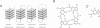Abstract
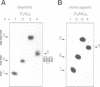
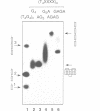
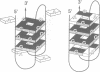
Telomeres are required for eukaryotic chromosome stability. They consist of regularly repeating guanine-rich sequences, with a single-stranded 3' terminus. Such sequences have been demonstrated to have the propensity to adopt four-stranded structures based on a tetrad of guanine bases. The formation of an intramolecular foldback tetraplex is associated with markedly increased mobility in polyacrylamide. Most telomeric sequences are based either on a repeat of d(TnGGGG) or d(TnAGGG) sequences. We have used a combination 7-deazaguanine or 7-deaza-adenine substitution, chemical modification and gel electrophoresis to address the following aspects of intramolecular tetraplex formation. (i) Intramolecular tetraplex formation by d(TTTTGGGG)4 sequences is prevented by very low levels of 7-deazaguanine substitution. This confirms the important role of guanine N7 in the formation of the tetraplex. (ii) The sequences d(TTAGGG)4 and d(TTTTAGGG)4 fold into tetraplexes. By contrast, the electrophoretic behaviour of d(TTTTGGGA)4, d(TTTTAGAG)4 and d(TTTTGAGA)4 does not indicate formation of stable intramolecular tetraplexes under available conditions. (iii) Selective 7-deazaguanine and 7-deaza-adenine substitutions in d(TTTTAGGG)4 give results consistent with tetraplex folding by the formation of three G4 tetrads, with the adenine bases formally part of the single-stranded loops, where they probably interact with thymine bases. These results demonstrate that eukaryotic cells appear to have selected just those sequences that can adopt the tetraplex conformation for their telomeres, while those that cannot have been avoided. This suggests that the conformation may be significant in the function of the telomere, such as attachment to nuclear structures.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboul-ela F., Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. NMR study of parallel-stranded tetraplex formation by the hexadeoxynucleotide d(TG4T). Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):280–282. doi: 10.1038/360280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagurumoorthy P., Brahmachari S. K., Mohanty D., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Hairpin and parallel quartet structures for telomeric sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4061–4067. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Hunter W. N., Kneale G., Kennard O. Molecular structure of the G.A base pair in DNA and its implications for the mechanism of transversion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2402–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Moore P. B. Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA tetraplex containing G- and U-quartet structures. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8406–8414. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G., Cech T. R. Oxytricha telomere-binding protein: DNA-dependent dimerization of the alpha and beta subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6056–6060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G., Cech T. R. The beta subunit of Oxytricha telomere-binding protein promotes G-quartet formation by telomeric DNA. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlong J. C., Lilley D. M. Highly selective chemical modification of cruciform loops by diethyl pyrocarbonate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):3995–4007. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLERT M., LIPSETT M. N., DAVIES D. R. Helix formation by guanylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2013–2018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Q., Lu M., Kallenbach N. R. Adenine affects the structure and stability of telomeric sequences. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15293–15300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin C. C., Henderson E., Watson T., Prosser J. K. Monovalent cation induced structural transitions in telomeric DNAs: G-DNA folding intermediates. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4460–4472. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Dempster M., Dunlop M. G., Thompson A. M., Green D. K., Allshire R. C. Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):866–868. doi: 10.1038/346866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Diethyl pyrocarbonate: a chemical probe for secondary structure in negatively supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8009–8013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin R., Gaffney B. L., Wang C., Jones R. A., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamics and structure of a DNA tetraplex: a spectroscopic and calorimetric study of the tetramolecular complexes of d(TG3T) and d(TG3T2G3T). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8832–8836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H., Rich A. Chemical probes of DNA conformation: detection of Z-DNA at nucleotide resolution. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C., Zhang X., Ratliff R., Moyzis R., Rich A. Crystal structure of four-stranded Oxytricha telomeric DNA. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):126–131. doi: 10.1038/356126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Cheong C., Moore P. B. Tetramerization of an RNA oligonucleotide containing a GGGG sequence. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):331–332. doi: 10.1038/351331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard N. J., McDonald J. J., Henderson R. E., Reichmann M. E. Reaction of diethyl pyrocarbonate with nucleic acid components. Adenosine. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3335–3342. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Frantz J. D., Gilbert W., Tye B. K. Identification and characterization of a nuclease activity specific for G4 tetrastranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3157–3161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Kurtz S., Shore D. Involvement of the silencer and UAS binding protein RAP1 in regulation of telomere length. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2237406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. Retinoblastoma susceptibility genes contain 5' sequences with a high propensity to form guanine-tetrad structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):49–53. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Deoxyguanosine-deoxyadenosine pairing in the d(C-G-A-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) duplex: conformation and dynamics at and adjacent to the dG X dA mismatch site. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3207–3217. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petracek M. E., Berman J. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii telomere repeats form unstable structures involving guanine-guanine base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):89–95. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privé G. G., Heinemann U., Chandrasegaran S., Kan L. S., Kopka M. L., Dickerson R. E. Helix geometry, hydration, and G.A mismatch in a B-DNA decamer. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):498–504. doi: 10.1126/science.3310237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe K., Fritsch V., Westhof E., Jovin T. M. Alternating d(G-A) sequences form a parallel-stranded DNA homoduplex. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3777–3786. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Feigon J. Quadruplex structure of Oxytricha telomeric DNA oligonucleotides. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):164–168. doi: 10.1038/356164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Heaphy S. Evidence for interstrand quadruplex formation in the dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 genomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Gualberto A. MyoD binds to the guanine tetrad nucleic acid structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13714–13718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Patel D. J. Guanine residues in d(T2AG3) and d(T2G4) form parallel-stranded potassium cation stabilized G-quadruplexes with anti glycosidic torsion angles in solution. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8112–8119. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., de los Santos C., Gao X. O., Greene K., Live D., Patel D. J. Multinuclear nuclear magnetic resonance studies of Na cation-stabilized complex formed by d(G-G-T-T-T-T-C-G-G) in solution. Implications for G-tetrad structures. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):819–832. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90513-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster G. D., Sanderson M. R., Skelly J. V., Neidle S., Swann P. F., Li B. F., Tickle I. J. Crystal structure and sequence-dependent conformation of the A.G mispaired oligonucleotide d(CGCAAGCTGGCG). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman-Shomer P., Fry M. QUAD, a protein from hepatocyte chromatin that binds selectively to guanine-rich quadruplex DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3306–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Williamson J. R., Cech T. R., Prescott D. M. Inhibition of telomerase by G-quartet DNA structures. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):718–720. doi: 10.1038/350718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T. Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):717–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]