T. W. Nuclease activity of 1,10-phenanthroline-copper in study of protein-DNA interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:414–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08022-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Multiple replication factors augment DNA synthesis by the two eukaryotic DNA polymerases, alpha and delta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3883–3889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Kelly T. J. Requirement for two DNA polymerases in the replication of simian virus 40 DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9742–9746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel R., Schweizer J., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 T-antigen DNA helicase is a hexamer which forms a binary complex during bidirectional unwinding from the viral origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):804–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.804-815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiekowski M., Schwarz M. W., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 large T antigen DNA helicase. Characterization of the ATPase-dependent DNA unwinding activity and its substrate requirements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):436–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]